Lab Med Online.
2019 Apr;9(2):99-102. 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.99.
A Case of Mature B-cell Neoplasm with Light Chain Clonality Confirmed by Cytoplasmic Light Chain Expression Using Flow Cytometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. duck.cho@skku.edu
- KMID: 2441831
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.99
Abstract
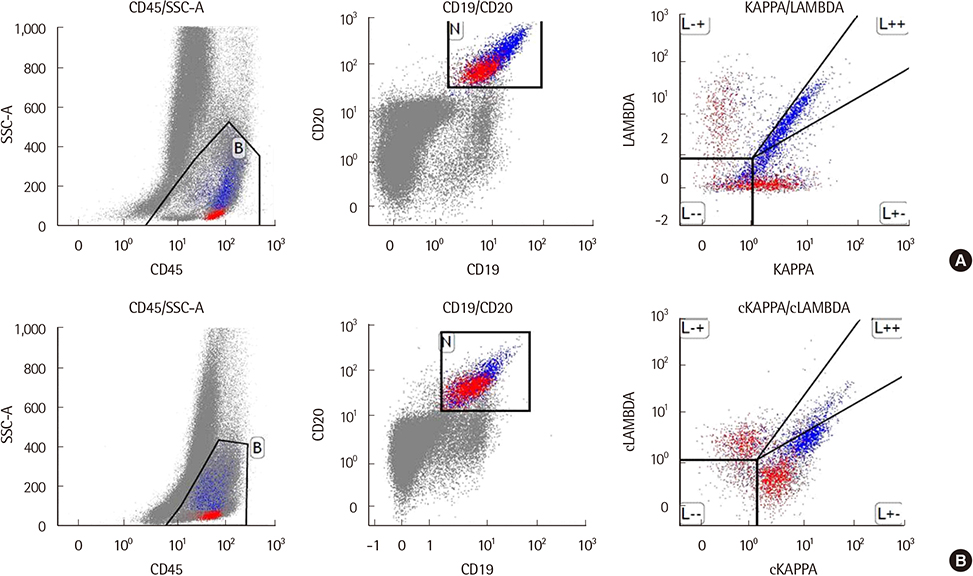
- Surface immunoglobulin light-chain restriction is evidence of clonality in mature B-cell neoplasms. An aberrant pattern of surface light-chain expression can also be considered evidence of clonality. However, because this result could occur due to nonspecific staining or failure to stain, careful interpretation is required for accurate diagnosis. According to a previous study, flow cytometric analysis of the cytoplasmic pattern of light-chain expression in mature B-cell neoplasms is a viable approach to confirming clonality. Herein, we report a case, in which clonality could not be proven by surface light-chain analysis, but was demonstrated by cytoplasmic light-chain analysis. The case was in a patient with B-cell lymphoma showing non-specific surface expression of light-chains. This case support consideration of flow cytometric analysis of cytoplasmic light-chain expression patterns when aberrant surface light chain expression is observed, to confirm clonality of mature B-cell neoplasms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hulspas R, O'Gorman MR, Wood BL, Gratama JW, Sutherland DR. Considerations for the control of background fluorescence in clinical flow cytometry. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2009; 76:355–364.
Article2. Pianezze G, Gentilini I, Casini M, Fabris P, Coser P. Cytoplasmic immunoglobulins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood. 1987; 69:1011–1014.
Article3. Lewis RE, Cruse JM, Pierce S, Lam J, Tadros Y. Surface and cytoplasmic immunoglobulin expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Exp Mol Pathol. 2005; 79:146–150.
Article4. Brozic A, Pohar Marinsek Z, Novakovic S, Kloboves Prevodnik V. Inconclusive flow cytometric surface light chain results; can cytoplasmic light chains, Bcl-2 expression and PCR clonality analysis improve accuracy of cytological diagnoses in B-cell lymphomas? Diagn Pathol. 2015; 10:191.
Article5. Alley CL, Wang E, Dunphy CH, Gong JZ, Lu CM, Boswell EL, et al. Diagnostic and clinical considerations in concomitant bone marrow involvement by plasma cell myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/ monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis: a series of 15 cases and review of literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013; 137:503–517.
Article6. Paiva B, Almeida J, Pérez-Andrés M, Mateo G, López A, Rasillo A, et al. Utility of flow cytometry immunophenotyping in multiple myeloma and other clonal plasma cell-related disorders. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2010; 78:239–252.
Article7. Xu D. Dual surface immunoglobulin light-chain expression in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006; 130:853–856.
Article8. Fujiwara T, Ishizawa K, Kohata K, Yamamoto J, Yamada MF, Kameoka J, et al. Aggressive B-cell lymphoma with dual surface immunoglobulin light-chain expression. Intern Med. 2007; 46:1458–1461.
Article9. Kaleem Z, Zehnbauer BA, White G, Zutter MM. Lack of expression of surface immunoglobulin light chains in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000; 113:399–405.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of laboratory diagnostic tests for light-chain clonality and bone marrow findings in AL amyloidosis
- A Case of Lambda-expressing Pulmonary MALT Lymphoma with Dual Clonal Rearrangements of Kappa and Lambda Immunoglobulin Light Chain Gene
- Simultaneous Detection of Intracytoplasmic CD3epsilon and Surface CD4 and CD8 Expression by Murine Thymocyte by Flow Cytometry
- Diagnostic Utility of a Clonality Test for Lymphoproliferative Diseases in Koreans Using the BIOMED-2 PCR Assay
- Non-Radioactive Detection of Clonality in Malignant Lymphoid Neoplasms using the Polymerase Chain Reaction