J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Apr;44(2):266-270.
Posterior Instability after Posterior Cruciate Ligament Substituted TKA: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Maryknoll Hospital, Busan, Korea. metacarpal@lycos.co.kr
Abstract
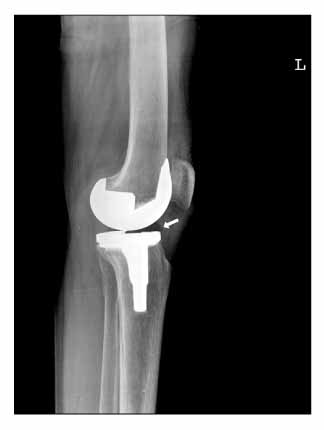
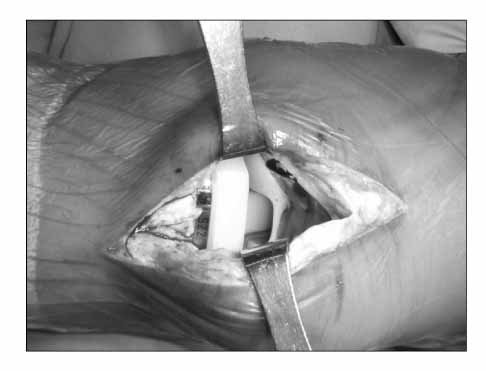
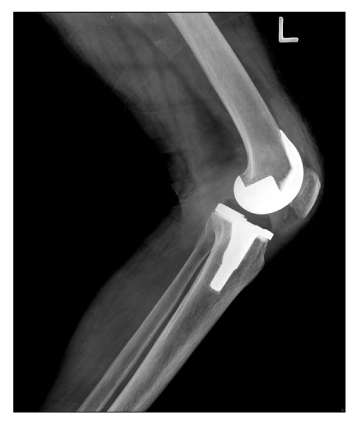
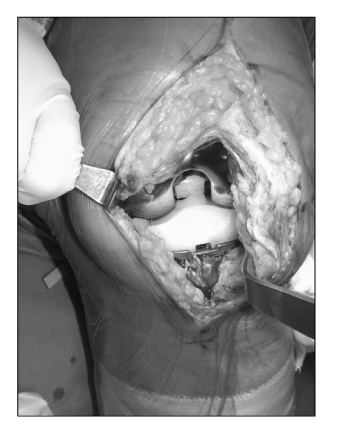
- Posterior instability after a posterior ligament substituted total knee replacement is considered impossible due to the cam and post mechanism. Therefore, it has not been considered easily as a problem necessitating revision surgery. We report two cases of posterior instability after a fixed bearing posterior cruciate ligament substituted total knee replacement with a review of relevant literature.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Callaghan JJ, O'Rourke MR, Goetz DD, Schmalzried TP, Campbell PA, Johnston RC. Tibial post impingement in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. 404:83–88.2. Chiu YS, Chen WM, Huang CK, Chiang CC, Chen TH. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in a NexGen posterior-stabilized knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19:1045–1049.
Article3. Galinat BJ, Vernace JV, Booth RE Jr, Rothman RH. Dislocation of the posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. A report of two cases. J Arthroplasty. 1988. 3:363–367.4. Gebhard JS, Kilgus DJ. Dislocation of a posterior stabilized total knee prosthesis. A report of two cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. 254:225–229.5. Mariconda M, Lotti G, Milano C. Fracture of posterior-stabilized tibial insert in a Genesis knee prosthesis. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15:529–530.
Article6. Mestha P, Shenava Y, D'Arcy JC. Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in posterior stabilized (Insall Burstein II) total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15:814–815.
Article7. Pagnano MW, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, Stuart MJ. Flexion instability after primary posterior cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. 356:39–46.
Article8. Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Booth RE Jr, Balderston RA, Rothman RH. Posterior dislocation of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. 278:128–133.
Article9. Su YP, Chiu FY, Chen TH. Posterior dislocation after posterior stabilization TKA. J Chin Med Assoc. 2003. 66:120–122.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dislocation of Tibial Insert after Fixed Bearing TKA using Minimal Invasive Surgery: A Case Report
- Ganglion of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament: 1 case report
- Ganglion Cyst of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament: A Case Report
- Reconstruction of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament Using the Medial Meniscus
- Extension Block by the Posterior Cruciate Ligament Partial Rupture in the Knee: A Case Report