Korean J Radiol.
2019 May;20(5):773-780. 10.3348/kjr.2018.0767.
Segmental Liver Stiffness Evaluated with Magnetic Resonance Elastography Is Responsive to Endovascular Intervention in Patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China. xuk_xuzhou@126.com
- 2Department of CT and MRI, Xuzhou Central Hospital, Xuzhou, China.
- 3The First School of Clinical Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
- KMID: 2442711
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0767
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
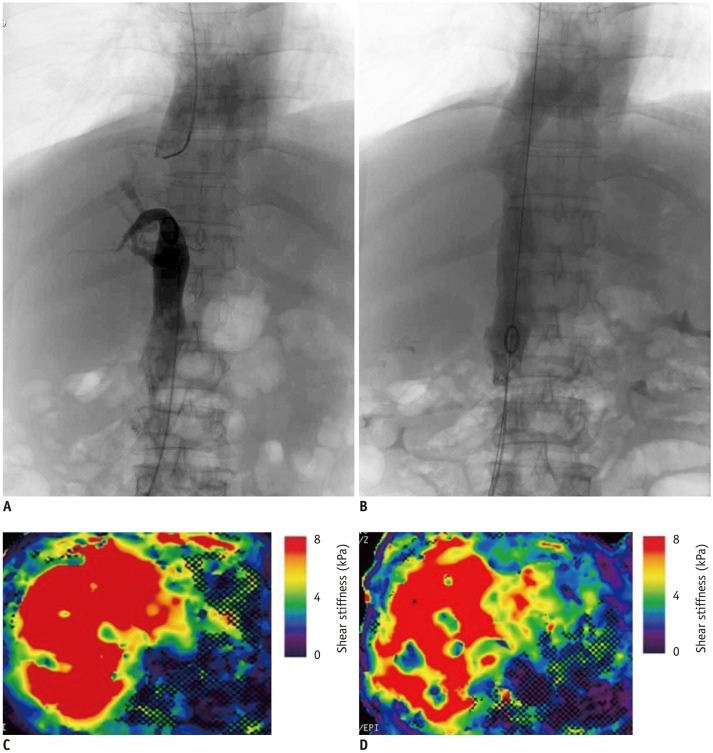
To assess segmental liver stiffness (LS) with MRI before and after endovascular intervention in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
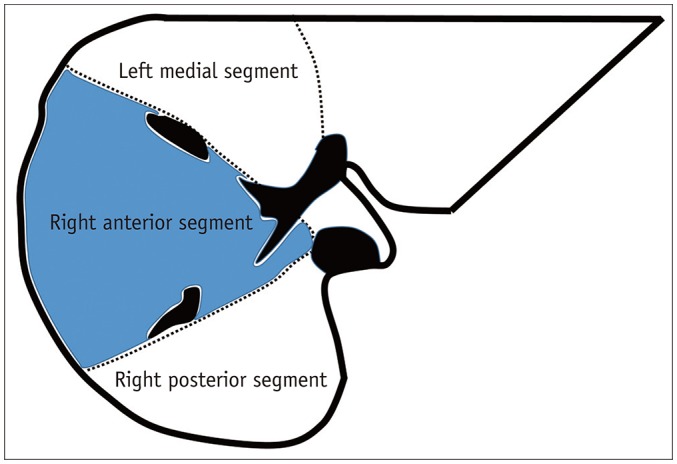
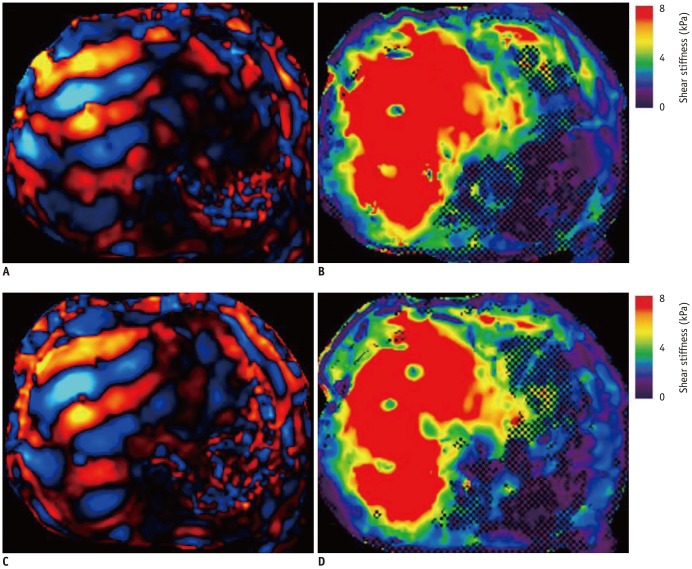
Twenty-three patients (13 males and 10 females; mean age, 42.6 ± 12.6 years; age range, 31-56 years) with BCS as a primary liver disease were recruited for this study. Two consecutive magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) examinations were performed before the endovascular treatment. Fifteen patients who underwent endovascular intervention treatment also had follow-up MRE scans within three days after the procedure. LS was measured in three liver segments: the right posterior, right anterior, and left medial segments. Inter-reader and inter-exam repeatability were analyzed with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Bland-Altman analysis. Segmental LS and clinical characteristics before and after the intervention were also compared.
RESULTS
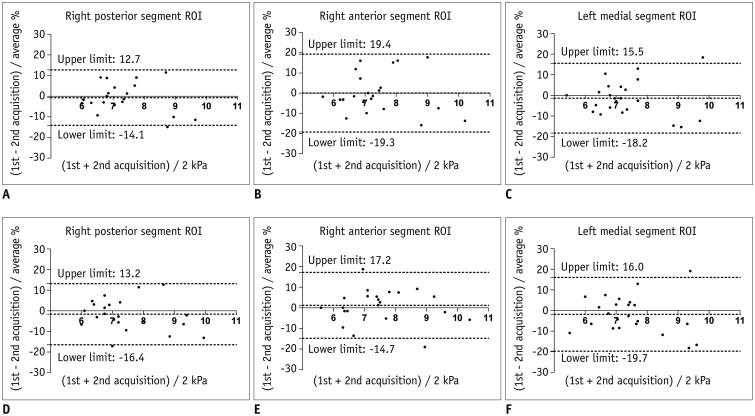
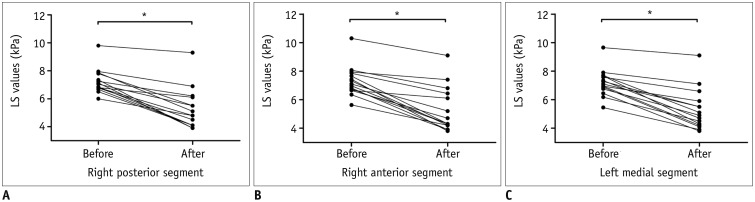
Within three days of the endovascular intervention, all three segmental LS values decreased: LS of the right posterior segment = 7.23 ± 0.88 kPa (before) vs. 4.94 ± 0.84 kPa (after), LS of the right anterior segment = 7.30 ± 1.06 kPa (before) vs. 4.77 ± 0.85 kPa (after), and LS of the left medial segment = 7.22 ± 0.87 kPa (before) vs. 4.87 ± 0.72 kPa (after) (all p = 0.001). There was a significant correlation between LS changes and venous pressure gradient changes before and after treatments (r = 0.651, p = 0.009). The clinical manifestations of all 15 patients significantly improved after therapy. The MRE repeatability was excellent, with insignificant variations (inter-reader, ICC = 0.839-0.943: inter-examination, ICC = 0.765-0.869). Bland-Altman analysis confirmed excellent agreement (limits of agreement, 13.4-19.4%).
CONCLUSION
Segmental LS measured by MRE is a promising repeatable quantitative biomarker for monitoring the treatment response to minimally invasive endovascular intervention in patients with BCS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Plessier A, Rautou PE, Valla DC. Management of hepatic vascular diseases. J Hepatol. 2012; 1:S25–S38.
Article2. Copelan A, Remer EM, Sands M, Nghiem H, Kapoor B. Diagnosis and management of Budd Chiari syndrome: an update. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015; 38:1–12.
Article3. Tang A, Cloutier G, Szeverenyi NM, Sirlin CB. Ultrasound elastography and MR elastography for assessing liver fibrosis: part 2, diagnostic performance, confounders, and future directions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 205:33–40. PMID: 25905762.
Article4. Han KH, Yoon KT. New diagnostic method for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Intervirology. 2008; 51(Suppl 1):11–16. PMID: 18544943.
Article5. Srinivasa Babu A, Wells ML, Teytelboym OM, Mackey JE, Miller FH, Yeh BM, et al. Elastography in chronic liver disease: modalities, techniques, limitations, and future directions. Radiographics. 2016; 36:1987–2006. PMID: 27689833.
Article6. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Woo HS, Yu MH, Joo I, Lee ES, et al. Staging of hepatic fibrosis: comparison of magnetic resonance elastography and shear wave elastography in the same individuals. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:202–212. PMID: 23483022.
Article7. Mukund A, Pargewar SS, Desai SN, Rajesh S, Sarin SK. Changes in liver congestion in patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome following endovascular interventions: assessment with transient elastography. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28:683–687. PMID: 28153486.
Article8. Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:32–40. PMID: 18471441.
Article9. Huwart L, Sempoux C, Salameh N, Jamart J, Annet L, Sinkus R, et al. Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology. 2007; 245:458–466. PMID: 17940304.
Article10. Trout AT, Sheridan RM, Serai SD, Xanthakos SA, Su W, Zhang B, et al. Diagnostic performance of MR elastography for liver fibrosis in children and young adults with a spectrum of liver diseases. Radiology. 2018; 287:824–832. PMID: 29470938.
Article11. Lee JE, Lee JM, Lee KB, Yoon JH, Shin CI, Han JK, et al. Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infection using magnetic resonance elastography. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:210–217. PMID: 24643284.
Article12. Yoshimitsu K, Mitsufuji T, Shinagawa Y, Fujimitsu R, Morita A, Urakawa H, et al. MR elastography of the liver at 3.0 T in diagnosing liver fibrosis grades; preliminary clinical experience. Eur Radiol. 2016; 26:656–663. PMID: 26060066.
Article13. Rouvière O, Yin M, Dresner MA, Rossman PJ, Burgart LJ, Fidler JL, et al. MR elastography of the liver: preliminary results. Radiology. 2006; 240:440–448. PMID: 16864671.
Article14. Venkatesh SK, Wang G, Lim SG, Wee A. Magnetic resonance elastography for the detection and staging of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24:70–78. PMID: 23928932.
Article15. Tan CH, Venkatesh SK. Magnetic resonance elastography and other magnetic resonance imaging techniques in chronic liver disease: current status and future directions. Gut Liver. 2016; 10:672–686. PMID: 27563019.
Article16. Lee YJ, Lee JM, Lee JE, Lee KB, Lee ES, Yoon JH, et al. MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: reproducibility of the examination and reproducibility and repeatability of the liver stiffness value measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 39:326–331. PMID: 23589232.
Article17. Noone TC, Semelka RC, Siegelman ES, Balci NC, Hussain SM, Kim PN, et al. Budd-Chiari syndrome: spectrum of appearances of acute, subacute, and chronic disease with magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2000; 11:44–50. PMID: 10676619.
Article18. Cai SF, Gai YH, Liu QW. Computed tomography angiography manifestations of collateral circulations in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 9:399–404. PMID: 25574205.
Article19. Cho OK, Koo JH, Kim YS, Rhim HC, Koh BH, Seo HS. Collateral pathways in Budd-Chiari syndrome: CT and venographic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996; 167:1163–1167. PMID: 8911174.
Article20. Wagner M, Corcuera-Solano I, Lo G, Esses S, Liao J, Besa C, et al. Technical failure of MR elastography examinations of the liver: experience from a large single-center study. Radiology. 2017; 284:401–412. PMID: 28045604.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Budd-Chiari syndrome with multiple large regenerative nodules
- Anesthetic Management for Surgery of Patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- A Case of Budd Chiari Syndrome Caused by Membraneous Obstruction of Suprahepatic Inferior Vena Cava
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome: Right hepatic vein obstruction and incomplete IVC obstruction with azygos continuation of IVC
- A Case of Budd-Chiari Syndrome with IVC Web Treated by Balloon Dilatation