J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2019 Feb;19(1):37-44. 10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.1.37.
Investigation of the effects of temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis on blood volume of the retinal structures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Adiyaman University, Adiyaman, Turkey. akeskinruzgar@gmail.com
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Medical School, Adiyaman University, Adiyaman, Turkey.
- KMID: 2439034
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.1.37
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Arthrocentesis is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is used to alleviate the symptoms of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of arthrocentesis on the blood supply to the retinal structures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
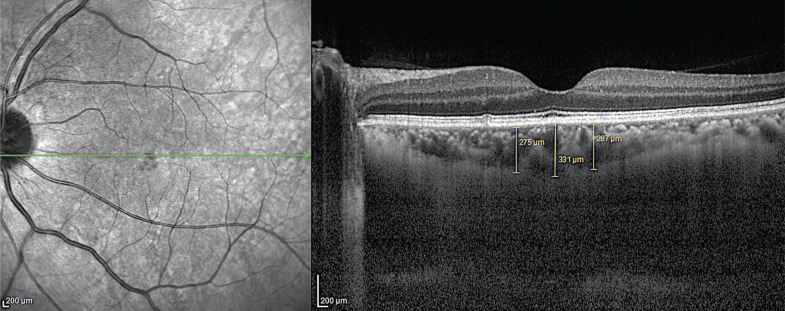
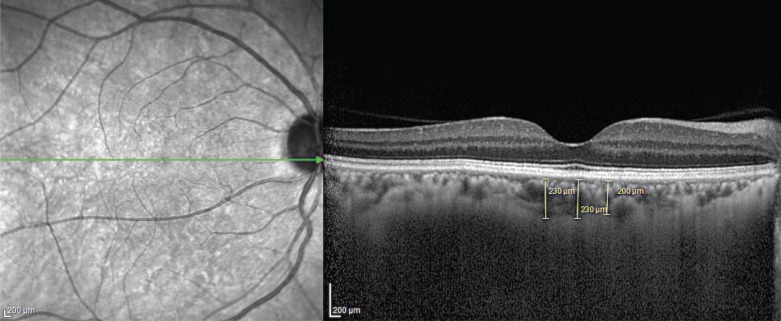
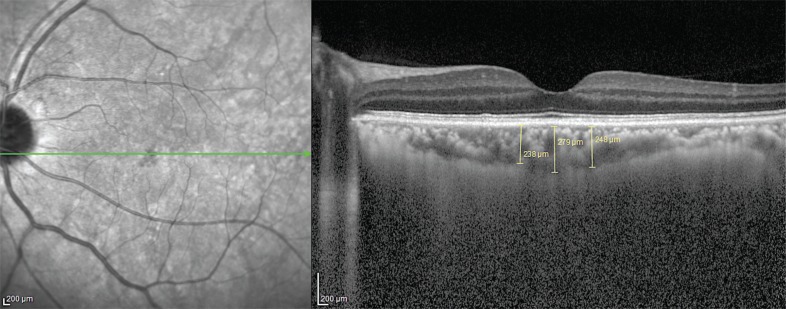
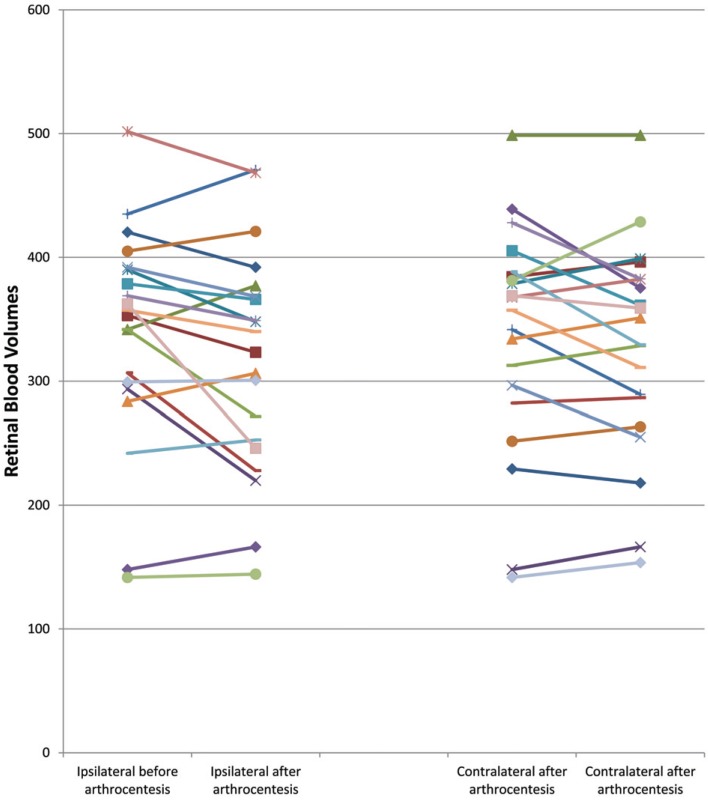
Arthrocentesis was performed on 20 patients with TMJ disorders, and choroidal thickness (CT) in patients was measured to evaluate retinal blood circulation. The blood volume of the retinal structures was evaluated ipsilaterally before and after arthrocentesis, and these measurements were then compared with measurements obtained from the contralateral side.
RESULTS
Before arthrocentesis, there were no differences in retinal blood volumes between the ipsilateral and contralateral sides (P = 0.96). When ipsilateral CT measurements taken before and after arthrocentesis were compared, retinal blood supply was found to have significantly decreased after arthrocentesis (P = 0.04). When contralateral CT measurements taken before and after arthrocentesis were compared, retinal blood supply was also found to have decreased after arthrocentesis, but not significantly (P = 0.19).
CONCLUSION
The solution of local anesthesia with epinephrine applied before the arthrocentesis procedure was found to reduce the blood volume of the retinal structures. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that has investigated the blood volume of the retinal structures following arthrocentesis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
An unusual complication during arthrocentesis: N. facialis paralysis, with N. lingualis and N. alveolaris inferior anesthesia
Toghrul Aliyev, Eynar Berdeli, Onur Şahin
J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019;19(2):115-118. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.2.115.
Reference
-
1. Nitzan DW, Dolwick MF, Martinez GF. Temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis: a simplified treatment for severe, limited mouth opening. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 49:1163–1167. PMID: 1941330.
Article2. Gouveia MV, Barbalho JC, Pereira Junior ED, Nascimento MM, Vasconcelos BC. Effectiveness and satisfaction evaluation of patients submitted to TMJ arthrocentesis: a case series. Braz Oral Res. 2015; 29:50. PMID: 25789507.3. Şentürk MF, Fındık Y, Baykul T. Intraoperative comparison of single-and double-puncture techniques in temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018; 47:1060–1064. PMID: 29685386.4. Laskin DM. Arthroscopy Versus Arthrocentesis for Treating Internal Derangements of the Temporomandibular Joint. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2018; 30:325–328. PMID: 29866452.
Article5. Vaira LA, Raho MT, Soma D, Salzano G, Orabena G, Piombino P, et al. Complications and post-operative sequelae of temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis. Cranio. 2017; 15:1–4.
Article6. Tvrdy P, Heinz P, Pink R. Arthrocentesis of the temporomandibular joint: a review. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015; 159:31–34. PMID: 23579112.
Article7. Alpaslan C, Dolwick MF, Heft MW. Five year retrospective evaluation of temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 32:263–267. PMID: 12767872.8. Yavuz GY, Keskinruzgar A. Evaluation of Complications of Arthrocentesis in the Management of the Temporomandibular Joint Disorders. Galore Int J Heal Sci Res. 2018; 3:50–53.9. Von Arx T, Lozanoff S, Zinkernagel M. Ophthalmologic complications after intraoral local anesthesia. Swiss Dent J. 2014; 124:784–806. PMID: 25120235.10. Cazaubon Y, Mauprivez C, Feliu C, Binet L, Oget O, Gozalo C, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of articaine with 1: 200,000 epinephrine during third molar surgery and simulation of high-dose regimens. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018; 114:38–45. PMID: 29197630.11. Fujimoto JG, Hee MR, Huang D. Principles of optical coherence tomography. In : Schuman JS, Puliafito CA, Fujimoto JG, editors. Optical coherence tomography of ocular diseases. Thorofare (NJ): Slack Inc;2004. p. 3–20.12. Huang D, Swanson EZ, Lin CP, Schuman JS, Stinson WG, Chang W, et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science. 1991; 254:1178–1181. PMID: 1957169.
Article13. Doğan S, Şimşek A, Bayraktar C, Yazıcı H, Sarıkaya Y, Karataş M, et al. Ocular blood flow alterations during inferior turbinate radiofrequency reduction under local anesthesia. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016; 30:185–188. PMID: 27305596.
Article14. Keskinruzgar A, Kalenderoglu A, Yapici Yavuz G, Koparal M, Simsek A, Karadag AS, et al. Investigation of neurodegenerative and inflammatory processes in sleep bruxism. Cranio. 2018; 1–7.
Article15. Berrones D, Salcedo-Villanueva G, Morales-Cantón V, Velez-Montoya R. Changes in Retinal and Choroidal Vascular Blood Flow after Oral Sildenafil: An Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Study. J Ophthalmol. 2017; 2017:7174540. PMID: 29129998.
Article16. Kumar S, Kiran K, Yadav A. Temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis: A prospective study and audit of 500 joints of central. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2018; 8:124–129. PMID: 29780737.17. Al-Khotani A, Naimi-Akbar A, Albadawi E, Ernberg M, Hedenberg-Magnusson B, Christidis N. Prevalence of diagnosed temporomandibular disorders among Saudi Arabian children and adolescents. J Headache Pain. 2016; 17:41. PMID: 27102118.
Article18. Carroll TA, Smith K, Jakubowski J. Extradural haematoma following temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis and lavage. Br J Neurosurg. 2000; 14:152–154. PMID: 10889893.19. Etoz OA, Er N, Alkan A. Accidental use of alcohol during arthrocentesis of the temporomandibular joint. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 49:e1–e2. PMID: 21168938.
Article20. Şentürk MF, Koçer G, Bülte M, Aksoy MÇ. Intra and post operative complications of temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis. J Dent Fac Atatürk Uni. 2016; 26:292–295.
Article21. Vaira LA, Soma D, Meloni SM, Orabena G, Piombino P, Deu Rio G. Vertiginous crisis following temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis: a case report. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017; 21:79–81. PMID: 27924428.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of sodium hyaluronate in treating temporomandibular joint disorders
- An unusual complication during arthrocentesis: N. facialis paralysis, with N. lingualis and N. alveolaris inferior anesthesia
- AN EFFECT OF COMBINATION WITH ARTHROCENTESIS AND STABILIZATION SPLINT TREATMENT ON TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISORDER PATIENT
- Clinical Aspect of Arthrocentesis
- An effect of hyaluronic acid on the temporomandibular joint arthrocentesis