Ann Dermatol.
2012 Aug;24(3):274-279. 10.5021/ad.2012.24.3.274.
A Survey of the Awareness, Knowledge and Behavior of Hair Dye Use in a Korean Population with Gray Hair
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. johnkang@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265299
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.3.274
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Gray hair naturally develops in the process of human aging. Many people with gray hair periodically dye their hair. Hair dyeing products are widely used and they can cause adverse effects. Therefore, the user's knowledge and recognition about hair dyeing and related side effects are important.
OBJECTIVE
The goal of this study was to lay the foundation for understanding, preventing and treating side effects caused by hair coloring products.
METHODS
We conducted a questionnaire survey for adult males and females aged over 20 who had gray hair. A total of 500 subjects were included in this study and statistical analysis was performed.
RESULTS
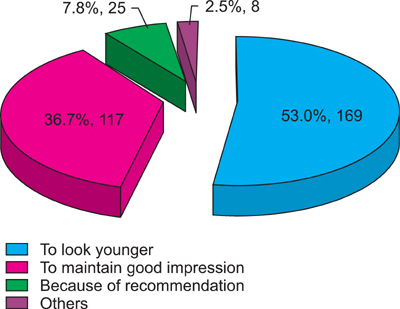
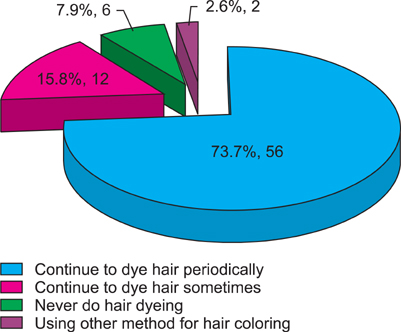
Large numbers of the people who had experience with hair dye (233 out of 319 people, 73.0%) did not know about the exact brand name of the hair dye product that they were using. Of 319 hair dye users, 23.8% (76 out of 319) people stated that they experienced side effects. Despite the occurrence of side effects from hair dyeing products, it seems they did not realize the seriousness of the side effects or the need for treatment.
CONCLUSION
It is advisable to introduce a system that enables users to become aware of the ingredients and side effects of hair coloring products and give opportunities for users to become aware of the side effects of hair coloring through education, publicity and publication of an informational booklet.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Analysis of the Results from the Patch Test to Para-Phenylenediamine in the TRUE Test in Patients with a Hair Dye Contact Allergy
Jin Yong Lee, Chul Woo Kim, Sang Seok Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2015;27(2):171-177. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.2.171.P-Phenylenediamine Hair Dye Allergy and Its Clinical Characteristics
Ju Hee Han, Hyun Ji Lee, Chul Hwan Bang, Ji Hyun Lee, Young Min Park, Jun Young Lee
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(3):316-321. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.3.316.
Reference
-
1. Park HY, Pongpudpunth M, Lee J, Yaar M. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Biology of melanocytes. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;591–608.2. Kim DW, Shin DJ, Lee SJ, Chung SL, Kim JC. Statistical and clinical study of gray hair. Korean J Dermatol. 1999. 37:1567–1575.3. Gibbs OS. The graying of hair. Science. 1942. 95:576.
Article4. Yaar M, Gilchrest BA. Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Aging of skin. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 2008. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hil;963–973.5. Chey WY, Kim KL, Yoo TY, Lee AY. Allergic contact dermatitis from hair dye and development of lichen simplex chronicus. Contact Dermatitis. 2004. 51:5–8.
Article6. Duarte I, Fusaro M, Lazzarini R. Etiology of para-phenylenediamine sensitization: hair dye and other products. Dermatitis. 2008. 19:342.
Article7. Mendelsohn JB, Li QZ, Ji BT, Shu XO, Yang G, Li HL, et al. Personal use of hair dye and cancer risk in a prospective cohort of Chinese women. Cancer Sci. 2009. 100:1088–1091.
Article8. Thun MJ, Altekruse SF, Namboodiri MM, Calle EE, Myers DG, Heath CW Jr. Hair dye use and risk of fatal cancers in U.S. women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994. 86:210–215.
Article9. Abdelraheem MB, El-Tigani MA, Hassan EG, Ali MA, Mohamed IA, Nazik AE. Acute renal failure owing to paraphenylene diamine hair dye poisoning in Sudanese children. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2009. 29:191–196.
Article10. El-Ansary EH, Ahmed ME, Clague HW. Systemic toxicity of para-phenylenediamine. Lancet. 1983. 1:1341.
Article11. Andrew AS, Schned AR, Heaney JA, Karagas MR. Bladder cancer risk and personal hair dye use. Int J Cancer. 2004. 109:581–586.
Article12. Grodstein F, Hennekens CH, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Stampfer MJ. A prospective study of permanent hair dye use and hematopoietic cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994. 86:1466–1470.
Article13. Rauscher GH, Shore D, Sandler DP. Hair dye use and risk of adult acute leukemia. Am J Epidemiol. 2004. 160:19–25.
Article14. Zhang Y, Sanjose SD, Bracci PM, Morton LM, Wang R, Brennan P, et al. Personal use of hair dye and the risk of certain subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Am J Epidemiol. 2008. 167:1321–1331.
Article15. Schwartz L, Barban C. Paraphenylenediamine hair dyes. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol. 1952. 66:233–239.
Article16. Carrascosa JM, Domingo H, Soria X, Ferrándiz C. Allergic contact dermatitis due to benzyl alcohol in a hair dye. Contact Dermatitis. 2006. 55:124–125.
Article17. Edwards EK Jr, Edwards EK. Allergic contact dermatitis to lead acetate in a hair dye. Cutis. 1982. 30:629–630.18. Eskelinen A, Molitor C, Kanerva L. Allergic contact dermatitis from 2,7-dihydroxynaphthalene in hair dye. Contact Dermatitis. 1997. 36:312–313.
Article19. Dejobert Y, Piette F, Thomas P. Contact dermatitis to 2-hydroxyethylamino-5-nitroanisole and 3-nitro-p-hydroxyethyl aminophenol in a hair dye. Contact Dermatitis. 2006. 54:217–218.
Article20. Belhadjali H, Ghannouchi N, Amri Ch, Youssef M, Amri M, Zili J. Contact dermatitis to henna used as a hair dye. Contact Dermatitis. 2008. 58:182.
Article21. Bowling JC, Scarisbrick J, Warin AP, Downs AM. Allergic contact dermatitis from trideceth-2-carboxamide monoethanolamine (MEA) in a hair dye. Contact Dermatitis. 2002. 47:116–117.
Article22. Krasteva M, Bons B, Ryan C, Gerberick GF. Consumer allergy to oxidative hair coloring products: epidemiologic data in the literature. Dermatitis. 2009. 20:123–141.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Statistical and Clinical Study of Gray Hair
- Analysis of the Results from the Patch Test to Para-Phenylenediamine in the TRUE Test in Patients with a Hair Dye Contact Allergy
- The Pattern of Hair Dyeing in Koreans with Gray Hair
- Survey of Awareness, Knowledge, Treatment and Behavior of Scalp and Hair Loss Disorders in Adults
- Alopecia