J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2019 Oct;45(5):241-253. 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.5.241.
Comparison of minimally invasive versus conventional open harvesting technique for iliac bone graft in secondary alveolar bone grafting in cleft palate patients: a systematic review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, Pimpri, Pune, India. sonalbshah@rediffmail.com
- KMID: 2461476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.5.241
Abstract
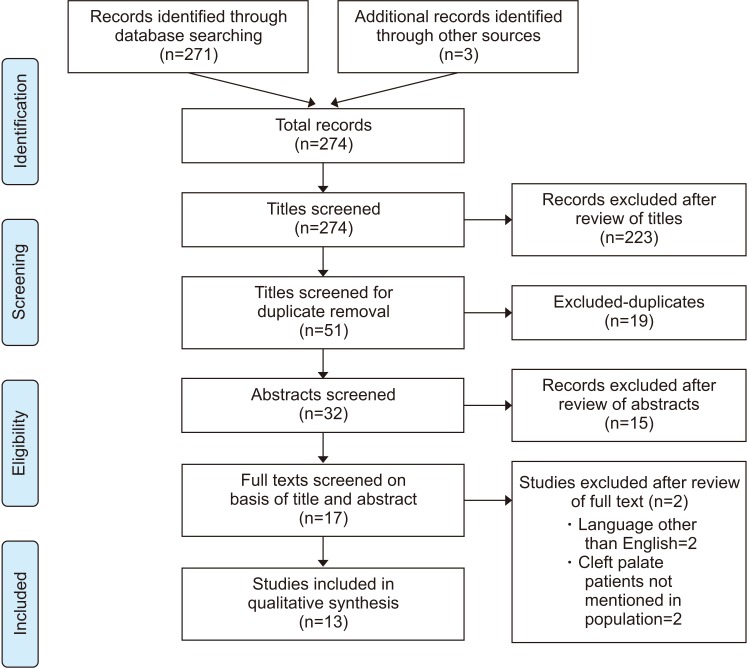
- This study evaluated and compared the donor site morbidity following minimally invasive and conventional open harvesting of iliac bone for secondary alveolar bone grafting in cleft palate patients. A thorough electronic search of PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, and an institutional library and manual search of various journals was done; Inclusion criteria: 1) full-text articles using a minimally invasive or conventional open harvesting technique for iliac bone for secondary alveolar grafting in cleft palate patients and 2) articles published between January 1, 2001 and June 30, 2017 and Exclusion criteria: 1) articles published in languages other than English, 2) case reports, case series, animal studies, in vitro studies, and letters to the editor, and 3) full-text article unavailable even after writing to the authors. Preliminary screening of 274 studies excluded 223 studies for not meeting the eligibility criteria. Of the remaining 51 studies, 19 were removed for being duplicates. Of the remaining 32 studies, 15 were excluded after reading the abstract. Of the 17 studies that were left, 2 were excluded because they were in a language other than English, and 2 were excluded because the study group did not mention cleft palate patients. Thus, 13 studies providing results for a total of 654 patients were included in this qualitative synthesis. Minimally invasive bone graft harvest techniques are better than the conventional open iliac bone harvest method because they offer shorter operative time, decreased requirement for pain medications, less pain on discharge, and a shorter hospital stay.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rawashdeh MA. Morbidity of iliac crest donor site following open bone harvesting in cleft lip and palate patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 37:223–227. PMID: 18272337.
Article2. Raposo-Amaral CA, Denadai R, Chammas DZ, Marques FF, Pinho AS, Roberto WM, et al. Cleft patient-reported postoperative donor site pain following alveolar autologous iliac crest bone grafting: comparing two minimally invasive harvesting techniques. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26:2099–2103. PMID: 26413958.3. Sharma S, Schneider LF, Barr J, Aarabi S, Chibbaro P, Grayson B, et al. Comparison of minimally invasive versus conventional open harvesting techniques for iliac bone graft in secondary alveolar cleft patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011; 128:485–491. PMID: 21788839.
Article4. Schaaf H, Lendeckel S, Howaldt HP, Streckbein P. Donor site morbidity after bone harvesting from the anterior iliac crest. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:52–58. PMID: 20123379.
Article5. Kolomvos N, Iatrou I, Theologie-Lygidakis N, Tzerbos F, Schoinohoriti O. Iliac crest morbidity following maxillofacial bone grafting in children: a clinical and radiographic prospective study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2010; 38:293–302. PMID: 19945294.
Article6. Rawashdeh MA, Telfah H. Secondary alveolar bone grafting: the dilemma of donor site selection and morbidity. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 46:665–670. PMID: 18760515.
Article7. Baqain ZH, Anabtawi M, Karaky AA, Malkawi Z. Morbidity from anterior iliac crest bone harvesting for secondary alveolar bone grafting: an outcome assessment study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:570–575. PMID: 19231782.
Article8. Kessler P, Thorwarth M, Bloch-Birkholz A, Nkenke E, Neukam FW. Harvesting of bone from the iliac crest--comparison of the anterior and posterior sites. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 43:51–56. PMID: 15620775.
Article9. Constantinides J, Chhabra P, Turner PJ, Richard B. A comparison of Shepard's osteotome versus trapdoor flap technique to harvest iliac crest bone for secondary alveolar bone grafting. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2008; 45:347–352. PMID: 18616364.
Article10. Witherow H, Lee RKL, Blenkinsopp PT, Waterhouse N. Comparison of a modified minimally invasive with an open technique following harvesting of cancellous iliac bone. Eur J Plast Surg. 2005; 28:268–271.
Article11. Swan MC, Goodacre TE. Morbidity at the iliac crest donor site following bone grafting of the cleft alveolus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 44:129–133. PMID: 15961201.
Article12. Missiuna PC, Gandhi HS, Farrokhyar F, Harnett BE, Dore EM, Roberts B. Anatomically safe and minimally invasive transcrestal technique for procurement of autogenous cancellous bone graft from the mid-iliac crest. Can J Surg. 2011; 54:327–332. PMID: 21933526.
Article13. Fasolis M, Boffano P, Ramieri G. Morbidity associated with anterior iliac crest bone graft. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012; 114:586–591. PMID: 22901642.
Article14. Vura N, Reddy K R, R S, G R, Kaluvala VR. Donor site evaluation: anterior iliac crest following secondary alveolar bone grafting. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7:2627–2630. PMID: 24392424.
Article15. Abdulrazaq SS, Issa SA, Abdulrazzak NJ. Evaluation of the trephine method in harvesting bone graft from the anterior iliac crest for oral and maxillofacial reconstructive surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26:e744–e746. PMID: 26594994.
Article16. Wheeler J, Sanders M, Loo S, Moaveni Z, Bartlett G, Keall H, et al. Iliac crest donor site for children with cleft lip and palate undergoing alveolar bone grafting: a long-term assessment. J Craniofac Surg. 2016; 27:598–601. PMID: 27035602.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Secondary bone grafting for alveolar clefts: surgical timing, graft materials, and evaluation methods
- Management of Alveolar Cleft
- Correction of Secondary Alveolar Cleft with Gingival Mucoperiosteal Flap and Iliac Bone Grafting:Use of a Percutaneous Bone Biopsy Set
- Oronasal fistula reconstruction using tongue flap with simultaneous iliac bone graft: a case report
- Assessment of the permanent canine bone support after secondary bone graft in UCLP patients