J Korean Med Sci.
2021 Jun;36(23):e152. 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e152.
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Adrenal Insufficiency and Fever
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516677
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e152
Abstract
- Background
Because persistent fever often occurs in adrenal insufficiency, it might be confused with infectious diseases. This study aimed to identify clinical characteristics and risk factors of patients with adrenal insufficiency and fever.
Methods
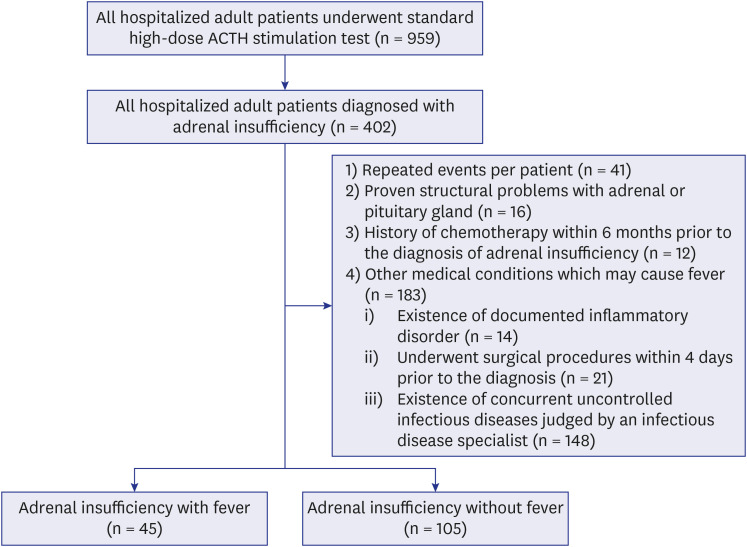
All adult patients (n = 150) admitted to a tertiary care hospital in South Korea and diagnosed with adrenal insufficiency between 1 March 2018, and 30 June 2019, were recruited. Patients were excluded if they had: 1) proven structural problems in the adrenal or pituitary gland; 2) a history of chemotherapy within 6 months prior to the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency; and 3) other medical conditions that may cause fever.
Results
Among the included patients, 45 (30.0%) had fever at the time of the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. The mean C-reactive protein level was higher (11.25 ± 8.54 vs. 4.36 ± 7.13 mg/dL) in patients with fever than in those without fever. A higher proportion of patients with fever changed antibiotics (33.3% vs. 1.0%). On multivariate logistic regression analysis, female sex (odds ratio [OR], 0.32) lowered the risk of adrenal insufficiency with fever, while a history of surgery within 6 months (OR, 4.35), general weakness (OR, 7.21), and cough (OR, 17.29) were significantly associated with that.
Conclusion
The possibility of adrenal insufficiency should be considered in patients with fever of unknown origin, especially those with risk factors.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bancos I, Hahner S, Tomlinson J, Arlt W. Diagnosis and management of adrenal insufficiency. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015; 3(3):216–226. PMID: 25098712.
Article2. Charmandari E, Nicolaides NC, Chrousos GP. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet. 2014; 383(9935):2152–2167. PMID: 24503135.
Article3. Wallace I, Cunningham S, Lindsay J. The diagnosis and investigation of adrenal insufficiency in adults. Ann Clin Biochem. 2009; 46(Pt 5):351–367. PMID: 19675057.
Article4. McIntosh TK, Lothrop DA, Lee A, Jackson BT, Nabseth D, Egdahl RH. Circadian rhythm of cortisol is altered in postsurgical patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981; 53(1):117–122. PMID: 7240369.
Article5. Naito Y, Fukata J, Tamai S, Seo N, Nakai Y, Mori K, et al. Biphasic changes in hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal function during the early recovery period after major abdominal surgery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991; 73(1):111–117. PMID: 1646214.
Article6. Speckart PF, Nicoloff JT, Bethune JE. Screening for adrenocortical insufficiency with cosyntropin (synthetic ACTH). Arch Intern Med. 1971; 128(5):761–763. PMID: 4330323.
Article7. Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987; 40(5):373–383. PMID: 3558716.
Article8. Richard AP, Steven HA, David HR, William EB. Cytokines and inflammatory response in the fetus and neonate. In : William WF, editor. Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Elsevier;2017. p. 1241–1254.9. Black S, Kushner I, Samols D. C-reactive Protein. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279(47):48487–48490. PMID: 15337754.
Article10. Kim HA, Kim SK, Seo YI. The pattern of prescription and promotion of medications for arthritis patients by pharmacists in Korea. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2002; 9:184–189.11. Allolio B. Extensive expertise in endocrinology. Adrenal crisis. Eur J Endocrinol. 2015; 172(3):R115–24. PMID: 25288693.
Article12. Arroyo V, García-Martinez R, Salvatella X. Human serum albumin, systemic inflammation, and cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2014; 61(2):396–407. PMID: 24751830.
Article13. Mulder AH, Nauta S, Pieters GF, Hermus AR. Addisonian crisis in patients with known adrenal insufficiency: the importance of early intervention. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2008; 152(27):1497–1500. PMID: 18681356.14. Nehring SM, Goyal A, Bansal P, Patel BC. C reactive protein (CRP). StatPearls [Internet]. Updated 2020. Accessed May 11, 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441843/.15. Kollef MH. Broad-spectrum antimicrobials and the treatment of serious bacterial infections: getting it right up front. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 47(Suppl 1):S3–13. PMID: 18713047.
Article16. Huttner A, Harbarth S, Carlet J, Cosgrove S, Goossens H, Holmes A, et al. Antimicrobial resistance: a global view from the 2013 World Healthcare-Associated Infections Forum. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2013; 2(1):31. PMID: 24237856.
Article17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. Updated 2019. Accessed May 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/DrugResistance/Biggest-Threats.html.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Adrenal Tuberculosis Combined with Tuberculous Peritonitis-Induced Adrenal Crisis
- A Case of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency in a Patient with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
- Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency Associated with Megestrol Acetate in a Patient with Lung Cancer
- Adrenal Tuberculosis Mimicking a Malignant Tumor with Primary Adrenal Insufficiency
- A Case of Adrenal Aplasia