Infect Chemother.
2008 Aug;40(4):237-240. 10.3947/ic.2008.40.4.237.
Vertebral Osteomyelitis due to Salmonella enterica serovar Othmarschen in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. yonathan@hanafos.com
- 2Division of Enteric Bacterial Infections, Center for Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Health, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2170240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2008.40.4.237
Abstract
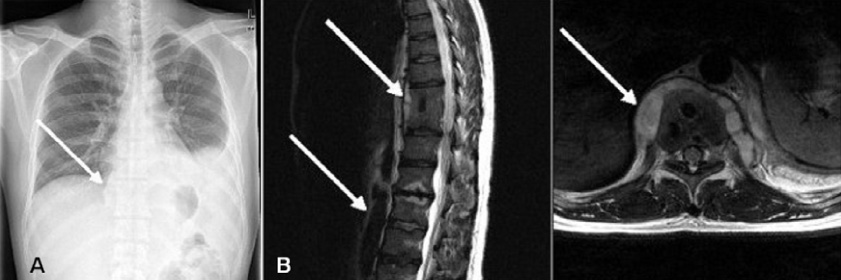
- Salmonellae have been recognized as uncommon etiological organisms causing osteomyelitis in patients with sickle cell anemia and other immunocompromised conditions. A 34-year old man who had no underlying illness except for congenital block vertebrae at T10-11 vertebrae was admitted to the hospital due to lower back pain and fever for a week. Vertebral osteomyelitis was diagnosed and surgical drainage was performed. Salmonella enterica serovar Othmarschen was isolated from the drained pus. Therapy with ciprofloxacin for 8 weeks was successful without relapse. We describe here a case of vertebral osteomyelitis which was caused by S. Othmarschen in an immunocompetent patient.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ortiz-Neu C, Marr JS, Cherubin CE, Neu HC. Bone and joint infections due to Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1978. 138:820–828.
Article2. Givner LB, Luddy RE, Schwartz AD. Etiology of osteomyelitis in patients with major sickle hemoglobinopathies. J Pediatr. 1981. 99:411–413.
Article3. Morosini MI, Blázquez J, Negri MC, Canton R, Loza E, Baquero F. Characterization of a nosocomial outbreak involving an epidemic plasmid encoding for TEM-27 in Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serotype Othmarschen. J Infect Dis. 1996. 174:1015–1020.
Article4. Kim S, Choi YG, Eom JW, Oh TJ, Lee KS, Kim SH, Lee ET, Park MS, Oh HB, Lee BK. An outbreak of Salmonella enterica serovar Othmarschen at a funeral service in Guri-si, South Korea. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2007. 60:412–413.5. Tsang RS, Chan KH, Lau NW, Choi DK, Law DK, Ng MH. Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies against serogroup B salmonellae and application as serotyping reagents. J Clin Microbiol. 1991. 29:1899–1903.
Article6. Kauffmann F. Serological diagnosis of Salmonella-species Kauffmann-White-Schema. 1972. Copenhagen, Denmark: Munksgaard.7. Saphra I, Winter JW. Clinical manifestations of salmonellosis in man; an evaluation of 7779 human infections identified at the New York Salmonella Center. N Engl J Med. 1957. 256:1128–1134.8. Cohen JI, Bartlett JA, Corey GR. Extra-intestinal manifestations of salmonella infections. Medicine (Baltimore). 1987. 66:349–388.
Article9. Santos EM, Sapico FL. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to salmonellae: report of two cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. 27:287–295.
Article10. D'Souza CR, Hopp PG, Kilam S. Osteomyelitis of the spine due to Salmonella: case report, review of clinical aspects, pathogenesis and treatment. Can J Surg. 1993. 36:311–314.11. Silverthorn KG, Gillespie WJ. Pyogenic spinal osteomyelitis: a review of 61 cases. N Z Med J. 1986. 99:62–65.12. Shimada T, Nishimura Y, Kimura G, Eto S, Tomita K. Vertebral osteomyelitis presenting with bilateral pleural effusions in a leprous patient. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996. 24:101–103.
Article13. Gupta SK, Pandit A, White DG, Evans PD. Salmonella osteomyelitis of the thoracic spine: an unusual presentation. Postgrad Med J. 2004. 80:110–111.
Article14. Easmon CS, Crane JP. Uptake of ciprofloxacin by macrophages. J Clin Pathol. 1985. 38:442–444.
Article15. Fong IW, Ledbetter WH, Vandenbroucke AC, Simbul M, Rahm V. Ciprofloxacin concentrations in bone and muscle after oral dosing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986. 29:405–408.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Salmonella Serovars from Foodborne and Waterborne Diseases in Korea, 1998-2007: Total Isolates Decreasing Versus Rare Serovars Emerging
- A case of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi endocarditis with multiple splenic infarctions
- A Virulent Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Phage SE2 with a Strong Bacteriolytic Activity of Planktonic and Biofilmed Cells
- Brodie's Abscess Caused by Salmonella enteritica serovar Senftenberg in a Healthy Child
- Isolation of Non-Hydrogen Sulfide-Producing Salmonella enterica Serovar Infantis from a Clinical Sample: the First Case in Korea