Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2016 Mar;8(2):170-173. 10.4168/aair.2016.8.2.170.
Papain Induced Occupational Asthma with Kiwi and Fig Allergy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy, Peking Union Hospital; Peking Union Medical College & Chinese Academy of Medical Science, Beijing, China. wendy_wenlp@163.com
- KMID: 2165934
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2016.8.2.170
Abstract
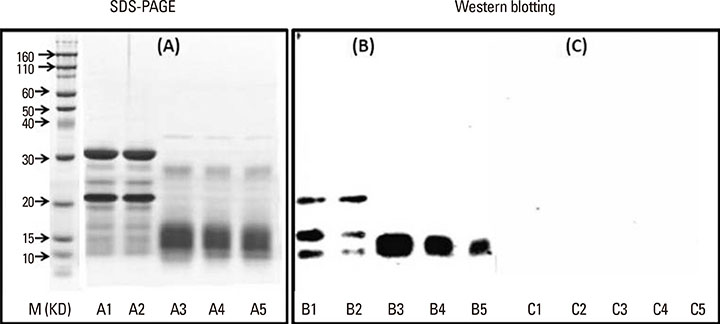
- Papain is a proteolytic enzyme which is widely used in food industry, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Occupational and non-occupational papain allergies have previously been documented; however, there are limited publications about papain allergy with its relative fruit allergy. Here, we present a case of occupational, IgE-mediated papain allergy with kiwi fruit and fig fruit allergy. A 53-year-old man suffered from rhinitis for several years, with the onset of his symptoms coinciding with the time he started to work at a sausage processing plant where papain is often used as a meat tenderizer. He began to experience symptoms of chest tightness, shortness of breath and wheezing shortly after starting work 5 years ago. Furthermore, he experienced several episodes of oral itching, and tongue and oropharyngeal angioedema after injestion of kiwi fruit and fig fruit. The patient had a lifelong history of allergic conjunctivitis, allergic rhinitis, and childhood asthma. Specific IgE was positive to kiwi fruit, papain and chymopapain (2.95 kUA/L, >100 kUA/L, and 95.0 kUA/L, respectively). Similar bands at 10-15 kDa in blotting with papain and kiwi fruit extracts were found. This patient showed a potential association between papain allergy and sensitization to kiwi fruit. We also reviewed 13 patients with papain allergy published in the literature, with 85% (11/13) of the patients sensitized through the respiratory tract, and 40% (4/11) having atopy. Further studies should focus on the determination of cross-reactive allergens between papain and its fruit relatives, and the prevalence of food allergy in patients with papain allergy should be investigated in a relatively large cohort.
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens
Angioedema
Asthma
Asthma, Occupational*
Chymopapain
Cohort Studies
Conjunctivitis, Allergic
Dyspnea
Food Hypersensitivity
Food Industry
Fruit
Humans
Hypersensitivity*
Immunoglobulin E
Meat
Middle Aged
Papain*
Plants
Prevalence
Pruritus
Respiratory Sounds
Respiratory System
Rhinitis
Thorax
Tongue
Allergens
Chymopapain
Immunoglobulin E
Papain
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amri E, Mamboya F. Papain, a plant enzyme of biological importance: a review. Am J Biochem Biotechnol. 2012; 8:99–104.2. Milne J, Brand S. Occupational asthma after inhalation of dust of the proteolytic enzyme, papain. Br J Ind Med. 1975; 32:302–307.3. Baur X, König G, Bencze K, Fruhmann G. Clinical symptoms and results of skin test, RAST and bronchial provocation test in thirty-three papain workers: evidence for strong immunogenic potency and clinically relevant 'proteolytic effects of airborne papain'. Clin Allergy. 1982; 12:9–17.4. Flindt ML. Respiratory hazards from papain. Lancet. 1978; 1:430–432.5. Goeminne PC, Adams E, Deschepper K, Valcke Y, Nemery B. Papain-induced asthma: a man with dyspnea from dawn till dust. Acta Clin Belg. 2013; 68:132–134.6. Soto-Mera MT, López-Rico MR, Filgueira JF, Villamil E, Cidrás R. Occupational allergy to papain. Allergy. 2000; 55:983–984.7. Bernstein DI, Gallagher JS, Grad M, Bernstein IL. Local ocular anaphylaxis to papain enzyme contained in a contact lens cleansing solution. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984; 74:258–260.8. Niinimäki A, Reijula K, Pirilä T, Koistinen AM. Papain-induced allergic rhinoconjunctivitis in a cosmetologist. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993; 92:492–493.9. Mansfield LE, Bowers CH. Systemic reaction to papain in a nonoccupational setting. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983; 71:371–374.10. Guillen D, Barranco P, Palacín A, Quirce S. Occupational rhinoconjunctivitis due to maize in a snack processor: a cross-reactivity study between lipid transfer proteins from different cereals and peach. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:470–473.11. Kwon SC, Song J, Kim YK, Calvert GM. Work-Related Asthma in Korea - findings from the Korea Work-Related Asthma Surveillance (KOWAS) program, 2004-2009. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:51–59.12. Quarre JP, Lecomte J, Lauwers D, Gilbert P, Thiriaux J. Allergy to latex and papain. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995; 95:922.13. Pastorello EA, Conti A, Pravettoni V, Farioli L, Rivolta F, Ansaloni R, et al. Identification of actinidin as the major allergen of kiwi fruit. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998; 101:531–537.14. Díez-Gómez ML, Quirce S, Aragoneses E, Cuevas M. Asthma caused by Ficus benjamina latex: evidence of cross-reactivity with fig fruit and papain. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998; 80:24–30.15. Novey HS, Keenan WJ, Fairshter RD, Wells ID, Wilson AF, Culver BD. Pulmonary disease in workers exposed to papain: clinicophysiological and immunological studies. Clin Allergy. 1980; 10:721–731.16. Baur X, Chen Z, Rozynek P, Düser M, Raulf-Heimsoth M. Cross-reacting IgE antibodies recognizing latex allergens, including Hev b 1, as well as papain. Allergy. 1995; 50:604–609.17. Novey HS, Marchioli LE, Sokol WN, Wells ID. Papain-induced asthma--physiological and immunological features. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:98–103.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of radish induced bronchial asthma in a patient with TDI (toluene diisocynate) induced occupational asthma
- Occupational asthma induced by powder of amoxicillin
- Occupational asthma in Japan
- Study of occupational asthma using an animal model
- A Case of Occupational Asthma and Rhinitis Induced by Ethylene Bis-stearamide