Korean J Neurotrauma.
2014 Oct;10(2):101-105. 10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.101.
Recurrence of the Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Burr-Hole Drainage with or without Intraoperative Saline Irrigation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. namdark@daum.net
- KMID: 2256241
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.101
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Although standard method has not been established for the chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH), burr-hole trephination and closed system drainage with or without irrigation has been widely accepted as the treatment of choice. The aim of this study is to analysis the post-operative recurrence rates after burr-hole trephination of the CSDH according to the conduction of irrigation.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed 184 patients with CSDH who underwent surgical treatment between January 2009 and December 2013. And 152 patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria as follows: 1) CSDH diagnosed on computed tomography (CT), 2) unilateral hematoma, 3) burr-hole trephination with closed system drainage, and 4) follow-up CT for at least 3 months. Those patients were divided into two groups. Group A (n=38) underwent burr-hole trephination without irrigation, and Group B (n=114), burr-hole trephination with saline irrigation.
RESULTS
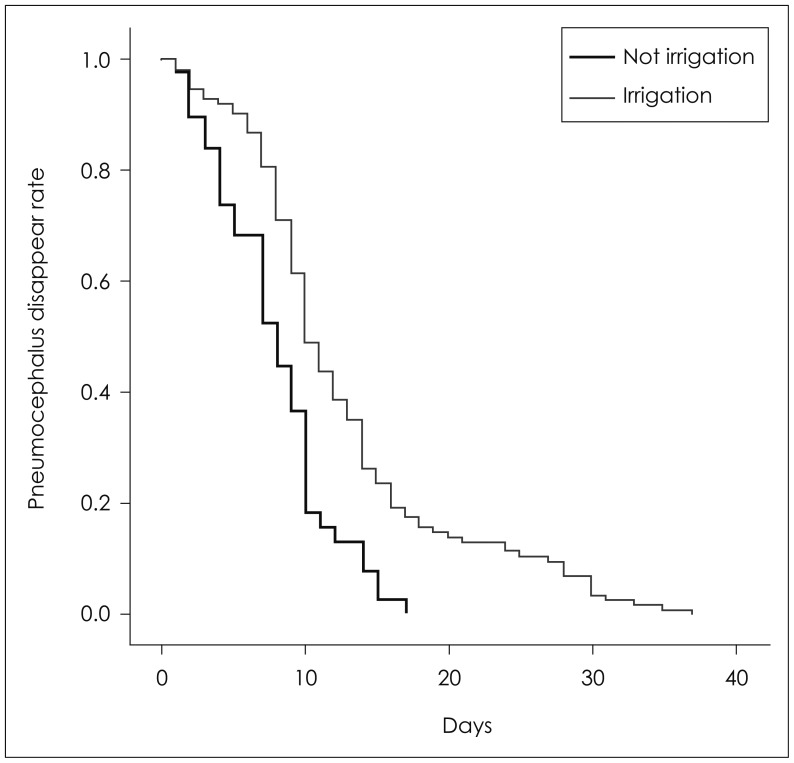
The overall post-operative recurrence rate was 19.1% (n=29) in this study. The majority of recurrence showed in Group B. Twenty-eight patients (24.6%) of Group B had recurrence and only 1 patient (2.6%) of Group A showed recurrence. The recurrence rate was significantly higher in Group B compared with Group A (p=0.003). Another affecting factor for the recurrence was the amount of postoperative pneumocephalus (p=0.02). No catastrophic complications were found in postoperative course.
CONCLUSION
Although there was no difference of clinical outcome in both groups, the recurrence rate was higher in saline irrigation group compared with no irrigation group. We suggest that saline irrigation procedure be reserved only for selected cases in CSDH burr-hole surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aung TH, Wong WK, Mo HP, Tsang CS. Management of chronic subdural haematoma: burr hole drainage, replacement with Hartmann's solution, and closed-system drainage. Hong Kong Med J. 1999; 5:383–386. PMID: 10870166.2. Camel M. Twist-drill craniostomy for the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:515–518. PMID: 10918023.
Article3. Ducruet AF, Grobelny BT, Zacharia BE, Hickman ZL, DeRosa PL, Anderson K, et al. The surgical management of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Rev. 2012; 35:155–169. discussion 169. PMID: 21909694.
Article4. Erol FS, Topsakal C, Faik Ozveren M, Kaplan M, Tiftikci MT. Irrigation vs. closed drainage in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2005; 12:261–263. PMID: 15851078.
Article5. Gurelik M, Aslan A, Gurelik B, Ozum U, Karadag O, Kars HZ. A safe and effective method for treatment of chronic subdural haematoma. Can J Neurol Sci. 2007; 34:84–87. PMID: 17352353.
Article6. Ishibashi A, Yokokura Y, Adachi H. A comparative study of treatments for chronic subdural hematoma: burr hole drainage versus burr hole drainage with irrigation. Kurume Med J. 2011; 58:35–39. PMID: 22027196.
Article7. Kim HS, Heo W, Cha JH, Song JS, Rhee DY. Factor affecting recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole drainage. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2012; 8:73–78.
Article8. Kim JH, Kang DS, Kim JH, Kong MH, Song KY. Chronic subdural hematoma treated by small or large craniotomy with membranectomy as the initial treatment. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 50:103–108. PMID: 22053228.
Article9. Kuroki T, Katsume M, Harada N, Yamazaki T, Aoki K, Takasu N. Strict closed-system drainage for treating chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:1041–1044. PMID: 11685612.
Article10. Lee JK, Choi JH, Kim CH, Lee HK, Moon JG. Chronic subdural hematomas: a comparative study of three types of operative procedures. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:210–214. PMID: 19844620.11. Lind CR, Lind CJ, Mee EW. Reduction in the number of repeated operations for the treatment of subacute and chronic subdural hematomas by placement of subdural drains. J Neurosurg. 2003; 99:44–46. PMID: 12854742.
Article12. Muzii VF, Bistazzoni S, Zalaffi A, Carangelo B, Mariottini A, Pal-ma L. Chronic subdural hematoma: comparison of two surgical techniques. Preliminary results of a prospective randomized study. J Neurosurg Sci. 2005; 49:41–46. discussion 46-47. PMID: 16247343.13. Nagata K, Asano T, Basugi N, Tango T, Takakura K. [Studies on the operative factors affecting the reduction of chronic subdural hematoma, with special reference to the residual air in the hematoma cavity]. No Shinkei Geka. 1989; 17:15–20. PMID: 2710282.14. Okada Y, Akai T, Okamoto K, Iida T, Takata H, Iizuka H. A comparative study of the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma--burr hole drainage versus burr hole irrigation. Surg Neurol. 2002; 57:405–409. discussion 410. PMID: 12176202.
Article15. Ramachandran R, Hegde T. Chronic subdural hematomas--causes of morbidity and mortality. Surg Neurol. 2007; 67:367–372. discussion 372-373. PMID: 17350403.
Article16. Sambasivan M. An overview of chronic subdural hematoma: experience with 2300 cases. Surg Neurol. 1997; 47:418–422. PMID: 9131021.
Article17. Seong HY, Park JB, Kwon SC, Sim HB, Kim Y, Lyo IU. Effect of saline irrigation in the surgical treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc. 2008; 4:19–23.
Article18. Sim YW, Min KS, Lee MS, Kim YG, Kim DH. Recent changes in risk factors of chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52:234–239. PMID: 23115667.
Article19. Sousa EB, Brandão LF, Tavares CB, Borges IB, Neto NG, Kessler IM. Epidemiological characteristics of 778 patients who underwent surgical drainage of chronic subdural hematomas in Brasília, Brazil. BMC Surg. 2013; 13:5. PMID: 23452673.
Article20. Stanišić M, Hald J, Rasmussen IA, Pripp AH, Ivanović J, Kolstad F, et al. Volume and densities of chronic subdural haematoma obtained from CT imaging as predictors of postoperative recurrence: a prospective study of 107 operated patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013; 155:323–333. discussion 333. PMID: 23229873.
Article21. Tabaddor K, Shulmon K. Definitive treatment of chronic subdural hematoma by twist-drill craniostomy and closed-system drainage. J Neurosurg. 1977; 46:220–226. PMID: 833639.
Article22. Williams GR, Baskaya MK, Menendez J, Polin R, Willis B, Nanda A. Burr-hole versus twist-drill drainage for the evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma: a comparison of clinical results. J Clin Neurosci. 2001; 8:551–554. PMID: 11683603.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Saline Irrigation Effect Using Closed System Drainage on Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Comparison of Outcomes and Recurrence in Chronic Subdural Hematoma Patients Treated by Burr-Hole Drainage with or without Irrigation
- Burr Hole Drainage versus Small Craniotomy of Chronic Subdural Hematomas
- Effect of Saline Irrigation in the Surgical Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Cerebellar Hemorrhage after Burr Hole Drainage of Supratentorial Chronic Subdural Hematoma