Korean J Pain.
2016 Jan;29(1):53-56. 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.53.
Pulsed Radiofrequency Application for the Treatment of Pain Secondary to Sacroiliac Joint Metastases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. gmhy2000@naver.com
- KMID: 2151661
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.1.53
Abstract
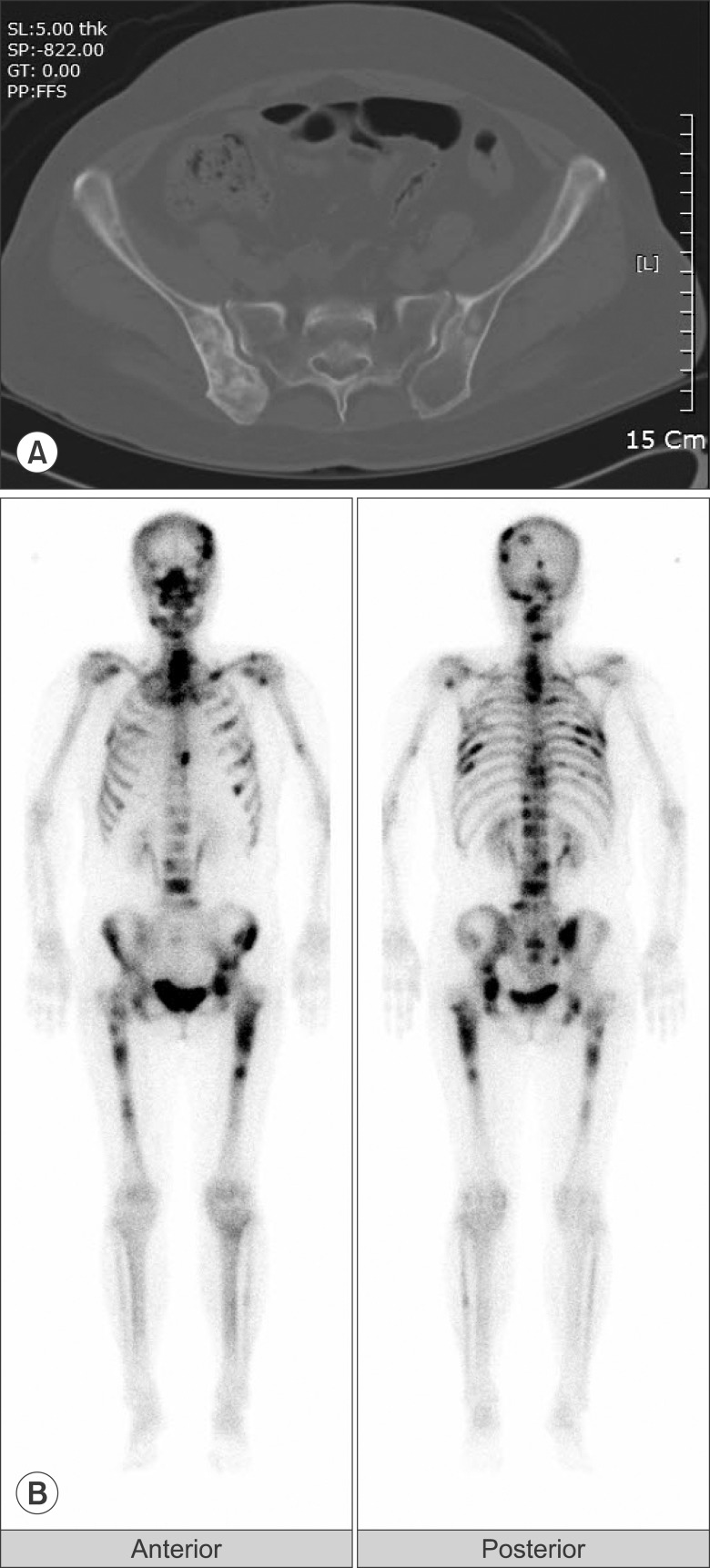
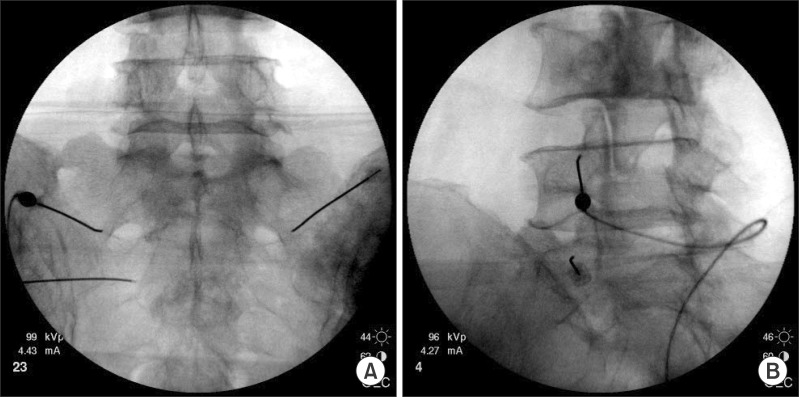
- Sacroiliac (SI) joint pain can result from degeneration, infection, malignancy, and trauma. Patients with metastatic bone pain who do not respond to conventional treatment may need more aggressive neuroinvasive approaches. Recently, pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) neuromodulation has emerged as a promising treatment alternative for refractory cases of SI joint pain. Nevertheless, there is no report on the treatment of pain arising from SI joint metastases with PRF. We are reporting about a 63-year-old woman suffering from buttock pain due to breast cancer metastases in the SI joint. We treated this patient with PRF neuromodulation of the L4-S3 primary dorsal rami and lateral branches using a rotating curved needle technique. The patient tolerated the procedures well, without any complications. She experienced about 70% reduction in pain, and pain relief was sustained for 10 months. This result suggests that PRF neuromodulation is a safe, effective treatment for pain from SI joint metastases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Extraspinal Percutaneous Osteoplasty for the Treatment of Painful Bony Metastasis
Jae-Heon Lee, Su-Young Kim, Hwoe-Gyeong Ok, Tae-Kyun Kim, Kyung-Hoon Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(8):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e61.
Reference
-
1. Raque GH Jr, Vitaz TW, Shields CB. Treatment of neoplastic diseases of the sacrum. J Surg Oncol. 2001; 76:301–307. PMID: 11320524.
Article2. Mercadante S, Fulfaro F. Management of painful bone metastases. Curr Opin Oncol. 2007; 19:308–314. PMID: 17545792.
Article3. Chua NH, Vissers KC, Sluijter ME. Pulsed radiofrequency treatment in interventional pain management: mechanisms and potential indications-a review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153:763–771. PMID: 21116663.
Article4. Vallejo R, Benyamin RM, Kramer J, Stanton G, Joseph NJ. Pulsed radiofrequency denervation for the treatment of sacroiliac joint syndrome. Pain Med. 2006; 7:429–434. PMID: 17014602.
Article5. Ripamonti C, Fulfaro F. Malignant bone pain: pathophysiology and treatments. Curr Rev Pain. 2000; 4:187–196. PMID: 10998732.
Article6. Ramasubba C, Cohen SP. Cooled sacroiliac radiofrequency denervation for the treatment of pain secondary to tumor infiltration: a case-based focused literature review. Pain Physician. 2013; 16:1–8. PMID: 23340529.7. Cahana A, Van Zundert J, Macrea L, van Kleef M, Sluijter M. Pulsed radiofrequency: current clinical and biological literature available. Pain Med. 2006; 7:411–423. PMID: 17014600.
Article8. Podhajsky RJ, Sekiguchi Y, Kikuchi S, Myers RR. The histologic effects of pulsed and continuous radiofrequency lesions at 42 degrees C to rat dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:1008–1013. PMID: 15864151.
Article9. Zeldin A, Ioscovich A. Pulsed radiofrequency for metastatic pain treatment. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:921–922. PMID: 19057638.10. Cohen SP, Strassels SA, Kurihara C, Crooks MT, Erdek MA, Forsythe A, et al. Outcome predictors for sacroiliac joint (lateral branch) radiofrequency denervation. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009; 34:206–214. PMID: 19587617.
Article11. Cohen SP, Hurley RW, Buckenmaier CC 3rd, Kurihara C, Morlando B, Dragovich A. Randomized placebo-controlled study evaluating lateral branch radiofrequency denervation for sacroiliac joint pain. Anesthesiology. 2008; 109:279–288. PMID: 18648237.
Article12. Karaman H, Kavak GO, Tüfek A, Çelik F, Yildirim ZB, Akdemir MS, et al. Cooled radiofrequency application for treatment of sacroiliac joint pain. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153:1461–1468. PMID: 21479801.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Rhizotomy of the Sacroiliac Joint with S2 Ganglionotomy
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment in Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: A report of 2 cases
- Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment for postherpetic neuralgia of supraorbital nerve: A case report
- Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency of the Third Occipital Nerve
- Sacroiliac Joint Injection in Patients with Low Back Pain or Buttock Pain: Short-term Follow-up Results