Clinical Features of Polyarteritis Nodosa in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ysong@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2157806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.4.591
Abstract
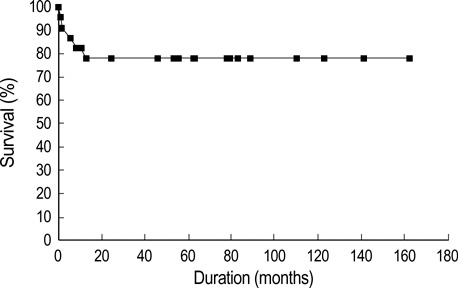
- Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic vasculitis characterized by multi-organ involvement with protean manifestations. We evaluated the clinical features of PAN in Korea. Twenty-seven patients were diagnosed as PAN at Seoul National University Hospital between January 1990 and July 2003. The male-to-female ratio was 1.7:1 and mean age at onset (+/-SD) was 47.4+/-20 yr. Their presenting features at diagnosis were similar to those reported previously, i.e., myalgia, muscle weakness or leg tenderness (70%), fever (52%), weight loss >4 kg (44%), skin rash (44%), peripheral edema (33%), abdominal pain (33%), and arthralgia/arthritis (30%). However, the prevalence of testicular pain or tenderness was higher (24%) than reported previously and only three (11.5%) had HBsAg positivity without liver enzyme elevation. Nine patients (33%) had a five-factor score (FFS) of 2. Fourteen patients (52%) responded to treatment, 2 patients relapsed and 4 died within 1 yr of diagnosis. During a median follow-up of 55.5 months, three of the four PAN-related deaths had an initial FFS of 2. The clinical features of PAN were not significantly different from those reported previously. However, testicular pain or tenderness was more frequent and patients with a high FFS tended to have a poorer prognosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Clinical Features and Outcomes of Microscopic Polyangiitis in Korea
Ji Seon Oh, Chang-Keun Lee, Yong Gil Kim, Seong-Su Nah, Hee-Bom Moon, Bin Yoo
J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(2):269-274. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.269.Chronic Hepatitis B Infection Is Significantly Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease: a Population-based, Matched Case-control Study
Sung-Eun Kim, Eun Sun Jang, Moran Ki, Geum-Youn Gwak, Kyung-Ah Kim, Gi-Ae Kim, Do Young Kim, Dong Joon Kim, Man Woo Kim, Yun Soo Kim, Young Seok Kim, In Hee Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Ho Dong Kim, Hyung Joon Kim, Neung Hwa Park, Soon Koo Baik, Jeong Ill Suh, Byung-Cheol Song, Il Han Song, Jong Eun Yeon, Byung Seok Lee, Youn Jae Lee, Young Kul Jung, Woo Jin Chung, Sung Bum Cho, Eun-Young Cho, Hyun Chin Cho, Gab Jin Cheon, Hee Bok Chae, DaeHee Choi, Sung-Kyu Choi, Hwa Young Choi, Won Young Tak, Jeong Heo, Sook-Hyang Jeong
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(42):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e264.Four Cases of Polyarteritis Nodosa Presenting Initially as Pain and Pitting Edema in Both Lower Extremities
Hyun Suk Lee, Jun Ho Lee, Yong Seok Lim, Eui Chang Kim, Hyun Mi Kwon, Seong-He Park, Byoong Yong Choi
J Rheum Dis. 2017;24(1):48-54. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.48.A Case of Polyarteritis Nodosa Mimicking Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Kwang Hoon Lee, Dong Hyuk Nam, Hye Won Lee, Tae Hyun Ryu, Chan Hee Lee, Soo Kon Lee
J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2007;14(4):427-430. doi: 10.4078/jkra.2007.14.4.427.ANCA Associated Vasculitis
Wan-sik Uhm
J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010;17(2):108-132. doi: 10.4078/jkra.2010.17.2.108.
Reference
-
1. Lightfoot RW, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Zvaifler NJ, McShane DJ, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, Leavitt RY, Lie JT, Masi AT, Mills JA, Stevens MB, Wallace SL. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Arthritis Rheum. 1990. 33:1088–1093.
Article2. Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Hunder GG, Kallenberg CG, Mccluskey RT, Sinico RA, Rees AJ, Es La, Waldherr R, Wiik A. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994. 37:187–192.3. Lee CW, Kim YJ, Park MH. Clinical features of cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa. Korean J Dermatol. 1995. 33:225–231.4. Yoon CH, Lee CW. Clinical patterns of cutaneous lesions on the legs in patients with cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa. Korean J Dermatol. 2003. 41:869–872.5. Guillevin L, Le Thi Huong D, Godeau P, Jais P, Wechsler B. Clinical findings and prognosis of polyarteritis nodosa and Churg-Strauss angiitis: a study in 165 patients. Br J Rheumatol. 1988. 27:258–264.
Article6. Guillevin L, Lhote F, Gayraud M, Cohen P, Jarrousse B, Lortholary O, Lortholary O, Thibult N, Casassus P. Prognostic factors in polyarteritis nodosa and Churg-Strauss syndrome. A prospective study in 342 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996. 75:17–28.
Article7. Guillevin L, Lhote F. Classification and management of necrotizing vasculitides. Drugs. 1997. 53:805–816.8. Cohen RD, Conn DL, Ilstrup DM. Clinical features, prognosis, and response to treatment in polyarteritis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980. 55:146–155.9. Fortin PR, Larson MG, Watters AK, Yeadon CA, Choquette D, Esdaile JM. Prognostic factors in systemic necrotizing vasculitis of the polyarteritis nodosa group: a review of 45 cases. J Rheumatol. 1995. 22:78–84.10. Guillevin L, Lhote F, Cohen P, Sauvaget F, Jarrousse B, Lortholary O, Noel LH, Trepo C. Polyarteritis nodosa related to hepatitis B virus. A prospective study with long-term observation of 41 patients. Medicine. 1995. 74:238–253.
Article11. Agard C, Mouthon L, Mahr A, Guillevin L. Microscopic polyangiitis and polyarteritis nodosa: how and when do they start? Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 49:709–715.
Article12. Lhote F, Guillevin L. Polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome. Clinical aspects and treatment. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1995. 21:911–947.13. Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Medium- and large-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:160–169.
Article14. Cupps TR, Fauci AS. The Vasculitides. Major Probl Intern Med. 1981. 21:1–211.15. Langford CA. 15. Vasculitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:S602–S612.
Article16. Fauci AS. Braunwald E, Isselbacher KI, Petersdorf RG, Wilson JD, Martin JB, Fauci AS, editors. The vasculitis syndromes. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 1998. 14th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1912–1914.17. Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Small-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 1997. 337:1512–1523.
Article18. Savage CO, Harper L, Adu D. Primary systemic vasculitis. Lancet. 1997. 349:553–558.
Article19. Hoffman G, Specks U. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1998. 41:1521–1537.
Article20. Wright LF, Bicknell SL. Systemic necrotizing vasculitis presenting as epididymitis. J Urol. 1986. 136:1094.
Article21. Tanuma Y, Oda T, Yokoo A, Ito S, Takeuchi K. Recurrent polyarteritis nodosa limited to the testis. J Urol. 2003. 170:1953.
Article22. Karyn SE, Stephen JF, Jacob R. Polyarteritis nodosa presenting as hematuria and a testicular mass. J Urol. 2001. 166:624.23. Mukamel E, Abarbanel J, Savion M, Konichezky M, Yachia D, Auslaender L. Testicular mass as a presenting symptom of isolated polyarteritis nodosa. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995. 103:215–217.
Article24. Sergent JS, Lockshin MD, Christian CL, Gocke DJ. Vasculitis with hepatitis B antigenemia: long-term observation in nine patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1976. 55:1–18.25. Michault A, Faulques B, Sevadjan B, Troalen D, Marais A, Barau G. Prevalence of hepatitis A, B, C virus markers in Reunion (south hospital and Saint Pierre prison). Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2000. 93:34–40.26. Aker MI, Mast EE. The epidemiology of the viral hepatitis in the United States. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1994. 23:437–455.27. Lepage L, Schiele F, Janot C, Siest G. Prevalence of viral hepatitis B markers in a sample population seen at a center of preventive medicine. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1986. 34:851–854.28. Hsu HM, Lu CF, Lee SC, Lin SR, Chen DS. Seroepidemiologic survey for hepatitis B virus infection in Taiwan: the effect of hepatitis B mass immunization. J Infect Dis. 1999. 179:367–370.
Article29. Furusyo N, Hayashi J, Sawayama Y, Kawakami Y, Kishihara Y, Kashiwagi S. The elimination of hepatitis B virus infection: changing seroepidemiology of hepatitis A and B virus infection in Okinawa, Japan over a 26-year period. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998. 59:693–698.
Article30. Andre F. Hepatitis B epidemiology in Asia, the Middle East and Africa. Vaccine. 2000. 18:Suppl 1. 20–22.
Article31. Joo KR, Bang S, Song B, Youn KH, Joo YH, Yang S, Kim KR, Chung Y, Lee YS, Suh DJ. Hepatitis B viral markers of Korean adults in the late 1990s: Survey data of 70,347 health screenees. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 33:642–652.32. Shurbaji MS, Epstein JI. Testicular vasculitis: Implications for systemic disease. Hum Pathol. 1988. 19:186–189.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Polyarteritis Nodosa Presented as Myositis
- Ischemic Pseudomembranous Colitis with Perforation due to Polyarteritis Nodosa
- A case of polyarteritis nodosa complicated by bilateral renal hematomas and U.G.I. bleeding
- Polyarteritis nodosa of the breast
- A case of polyarteritis nodosa, possibly of cutaneous type