Asian Oncol Nurs.
2016 Dec;16(4):226-233. 10.5388/aon.2016.16.4.226.
Effect of Abdominal Skin Massage and Warming Therapy on the Pain and Anxiety in Breast Cancer Patients who Underwent Hormone Injections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ambulatory Treatment Center, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. snlee0625@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 2366577
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5388/aon.2016.16.4.226
Abstract
- PURPOSE
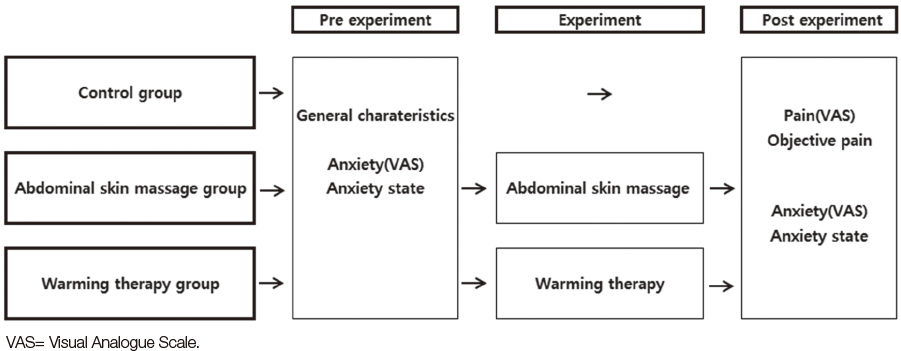
The purpose of this study was to identify effects of abdominal skin massage and warming therapy on the pain and anxiety to breast cancer patients who underwent hormone injections.
METHODS
The subjects for the study were 60 breast cancer patients who underwent hormone injections (20 in the control group, 20 in the abdominal skin massage group, and 20 in the warming therapy group). Abdominal skin massage was conducted following KSMA's (Korea science massage association) advice and warming therapy was executed at 48 ℃ for 20 minutes. The results were checked using subjective and objective measurement tools.
RESULTS
After abdominal skin massage and warming therapy, subjective (Visual Analogue Scale, VAS) and objective (facial expression and vocal change) pain scores were significantly decreased (p<.001) Also, Anxiety state was significantly decreased compared to the control group (p =.043).
CONCLUSION
The results of this study indicate that abdominal skin massage and warming therapy were highly effective in alleviating pain and anxiety in patients who underwent hormone injections.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oh CM, Won YJ, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Cho H, Lee JK, et al. Cancer statistics in korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2013. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:436–450.
Article2. Hwang E, Yi M. Factors influencing quality of life in patients with breast cancer on hormone therapy. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2014; 44:108–117.
Article3. Naya Y, Hagiwara N, Takeuchi I, Mori M, Inagaki A, Nakanouchi T. Fifteen-second skin icing using a frozen gel pack is effective for reducing goserelin injection pain. Urol Int. 2014; 93:202–206.
Article4. Park YH. Drug therapy for breast cancer. J Korean Med Assoc. 2009; 52:963–974.
Article5. Park JS. The effect of cutaneous stimulation and distraction on IV injection pain of chemotherapy patients. J Korean Acad Nurs. 1998; 28:303–318.
Article6. Choi SH, Baek KH, Lim HB, Lee JY, Kim HJ, Kim YS, et al. The effect of warm and ice application for pain control caused by arteriovenous fistula needling under hemodialysis. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2006; 12:179–189.7. Buhse M. Efficacy of EMLA cream to reduce fear and pain associated with interferon beta-1a injection in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci Nurs. 2006; 38:222–226.
Article8. McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF. Manual for the profile of mood states. 1971.9. Lee M. The effect of foot massage on patients with post-operative pain and anxiety following abdominal surgery [master thesis]. Daejeon: Eulji Univ.;2009.10. Loving JE. Massage therapy: theory and practice. Stanford, Connecticut: Appl.11. Jeong KT, Yeon LH, A LJ. Effects of electric heating pad on abdominal pain and anxiety during the colonoscopy. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2008; 14:47–57.12. Kang IS, Cho KJ. The effect of thermotherapy on high school girls' dysmenorrhea. J Korean Community Nurs. 2001; 12:773–784.13. Jung M. The effect of warm and ice application on the pain and stress in needling under hemodialysis [master's thesis]. Kangneung: Kwandong Univ.;2002.14. Malanga GA, Yan N, Stark J. Mechanisms and efficacy of heat and cold therapies for musculoskeletal injury. Postgrad Med. 2015; 127:57–65.
Article15. Barnhill BJ, Holbert MD, Jackson NM, Erickson RS. Using pressure to decrease the pain of intramuscular injections. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1996; 12:52–58.
Article16. Lee SJ, Chon SJ, Roh YS, Park YM. Change in the sensation of the arms, the range of motion in the shoulders and depression in breast cancer patients. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2008; 19:398–407.17. Park J. Effect of nursing intervention on alleviating pain after intramuscular unjection: application of massage device using vibration and pressure [master's thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang Univ.;2014.18. Rosdahl CB, Kowalski MT. Textbook of basic nursing. New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2008.19. Speirs AF, Taylor K, Joanes D, Girdler N. Anaesthetics: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, comparative study of topical skin analgesics and the anxiety and discomfort associated with venous cannulation. Br Dent J. 2001; 190:444–449.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Aroma Hand Massage on Pain, State Anxiety and Depression in Hospice Patients with Terminal Cancer
- Analysis of Studies on Hand Massage Published in Korea: On the Effects of Sleep, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
- Effects of Postpartum Massage Program on Stress response in the Cesarean section Mothers
- Comparison of Effects Lavender Abdominal Massage and Inhalation on Dysmenorrhea, Pain, Anxiety and Depression
- The Effect of Pre-warming for Patients under Abdominal Surgery on Body Temperature, Anxiety, Pain, and Thermal Comfort