Int J Thyroidol.
2017 May;10(1):42-45. 10.11106/ijt.2017.10.1.42.
Atypical Thyroiditis Following Influenza B Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. cgchomd@naver.com
- 2Department of Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Wonkwang University Sanbon Hospital, Gunpo, Korea.
- KMID: 2379360
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2017.10.1.42
Abstract
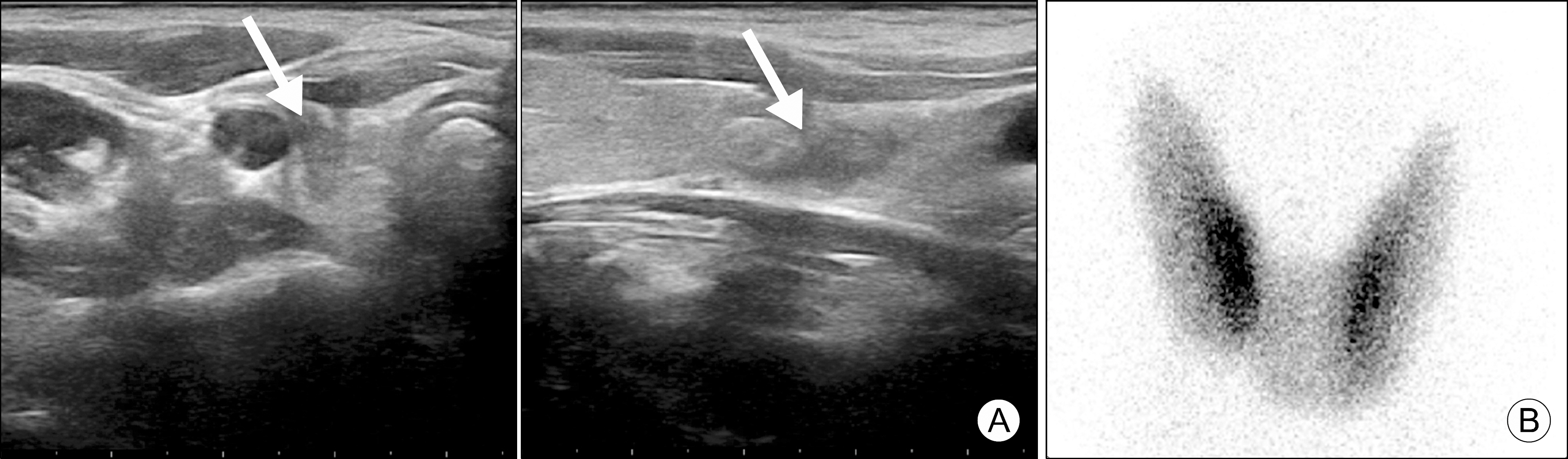
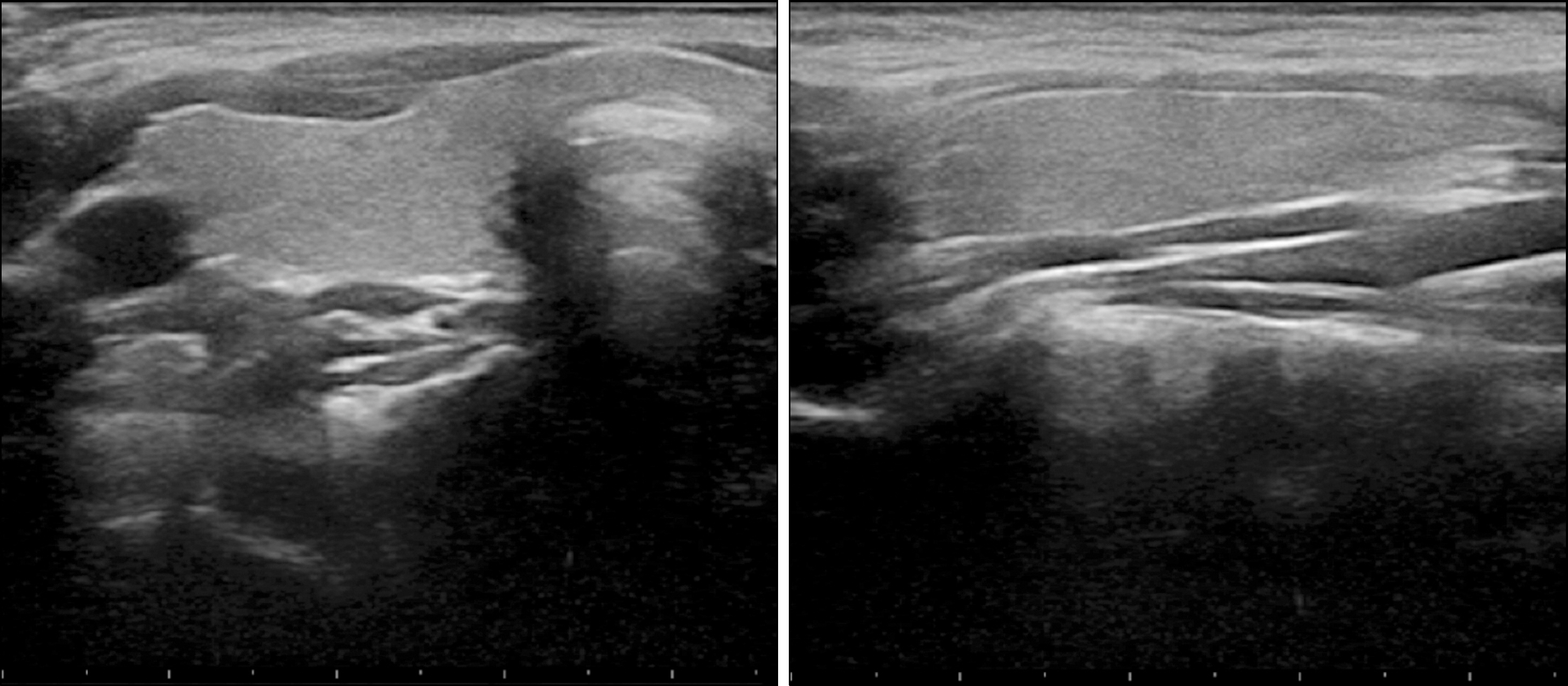
- Viral infections are known to be a predisposing factor for subacute (De Quervain's) thyroiditis. In this report, we document a novel case of thyroiditis, with an atypical presentation, following an influenza B infection. A 13-year-old previously healthy female visited the outpatient clinic complaining of right neck pain. She had been diagnosed with an influenza B infection at a local clinic 3 weeks earlier. All laboratory tests were normal. A thyroid ultrasound showed an ill-defined hypoechoic mass (1.0×0.5×1.5 cm) in the right lower thyroid, and scintigraphy of the thyroid with Technetium-99m (99m-Tc) demonstrated the normal uptake of the radiotracer. Fine-needle aspiration from the nodule showed the presence of a few neutrophils. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of atypical thyroiditis associated with an influenza B infection described in the literature. Influenza B infection should be considered as a possible cause of atypical thyroiditis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Prummel MF, Strieder T, Wiersinga WM. The environment and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004; 150(5):605–18.
Article2). Dimos G, Pappas G, Akritidis N. Subacute thyroiditis in the course of novel H1N1 influenza infection. Endocrine. 2010; 37(3):440–1.
Article3). Cunha BA, Berbari N. Subacute thyroiditis (de Quervain's) due to influenza A: presenting as fever of unknown origin (FUO). Heart Lung. 2013; 42(1):77–8.
Article4). Michas G, Alevetsovitis G, Andrikou I, Tsimiklis S, Vryonis E. De Quervain thyroiditis in the course of H1N1 influenza infection. Hippokratia. 2014; 18(1):86–7.5). Altay FA, Guz G, Altay M. Subacute thyroiditis following seasonal influenza vaccination. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016; 12(4):1033–4.
Article6). Pearce EN, Farwell AP, Braverman LE. Thyroiditis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348(26):2646–55.
Article7). Sari O, Erbas B, Erbas T. Subacute thyroiditis in a single lobe. Clin Nucl Med. 2001; 26(5):400–1.8). Singer PA. Thyroiditis. Acute, subacute, and chronic. Med Clin North Am. 1991; 75(1):61–77.
Article9). Mordes DA, Brachtel EF. Cytopathology of subacute thyroiditis. Diagn Cytopathol. 2012; 40(5):433–4.
Article10). Vural C, Paksoy N, Gok ND, Yazal K. Subacute granu-lomatous (De Quervain's) thyroiditis: Fine-needle aspiration cytology and ultrasonographic characteristics of 21 cases. Cytojournal. 2015; 12:9.
Article