J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2011 Jun;52(6):653-657. 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.6.653.
Effect of Epinephrine in Reconstruction of an Orbital Wall Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. ahnmin@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2214635
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2011.52.6.653
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the effect of epinephrine on pupil size in reconstruction of an orbital wall fracture.
METHODS
The authors of the present study describe 27 patients (27 eyes) who had reconstruction of an orbital wall fracture from January to July of 2009. Patients were divided into two groups according to the use of epinephrine during surgery. Preoperative and postoperative pupil sizes, operation times, and epinephrine dosages were collected.
RESULTS
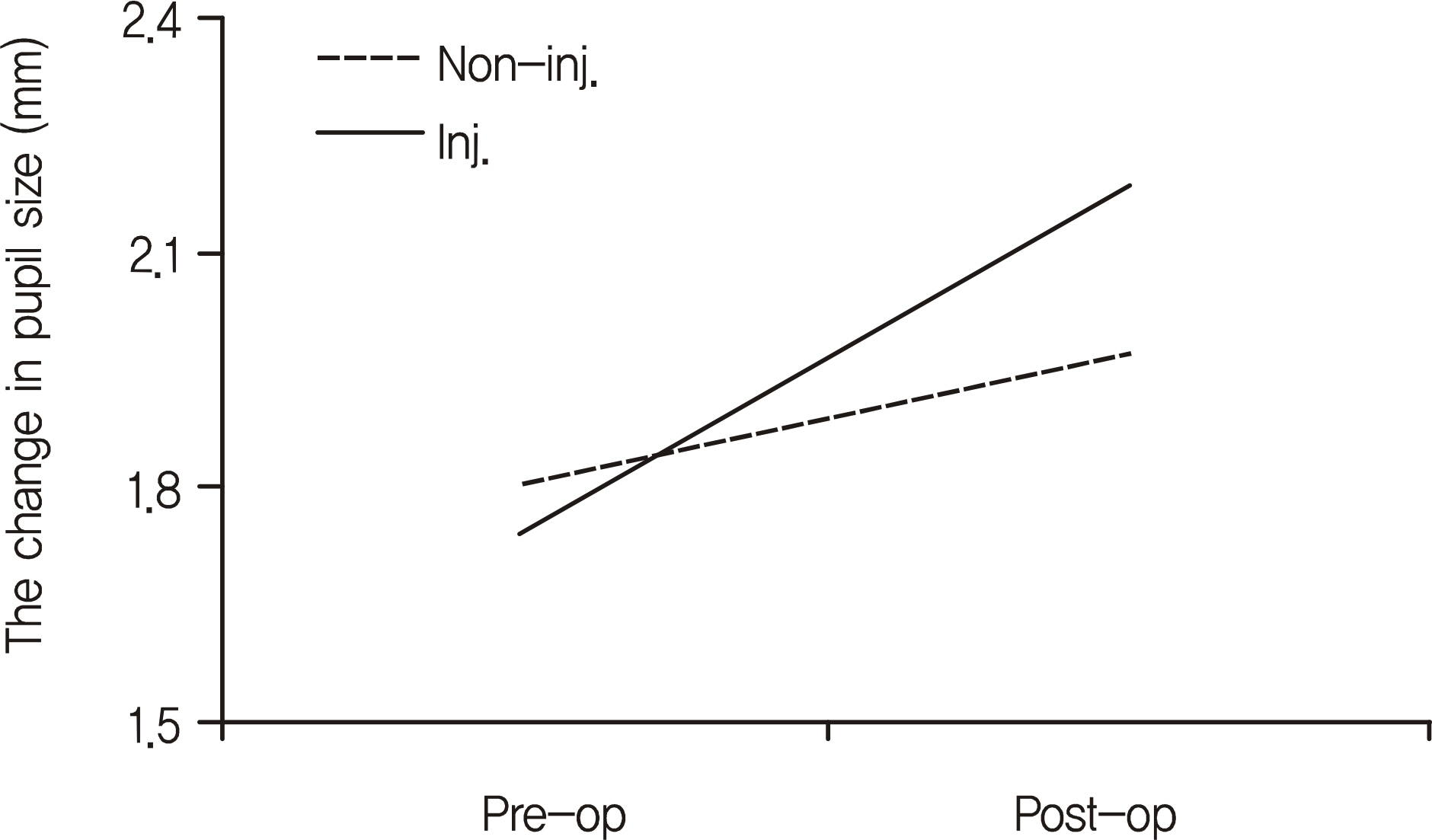
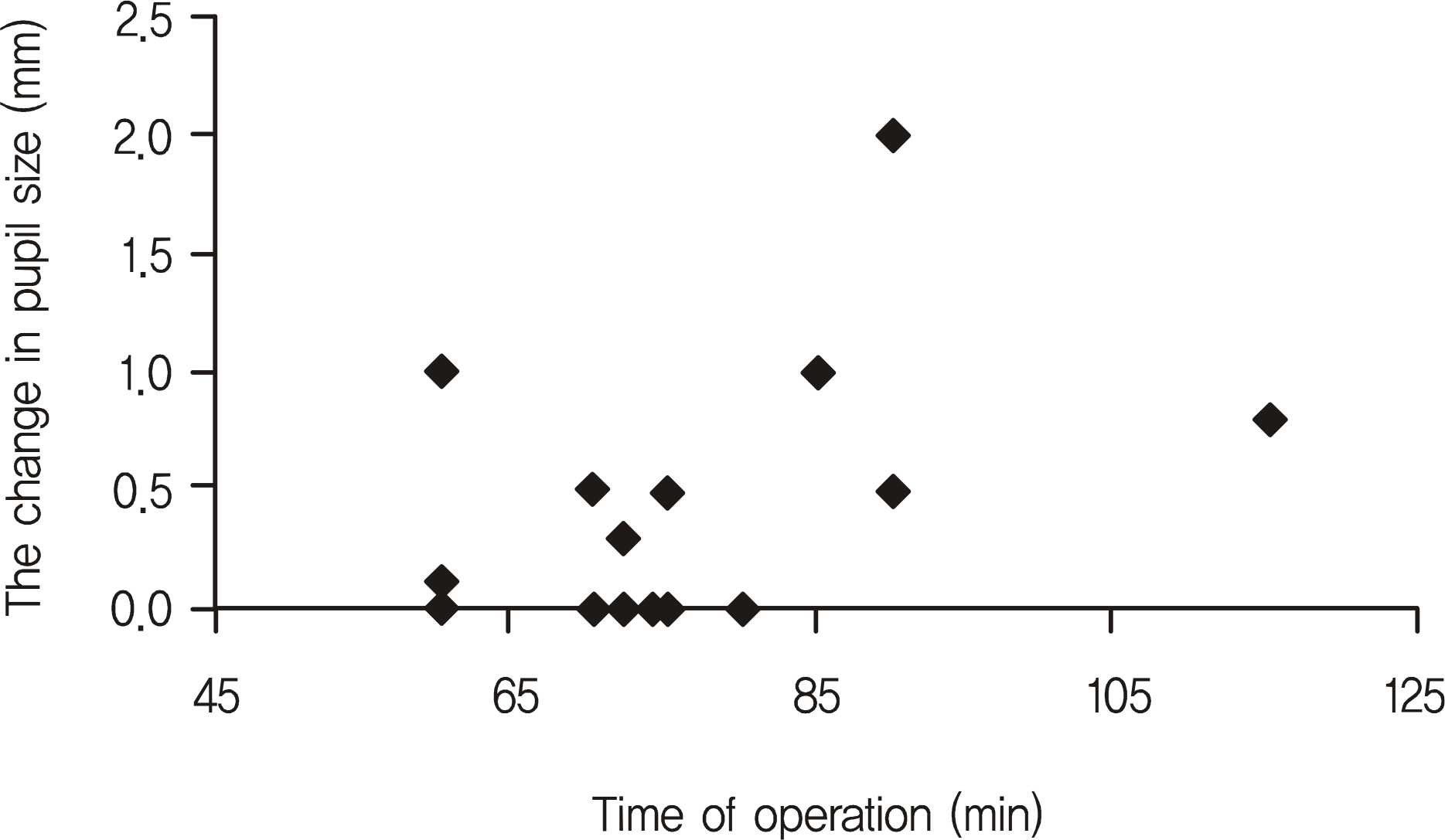
Preoperative pupil sizes were 1.80 +/- 0.37 mm, 1.74 +/- 0.36 mm and postoperative pupil sizes were 1.97 +/- 0.43 mm (p = 0.042), 2.18 +/- 0.52 mm (p = 0.003) in the group with of epinephrine and the group without epinephrine, respectively. Postoperative pupil size significantly increased in all groups. However, no significant difference was found regarding change in pupil size after surgery (p = 0.258). In the group with epinephrine, change in pupil size did not show a significant association with operation time (p = 0.228), nor did change in pupil size and epinephrine dosage (p = 0.922).
CONCLUSIONS
The use of epinephrine is an effective modality for bleeding control and securing a clear view in orbital wall fracture reconstruction.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Burnstine MA. Clinical recommendations for repair of isolated orbital floor fractures: an evidence-based analysis. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1207–10.2. Gosau M, Schöneich M, Draenert FG, et al. Retrospective analysis of orbital floor fractures-complications, outcome, and review of literature. Clin Oral Investig. 2011; 15:305–13.
Article3. Bennett MR. One hundred years of adrenaline: the discovery of autoreceptors. Clin Auton Res. 1999; 9:145–59.
Article4. Liou SW, Chen CC. Maintenance of mydriasis with one bolus of epinephrine injection during phacoemulsification. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2001; 17:249–53.
Article5. Corbett MC, Richards AB. Intraocular adrenaline maintains mydriasis during cataract surgery. Br J Ophthalmol. 1994; 78:95–8.
Article6. Duffin RM, Pettit TH, Straatsma BR. Maintenance of mydriasis with epinephrine during cataract surgery. Ophthalmic Surg. 1983; 14:41–5.
Article7. Wang YL, Hayashi M, Yablonski ME, Toris CB. Effects of multi-ple dosing of epinephrine on aqueous humor dynamics in human eyes. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 18:53–63.
Article8. Bodker FS, Cytryn AS, Putterman AM, Marschall MA. Postoperative mydriasis after repair of orbital floor fracture. Am J Ophthalmol. 1993; 115:372–5.
Article9. Okinaka Y, Hara J, Takahashi M. Orbital blowout fracture with persistent mobility deficit due to fibrosis of the inferior rectus muscle and perimuscular tissue. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999; 108:1174–6.
Article10. Biesman BS, Hornblass A, Lisman R, Kazlas M. Diplopia after surgical repair of orbital floor fractures. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996; 12:9–16.
Article11. Liu D. Blindness after blow-out fracture repair. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994; 10:206–10.
Article12. Girotto JA, Gamble WB, Robertson B, et al. Blindness after reduction of facial fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 102:1821–34.
Article13. Folkestad L, Westin T. Long-term sequelae after surgery for orbital floor fractures. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999; 120:914–21.
Article14. Jordan DR, St Onge P, Anderson RL, et al. Complications associated with alloplastic implants used in orbital fracture repair. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:1600–8.
Article15. Sobel AM. Anisocoria during general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1965; 44:522–6.
Article16. Kuhn I, Wissing H. Anisocoria during isoflurane anaesthesia in a six-year-old girl. Paediatr Anaesth. 1996; 6:411–3.
Article17. D'Souza MG, Hadzic A, Wider T. Unilateral mydriasis after nasal reconstruction surgery. Can J Anaesth. 2000; 47:1119–21.18. Jay WM, Aziz MZ, Green K. Further studies on the effect of retrobulbar epinephrine injection on ocular and optic nerve blood flow. Curr Eye Res. 1986; 5:63–7.
Article19. Netland PA, Siegner SW, Harris A. Color Doppler ultrasound measurements after topical and retrobulbar epinephrine in primate eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997; 38:2655–61.20. Hessemer V, Heinrich A, Jacobi KW. Ocular circulatory changes caused by retrobulbar anesthesia with and without added adrenaline. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1990; 197:470–9.21. Kumar CM, Williamson S, Manickam B. A review of sub-Tenon's block: current practice and recent development. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005; 22:567–77.22. Sarvela J, Nikki P, Paloheimo M. Orbicular muscle akinesia in regional ophthalmic anaesthesia with pH-adjusted bupivacaine: effects of hyaluronidase and epinephrine. Can J Anaesth. 1993; 40:1028–33.
Article23. Morsman CD, Holden R. The effects of adrenaline, hyaluronidase and age on peribulbar anaesthesia. Eye (Lond). 1992; 6:290–2.
Article24. Wang HS. Peribulbar anesthesia for ophthalmic procedures. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1988; 14:441–3.
Article25. Sanders R, Ahmed S, Craig EW, Young JD. Comparison of catecholamine and pressor effects in peribulbar and retrobulbar anaesthesia in cataract surgery. Eye (Lond). 1997; 11:644–8.
Article26. Koppanyi T, Lieberson A. Studies on the duration of action of drugs II. Mydriatic actions of epinephrine and atropine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1930; 39:187–99.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management Of Medial Orbital Wall Fracture
- The Inferior Orbital Wall Reconstruction by Titanium Micro-mesh Remodeling
- Anatomical Reconstruction of the Medial Orbital Wall Fracture
- Comparison of Titanium Micro Mesh(R) with Titanium Mesh Screen 1.3(R) in the Reconstruction of Medial Orbital wall Fracture
- Long-Term Results of Reconstruction of Orbital Wall Fracture With Resorbable Copolymer Mesh