Neurointervention.
2020 Nov;15(3):133-139. 10.5469/neuroint.2020.00052.
Carotid Artery Angioplasty and Stenting for Carotid Stenosis: A Single-Center Experience from Saudi Arabia
- Affiliations
-
- 1King Abdulaziz Medical City, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- 2King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- 3King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- 4College of Medicine, King Khalid University, Abha, Saudi Arabia
- KMID: 2508065
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2020.00052
Abstract
- Purpose
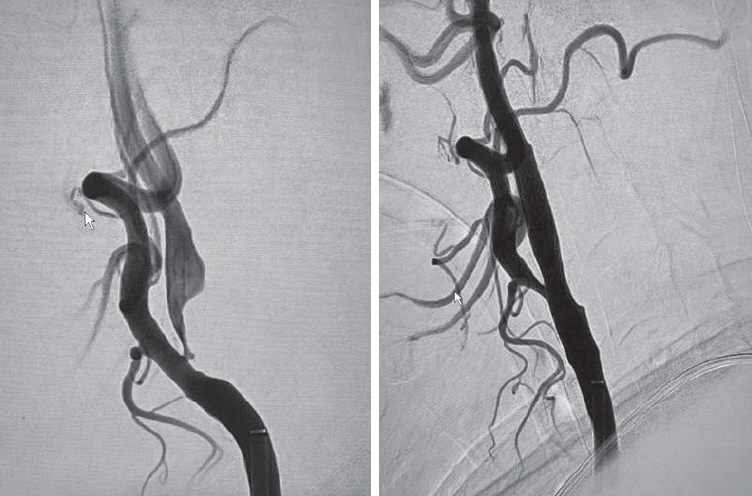
Atherosclerotic stenosis of the extracranial carotid artery accounts for approximately 20% of all strokes. Both carotid artery endarterectomy and carotid artery angioplasty with stenting (CAAS) are recommended for symptomatic patients with 50% or more stenosis or asymptomatic patients with 70% or more stenosis. CAAS is under-reported in Saudi Arabia, as evidenced by a thorough literature search. In this article, we aim to share our experience of CAAS to call for the necessity of conducting more research on stroke and emphasize the local need of utilizing more endovascular treatments like CAAS.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective single-center observational study was conducted at King Abdulaziz Medical City in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. The inclusion criteria consisted of all adult patients (18 years and above) with carotid stenosis who were treated with CAAS.
Results
A total of 16 patients were included in the study. The mean age of the participants was 66.9±13.5 years (range 30–87 years). All patients were symptomatic (had a previous stroke or transient ischemic attack). The procedure was successful in 14 patients (87.5%), while it failed in 2 patients (12.5%) due to technical reasons. All patients had no stroke or myocardial infarction within 30 days of the procedure.
Conclusion
Despite the advancement in medicine with free healthcare services in Saudi Arabia, the interventional procedures for secondary prevention of strokes are underutilized. Collaboration between different hospitals will be extremely helpful since few centers in each city are providing such treatments by an expert neurointerventionist and/or strokologist. The good selection of candidates, optimal management of comorbid conditions, and multidisciplinary care may improve outcomes and reduce mortality.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Katan M, Luft A. Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018; 38:208–211.
Article2. Awada A, al Rajeh S. The Saudi stroke data bank. Analysis of the first 1000 cases. Acta Neurol Scand. 1999; 100:265–269.
Article3. Lu J, Wang D. Advances in endovascular therapy for ischemic cerebrovascular diseases. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2016; 2:135–139.
Article4. Langhoff R. Carotid stenosis - basing treatment on individual patients’ needs. Optimal medical therapy alone or accompanied by stenting or endarterectomy. Vasa. 2018; 47:7–16.5. Moresoli P, Habib B, Reynier P, Secrest MH, Eisenberg MJ, Filion KB. Carotid stenting versus endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2017; 48:2150–2157.6. Sardar P, Chatterjee S, Aronow HD, Kundu A, Ramchand P, Mukherjee D, et al. Carotid artery stenting versus endarterectomy for stroke prevention: a meta-analysis of clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 69:2266–2275.7. Arhuidese IJ, Rizwan M, Nejim B, Malas M. Outcomes of primary and secondary carotid artery stenting. Stroke. 2017; 48:3086–3092.
Article8. Safian RD. Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis: revascularization. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2017; 59:591–600.
Article9. Shaheen MA, Albelali AA, AlKanhal RM, AlSaqabi MK, AlTurki RM, AlAskar RS, et al. Frequency, risk factors, and outcomes in patients with significant carotid artery disease admitted to King Abdulaziz Medical City, Riyadh with ischemic stroke. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2019; 24:264–268.
Article10. Elsharawy MA. Carotid endarterectomy in high-risk Arab patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009; 8:100–103.
Article11. Clinical alert: benefit of carotid endarterectomy for patients with high-grade stenosis of the internal carotid artery. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Stroke and Trauma Division. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) investigators. Stroke. 1991; 22:816–817.12. European Carotid Surgery Trialists’ Collaborative Group. MRC European carotid surgery trial: interim results for symptomatic patients with severe (70-99%) or with mild (0-29%) carotid stenosis. Lancet. 1991; 337:1235–1243.13. Marulanda-Londoño E, Chaturvedi S. Carotid stenosis in women: time for a reappraisal. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2016; 1:192–196.
Article14. Khaleghi M, Isseh IN, Jouni H, Sohn S, Bailey KR, Kullo IJ. Family history as a risk factor for carotid artery stenosis. Stroke. 2014; 45:2252–2256.
Article15. Rincon F, Sacco RL, Kranwinkel G, Xu Q, Paik MC, Boden-Albala B, et al. Incidence and risk factors of intracranial atherosclerotic stroke: the Northern Manhattan stroke study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009; 28:65–71.
Article16. Trystuła M, Pąchalska M. Comorbidities and health-related quality of life following revascularization for asymptomatic critical internal carotid artery stenosis treated with carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty with stenting. Med Sci Monit. 2019; 25:4734–4743.
Article17. Jonas DE, Feltner C, Amick HR, Sheridan S, Zheng ZJ, Watford DJ, et al. Screening for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2014; 161:336–346.
Article18. Mortimer R, Nachiappan S, Howlett DC. Carotid artery stenosis screening: where are we now? Br J Radiol. 2018; 91:20170380.
Article19. Choi HM, Hobson RW, Goldstein J, Chakhtoura E, Lal BK, Haser PB, et al. Technical challenges in a program of carotid artery stenting. J Vasc Surg. 2004; 40:746–751.
Article20. Kim NY, Choi JW, Whang K, Cho SM, Koo YM, Kim JY. Neurologic complications in patients with carotid artery stenting. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2019; 21:86–93.
Article21. Texakalidis P, Tzoumas A, Giannopoulos S, Jonnalagadda AK, Jabbour P, Rangel-Castilla L, et al. Risk factors for restenosis after carotid revascularization: a meta-analysis of hazard ratios. World Neurosurg. 2019; 125:414–424.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Transseptal Approach to Carotid Artery Stenting in Right Internal Carotid Stenosis
- Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty with Palmaz-Schatz Stent in the Carotid Artery Stenosis
- Delayed Carotid Wallstent Shortening Resulting in Restenosis Following Successful Carotid Artery Angioplasty and Stenting
- Subacute In-stent Thrombosis after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Case Report
- Carotid Artery Stenting