J Stroke.
2021 May;23(2):289-292. 10.5853/jos.2021.00647.
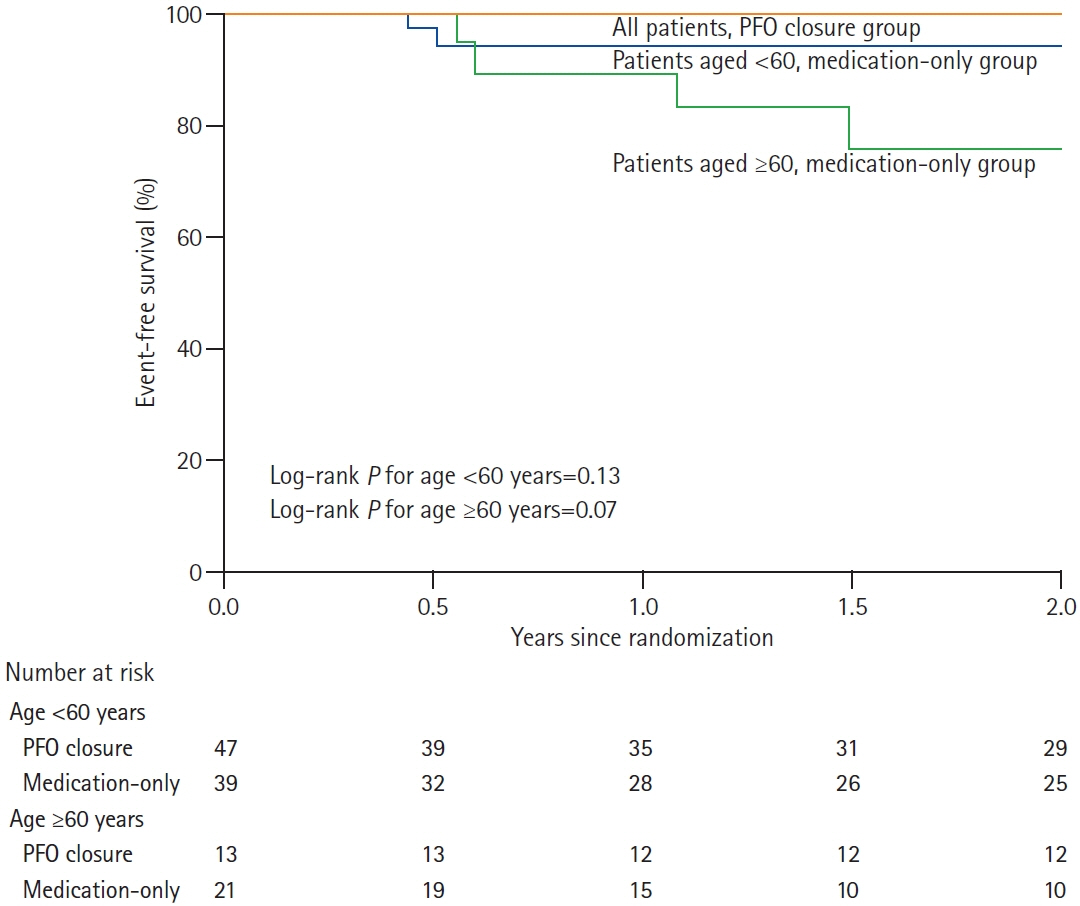
Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Old Stroke Patients: A Subgroup Analysis of the DEFENSE-PFO Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Cardiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516420
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2021.00647
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: Opportunity Closed in Old Patients?
Jong S. Kim, Keun-Sik Hong
J Stroke. 2021;23(2):147-148. doi: 10.5853/jos.2021.01690.
Reference
-
References
1. Saver JL, Carroll JD, Thaler DE, Smalling RW, MacDonald LA, Marks DS, et al. Long-term outcomes of patent foramen ovale closure or medical therapy after stroke. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1022–1032.
Article2. Mas JL, Derumeaux G, Guillon B, Massardier E, Hosseini H, Mechtouff L, et al. Patent foramen ovale closure or anticoagulation vs. antiplatelets after stroke. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1011–1021.
Article3. Søndergaard L, Kasner SE, Rhodes JF, Andersen G, Iversen HK, Nielsen-Kudsk JE, et al. Patent foramen ovale closure or antiplatelet therapy for cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1033–1042.
Article4. Messé SR, Gronseth GS, Kent DM, Kizer JR, Homma S, Rosterman L, et al. Practice advisory update summary: patent foramen ovale and secondary stroke prevention: report of the Guideline Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2020; 94:876–885.5. Köhrmann M, Schellinger PD, Tsivgoulis G, Steiner T. Patent foramen ovale: story closed? J Stroke. 2019; 21:23–30.
Article6. Lee PH, Song JK, Kim JS, Heo R, Lee S, Kim DH, et al. Cryptogenic stroke and high-risk patent foramen ovale: the DEFENSE- PFO trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018; 71:2335–2342.7. Hagen PT, Scholz DG, Edwards WD. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: an autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984; 59:17–20.
Article8. Homma S, DiTullio MR, Sacco RL, Sciacca RR, Mohr JP; PICSS Investigators. Age as a determinant of adverse events in medically treated cryptogenic stroke patients with patent foramen ovale. Stroke. 2004; 35:2145–2149.
Article9. Mazzucco S, Li L, Rothwell PM. Prognosis of cryptogenic stroke with patent foramen ovale at older ages and implications for trials: a population-based study and systematic review. JAMA Neurol. 2020; 77:1279–1287.10. Gregson J, Kaptoge S, Bolton T, Pennells L, Willeit P, Burgess S, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors associated with venous thromboembolism. JAMA Cardiol. 2019; 4:163–173.
Article11. McQuillan BM, Picard MH, Leavitt M, Weyman AE. Clinical correlates and reference intervals for pulmonary artery systolic pressure among echocardiographically normal subjects. Circulation. 2001; 104:2797–2802.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcatheter Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale in a Stroke Patient under the Guidance of Transesophageal Echocardiography
- Patent Foramen Ovale and Stroke-Current Status
- Percutaneous Patent Foramen Ovale Closure After Stroke
- Transcatheter Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Stroke Patients with Thrombophilia: Current Status and Future Perspectives
- Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke