Immune Netw.
2015 Dec;15(6):313-318. 10.4110/in.2015.15.6.313.
Comparative Analysis of Dibutyric cAMP and Butyric Acid on the Differentiation of Human Eosinophilic Leukemia EoL-1 Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Gachon University, Incheon 21936, Korea. yjjung@gachon.ac.kr
- KMID: 2132705
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2015.15.6.313
Abstract
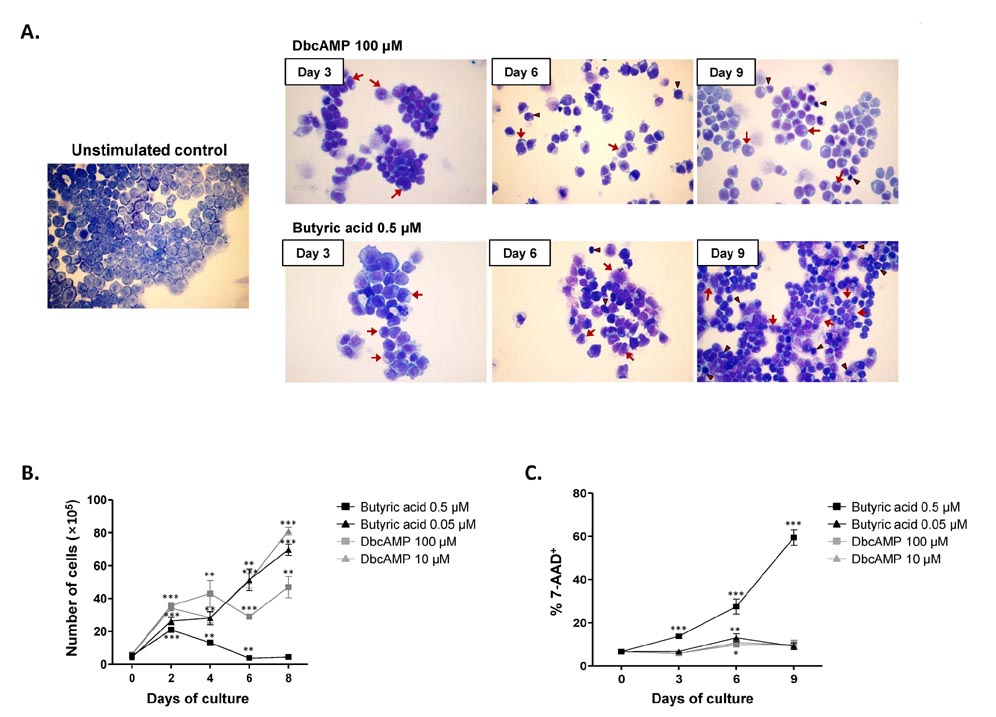
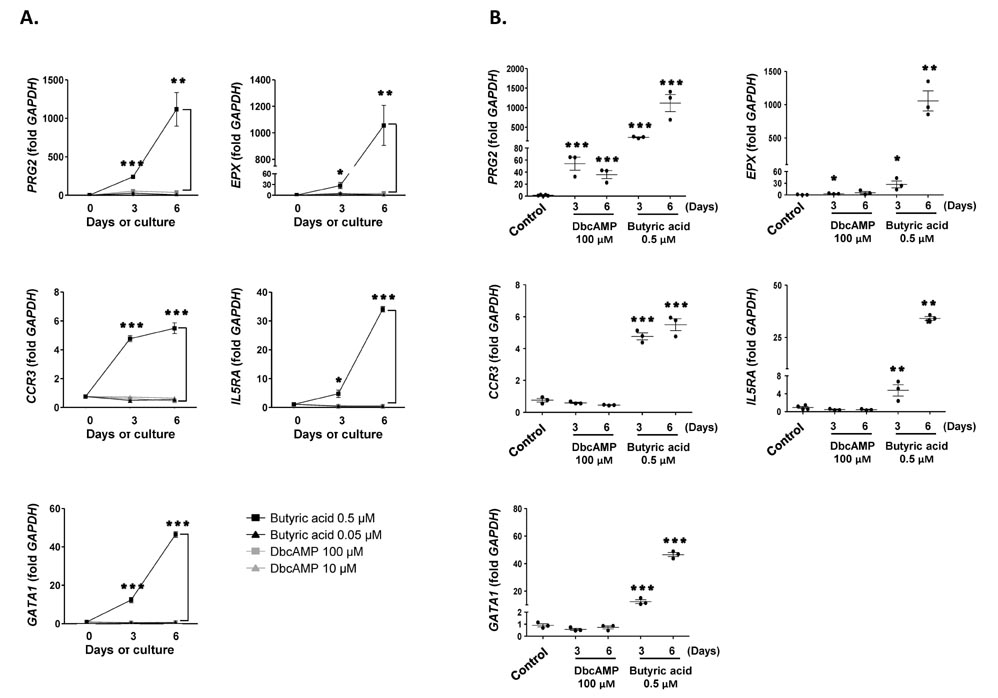
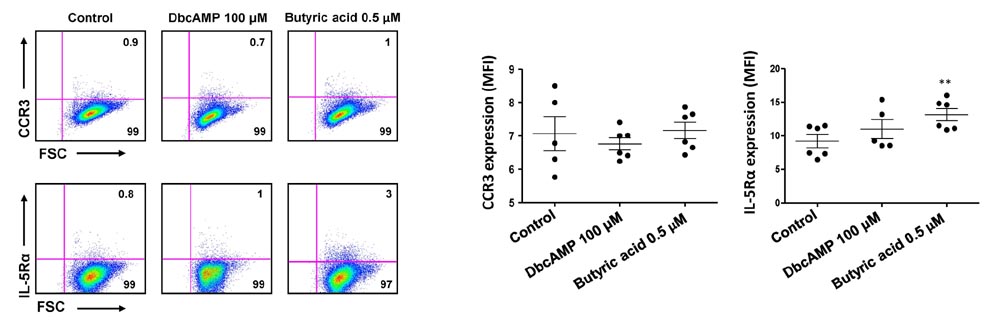
- Purification of enough numbers of circulating eosinophils is difficult because eosinophils account for less than 5% peripheral blood leukocytes. Human eosinophilic leukemia EoL-1 cells have been considered an in vitro source of eosinophils as they can differentiate into mature eosinophil-like cells when incubated with dibutyryl cAMP (dbcAMP) or butyric acid. In this study, the viability and phenotypic maturation of EoL-1 cells stimulated by either dbcAMP or butyric acid were comparatively analyzed. After treatment with 100 microM dbcAMP or 0.5 microM butyric acid, EoL-1 cells showed morphological signs of differentiation, although the number of nonviable EoL-1 cells was significantly increased following butyric acid treatment. Stimulation of EoL-1 cells with 0.5 microM butyric acid more effectively induced the expression of mature eosinophil markers than stimulation with dbcAMP. These results suggest that treatment of EoL-1 cells with 0.5 microM butyric acid for limited duration could be an effective strategy for inducing their differentiation. Considering that expression of CCR3 was not sufficient in EoL-1 cells stimulated with 0.5 microM butyric acid, treatment of the chemically stimulated EoL-1 cells with cytokines, which primarily support eosinophil maturation, would help to obtain differentiated EoL-1 cells with greater functional maturity.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Terminally Differentiating Eosinophils Express Neutrophil Primary Granule Proteins as well as Eosinophil-specific Granule Proteins in a Temporal Manner
Karam Kim, Sae Mi Hwang, Sung Min Kim, Sung Woo Park, Yunjae Jung, Il Yup Chung
Immune Netw. 2017;17(6):410-423. doi: 10.4110/in.2017.17.6.410.
Reference
-
1. Rothenberg ME, Hogan SP. The eosinophil. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006; 24:147–174.
Article2. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:11–28.
Article3. Milanovic M, Terszowski G, Struck D, Liesenfeld O, Carstanjen D. IFN consensus sequence binding protein (Icsbp) is critical for eosinophil development. J Immunol. 2008; 181:5045–5053.
Article4. Hogan SP, Waddell A, Fulkerson PC. Eosinophils in infection and intestinal immunity. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2013; 29:7–14.
Article5. Jung Y, Rothenberg ME. Roles and regulation of gastrointestinal eosinophils in immunity and disease. J Immunol. 2014; 193:999–1005.
Article6. Jung YJ, Woo SY, Jang MH, Miyasaka M, Ryu KH, Park HK, Seoh JY. Human eosinophils show chemotaxis to lymphoid chemokines and exhibit antigen-presenting-cell-like properties upon stimulation with IFN-gamma, IL-3 and GM-CSF. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2008; 146:227–234.
Article7. Saito H, Bourinbaiar A, Ginsburg M, Minato K, Ceresi E, Yamada K, Machover D, Breard J, Mathe G. Establishment and characterization of a new human eosinophilic leukemia cell line. Blood. 1985; 66:1233–1240.
Article8. Mayumi M. EoL-1, a human eosinophilic cell line. Leuk Lymphoma. 1992; 7:243–250.
Article9. Wong CK, Ho CY, Lam CW, Zhang JP, Hjelm NM. Differentiation of a human eosinophilic leukemic cell line, EoL-1: characterization by the expression of cytokine receptors, adhesion molecules, CD95 and eosinophilic cationic protein (ECP). Immunol Lett. 1999; 68:317–323.
Article10. Yoshida T, Ikuta K, Sugaya H, Maki K, Takagi M, Kanazawa H, Sunaga S, Kinashi T, Yoshimura K, Miyazaki J, Takaki S, Takatsu K. Defective B-1 cell development and impaired immunity against Angiostrongylus cantonensis in IL-5R alpha-deficient mice. Immunity. 1996; 4:483–494.
Article11. Kitaura M, Nakajima T, Imai T, Harada S, Combadiere C, Tiffany HL, Murphy PM, Yoshie O. Molecular cloning of human eotaxin, an eosinophil-selective CC chemokine, and identification of a specific eosinophil eotaxin receptor, CC chemokine receptor 3. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:7725–7730.
Article12. Ishihara K, Takahashi A, Kaneko M, Sugeno H, Hirasawa N, Hong J, Zee O, Ohuchi K. Differentiation of eosinophilic leukemia EoL-1 cells into eosinophils induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Life Sci. 2007; 80:1213–1220.
Article13. Saito H, Hayakawa T, Mita H, Akiyama K, Shida T. Effect of butyric acid on induction of differentiation into eosinophil-like cells in human eosinophilic leukemia cells, EoL-1 cell line: possible role of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as an autocrine differentiating factor. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1993; 100:240–247.
Article14. Morita M, Saito H, Honjo T, Saito Y, Tsuruta S, Kim KM, Tanaka M, Mori KJ, Mayumi M, Mikawa H. Differentiation of a human eosinophilic leukemia cell line (EoL-1) by a human T-cell leukemia cell line (HIL-3)-derived factor. Blood. 1991; 77:1766–1775.
Article15. Iwasaki H, Mizuno S, Mayfield R, Shigematsu H, Arinobu Y, Seed B, Gurish MF, Takatsu K, Akashi K. Identification of eosinophil lineage-committed progenitors in the murine bone marrow. J Exp Med. 2005; 201:1891–1897.
Article16. Clutterbuck EJ, Hirst EM, Sanderson CJ. Human interleukin-5 (IL-5) regulates the production of eosinophils in human bone marrow cultures: comparison and interaction with IL-1, IL-3, IL-6, and GMCSF. Blood. 1989; 73:1504–1512.
Article17. Fulkerson PC, Schollaert KL, Bouffi C, Rothenberg ME. IL-5 triggers a cooperative cytokine network that promotes eosinophil precursor maturation. J Immunol. 2014; 193:4043–4052.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Differentiation of HL-60 Cells Causes to Lose their Ability to Express TNF mRNA
- House Dust Mite Induces Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in EoL-1 Human Eosinophilic Leukemic Cells
- Butyric acid and prospects for creation of new medicines based on its derivatives: a literature review
- The Effect of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in Decidualizing Human Endometrial Stromal Cells
- DNA-Protein Interaction of gamma-Globin Gene Promoter by Differentiation Inducers