J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2015 Jun;22(2):50-54. 10.4184/jkss.2015.22.2.50.
Clinical Outcomes of Coccygectomy for Chronic Coccygodynia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wonkwang University, Gunpo, Korea. niceo@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan, Korea.
- 3Institute of Wonkwang Medical Science, Iksan, Korea.
- KMID: 2322952
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2015.22.2.50
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
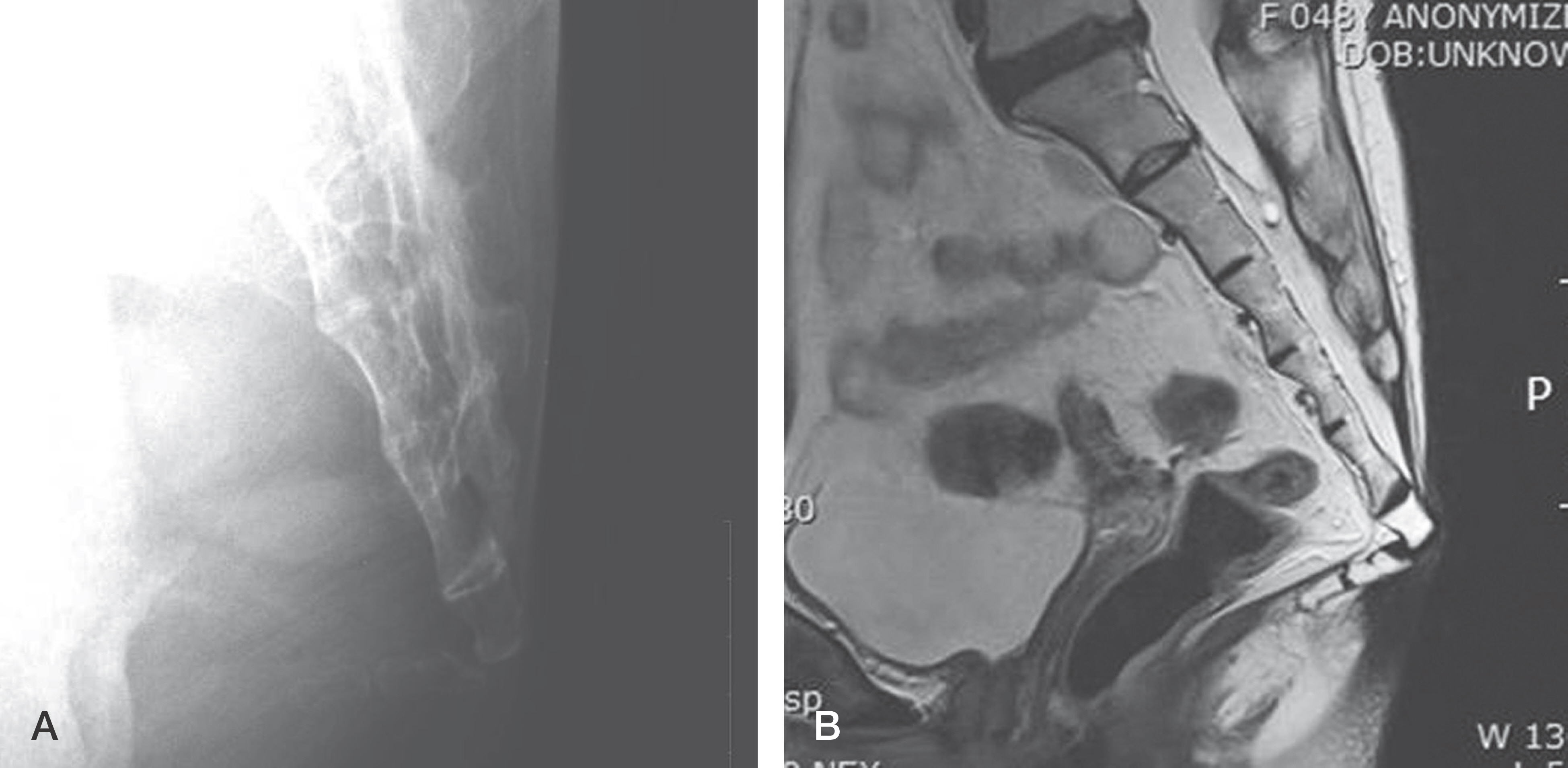
To confirm the clinical outcomes of coccygectomy for intractable chronic coccygodynia. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Coccygectomy has been reported to be one of the good options for the failure of conservative treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective review was conducted, including nine patients who underwent coccygectomy for intractable chronic coccygodynia.
RESULTS
Improvements in the mean visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, from 5.6 to 2.1, were observed. As for patient satisfaction, there were four cases with excellent outcomes, three with good outcomes, one with a fair outcome, and only one with a poor outcome. Surgical complications, such as wound infection, did not occur in any of the cases.
CONCLUSIONS
Irrespective of the causes, coccygectomy for chronic coccygodynia, for which nonsurgical management, including cushions, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroid injections, has no effect, is considered a useful method because it brings definite pain relief and leads to high patient satisfaction.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Balain B, Eisenstein S.M, Alo G.O, et al. Coccygectomy for coccydynia: case series and review of literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:414–20.
Article2. Fogel G.R., Cunningham P.Y.3rd, Esses S.I. Coccygodynia: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:49–54.
Article3. Patel R, Appannagari A, Whang P.G. Coccydynia. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008; 1:223–6.
Article4. Postacchini F, Massobrio M. Idiopathic coccygodynia. Analysis of fifty-one operative cases and a radiographic study of the normal coccyx. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65:1116–24.
Article5. Feldbrin Z, Singer M, Keynan O, et al. Coccygectomy for intractable coccygodynia. Isr Med Assoc J. 2005; 7:160–2.6. Traub S, Glaser J, Manino B. Coccygectomy for the treatment of therapy-resistant coccygodynia. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2009; 18:147–9.7. Wood K.B, Mehbod A.A. Operative treatment for coccygodynia. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004; 17:511–5.
Article8. Maigne JY, Chatellier G, Faou ML, et al. The treatment of chronic coccydynia with intrarectal manipulation: a randomized controlled study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:621–7.9. Wray C.C, Easom S, Hoskinson J. Coccydynia. Aetiology and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:335–8.
Article10. Bilgic S, Kurklu M, Yurttas Y, et al. Coccygectomy with or without periosteal resection. Int Orthop. 2010; 34:537–41.
Article11. Trollegaard AM, Aarby NS, Hellberg S. Coccygectomy: an effective treatment option for chronic coccydynia: retrospective results in 41 consecutive patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92:242–5.12. Cebesoy O., Guclu B., Kose K.C., et al. Coccygectomy for coccygodynia: do we really have to wait? Injury. 2007; 38:1183–8.
Article13. Hong CH, Lee TK, Kim SB, et al. Coccygectomy for Treatment of Coccygodynia. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2014; 49:209–13.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coccygodynia and Coccygectomy
- Coccygectomy for Treatment of Coccygodynia
- Coccygectomy as a Surgical Option in the Treatment of Chronic Traumatic Coccygodynia: A Single-Center Experience and Literature Review
- First Coccygeal Vertebra Dislocation Treated by Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
- The Use of Radiofrequency Lesion Generation on the Ganglion Impar for the Treatment of Chronic Coccygodynia: A case report