Clin Endosc.
2013 Nov;46(6):671-674.
A Case of Parasite Invasion of the Intestinal Tract: A Missed Diagnosis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Onnuri-Su Medical Clinic, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute for Medical Science, Chonbuk National University College of Medicine, Jeonju, Korea. clickm@jbnu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine Eulji University Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
Abstract
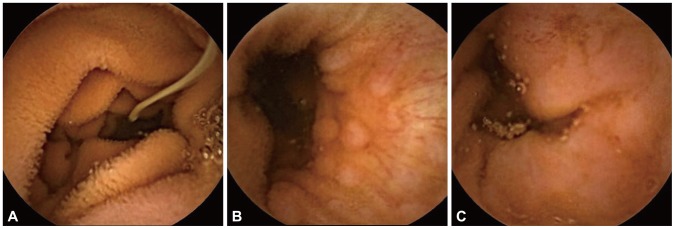
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal disorder characterized by chronic abdominal pain and altered bowel habits in the absence of any organic cause. As the clinical manifestations are very diverse and associated with nonspecific symptoms, research seeking to identify organic causes to rule out IBS and to enable differential diagnosis is required. A 24-year-old man was referred to our hospital for specialized management of IBS. He had a 7-month history of intermittent epigastric and lower abdominal pain. On the basis of clinical examination, he was diagnosed with IBS and administered medication at a primary clinic. However, his symptoms did not improve after treatment. We performed capsule endoscopy at our hospital and identified a parasite (Ancylostoma duodenale) in the proximal jejunum. We therefore report a case of parasitic infection found by additional examination while evaluating symptoms associated with a previous diagnosis of refractory IBS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morgan DR, Benshoff M, Cáceres M, et al. Irritable bowel syndrome and gastrointestinal parasite infection in a developing nation environment. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012; 2012:343812. PMID: 22474433.
Article2. Pokkunuri V, Pimentel M, Morales W, et al. Role of cytolethal distending toxin in altered stool form and bowel phenotypes in a rat model of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012; 18:434–442. PMID: 23106005.
Article3. Thabane M, Kottachchi DT, Marshall JK. Systematic review and meta-analysis: the incidence and prognosis of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 26:535–544. PMID: 17661757.
Article4. Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:1480–1491. PMID: 16678561.
Article5. Spiller R, Lam C. An update on post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome: role of genetics, immune activation, serotonin and altered microbiome. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012; 18:258–268. PMID: 22837873.
Article6. Swarbrick ET, Hegarty JE, Bat L, Williams CB, Dawson AM. Site of pain from the irritable bowel. Lancet. 1980; 2:443–446. PMID: 6106097.
Article7. Whorwell PJ, McCallum M, Creed FH, Roberts CT. Non-colonic features of irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1986; 27:37–40. PMID: 3949235.
Article8. Hershfield NB. Nongastrointestinal symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome: an office-based clinical survey. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005; 19:231–234. PMID: 15861265.
Article9. De Giorgio R, Barbara G, Stanghellini V, et al. Diagnosis and therapy of irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 20(Suppl 2):10–22. PMID: 15335409.
Article10. Jellema P, van der Windt DA, Schellevis FG, van der Horst HE. Systematic review: accuracy of symptom-based criteria for diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome in primary care. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 30:695–706. PMID: 19575763.
Article11. Ramirez-Miranda ME, Hernandez-Castellanos R, Lopez-Escamilla E, et al. Parasites in Mexican patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a case-control study. Parasit Vectors. 2010; 3:96. PMID: 20942938.
Article12. Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology. 2006; 130:1377–1390. PMID: 16678553.
Article13. Vanner SJ, Depew WT, Paterson WG, et al. Predictive value of the Rome criteria for diagnosing the irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999; 94:2912–2917. PMID: 10520844.
Article14. Cash BD, Chey WD. Irritable bowel syndrome: an evidence-based approach to diagnosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 19:1235–1245. PMID: 15191504.15. de Silva NR, Brooker S, Hotez PJ, Montresor A, Engels D, Savioli L. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: updating the global picture. Trends Parasitol. 2003; 19:547–551. PMID: 14642761.
Article16. Haas W, Haberl B, Syafruddin , et al. Behavioural strategies used by the hookworms Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale to find, recognize and invade the human host. Parasitol Res. 2005; 95:30–39. PMID: 15614587.
Article17. Hotez PJ, Brooker S, Bethony JM, Bottazzi ME, Loukas A, Xiao S. Hookworm infection. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:799–807. PMID: 15317893.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- The Role of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in the Pathophysiology of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Mast Cell May Be the Master Key to Solve the Mystery of Pathogenesis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Decreased Neuroplasticity May Play a Role in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Implication From the Comorbidity of Depression and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome