Electrolyte Blood Press.
2007 Dec;5(2):68-74. 10.5049/EBP.2007.5.2.68.
Dysregulation of Renal Cyclooxygenase-2 in Rats with Lithium-induced Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. thkwon@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2052288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2007.5.2.68
Abstract
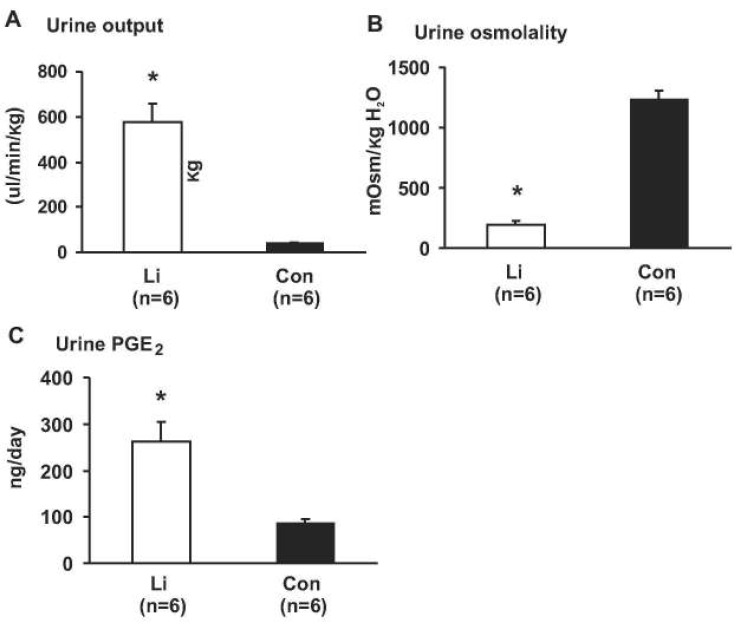
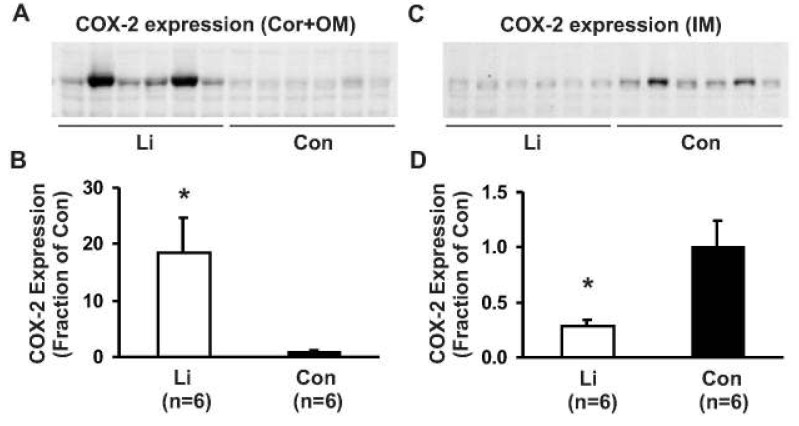
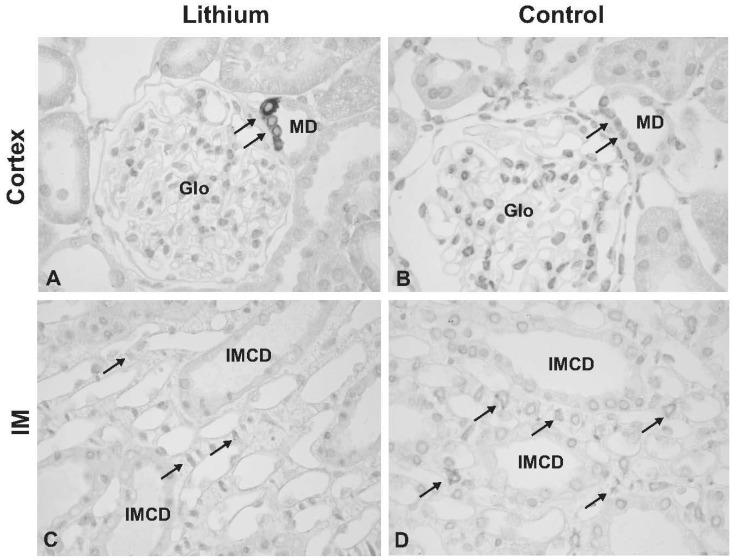
- This study aimed to examine whether the expression of major prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthesis enzyme, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), is changed in the kidneys of the rats with lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (Li-NDI). Sprague- Dawley rats treated with lithium for 4 weeks were used as the NDI model and expression of renal COX-2 was determined by immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. In Li-NDI where urine output was markedly increased and urine osmolality was significantly decreased, COX-2 expression in the inner medulla was decreased (28% of control), while it increased 18-fold in the cortex and outer medulla. Consistent with this, labeling intensity of COX-2 in macula densa region was increased, whereas it was decreased in the interstitial cells in the inner medulla, indicating a differential regulation of COX-2 between the cortex and inner medulla in Li-NDI. Accordingly, urinary PGE2 excretion was significantly increased in Li-NDI. In conclusion, there is a differential regulation of COX-2 between cortex and inner medulla in Li- NDI and urinary PGE2 excretion is increased in Li-NDI, possibly due to an increased renal production. This may suggest that increased renal production of PGE2 could play a role in modulating water reabsorption in the renal collecting duct in Li-NDI.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Renal Effects of Prostaglandins and Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors
Gheun-Ho Kim
Electrolyte Blood Press. 2008;6(1):35-41. doi: 10.5049/EBP.2008.6.1.35.
Reference
-
1. Harris RC, Breyer MD. Physiological regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001; 281:F1–F11. PMID: 11399641.
Article2. Harris RC. Interactions between COX-2 and the renin-angiotensin system in the kidney. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003; 177:423–427. PMID: 12648159.
Article3. Berl T, Schrier RW. Mechanism of effect of prostaglandin E 1 on renal water excretion. J Clin Invest. 1973; 52:463–471. PMID: 4683884.4. Campean V, Theilig F, Paliege A, Breyer M, Bachmann S. Key enzymes for renal prostaglandin synthesis: site-specific expression in rodent kidney (rat, mouse). Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003; 285:F19–F32. PMID: 12657565.5. Hebert RL, Jacobson HR, Breyer MD. PGE2 inhibits AVP-induced water flow in cortical collecting ducts by protein kinase C activation. Am J Physiol. 1990; 259:F318–F325. PMID: 2167017.
Article6. Zelenina M, Christensen BM, Palmer J, Nairn AC, Nielsen S, Aperia A. Prostaglandin E(2) interaction with AVP: effects on AQP2 phosphorylation and distribution. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 278:F388–F394. PMID: 10710543.7. Nadler SP, Zimpelmann JA, Hebert RL. PGE2 inhibits water permeability at a post-cAMP site in rat terminal inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1992; 262:F229–F235. PMID: 1311524.
Article8. Tamma G, Wiesner B, Furkert J, Hahm D, Oksche A, Schaefer M, Valenti G, Rosenthal W, Klussmann E. The prostaglandin E2 analogue sulprostone antagonizes vasopressin-induced antidiuresis through activation of Rho. J Cell Sci. 2003; 116:3285–3294. PMID: 12829746.
Article9. Yang T, Schnermann JB, Briggs JP. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in renal medulla by tonicity in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1999; 277:F1–F9. PMID: 10409291.10. Timmer RT, Sands JM. Lithium intoxication. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:666–674. PMID: 10073618.
Article11. Christensen S, Kusano E, Yusufi AN, Murayama N, Dousa TP. Pathogenesis of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus due to chronic administration of lithium in rats. J Clin Invest. 1985; 75:1869–1879. PMID: 2989335.
Article12. Kwon TH, Laursen UH, Marples D, Maunsbach AB, Knepper MA, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Altered expression of renal AQPs and Na(+) transporters in rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000; 279:F552–F564. PMID: 10966935.13. Sugawara M, Hashimoto K, Ota Z. Involvement of prostaglandin E2, cAMP, and vasopressin in lithium induced polyuria. Am J Physiol. 1988; 254:R863–R869. PMID: 2454589.14. Nielsen J, Kwon TH, Praetorius J, Kim YH, Frokiaer J, Knepper MA, Nielsen S. Segment-specific ENaC downregulation in kidney of rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003; 285:F1198–F1209. PMID: 12928314.
Article15. Marples D, Christensen S, Christensen EI, Ottosen PD, Nielsen S. Lithium-induced downregulation of aquaporin-2 water channel expression in rat kidney medulla. J Clin Invest. 1995; 95:1838–1845. PMID: 7535800.
Article16. Kwon TH, Nielsen J, Kim YH, Knepper MA, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Regulation of sodium transporters in the thick ascending limb of rat kidney: response to angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003; 285:F152–F165. PMID: 12657563.17. Kotnik P, Nielsen J, Kwon TH, Krzisnik C, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Altered expression of COX-1, COX-2, and mPGES in rats with nephrogenic and central diabetes insipidus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005; 288:F1053–F1068. PMID: 15644490.
Article18. Klein JD, Gunn RB, Roberts BR, Sands JM. Down-regulation of urea transporters in the renal inner medulla of lithium-fed rats. Kidney Int. 2002; 61:995–1002. PMID: 11849454.
Article19. Hober C, Vantyghem MC, Racadot A, Cappoen JP, Lefebvre J. Normal hemodynamic and coagulation responses to 1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin in a case of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Results of treatment by a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor (indomethacin). Horm Res. 1992; 37:190–195. PMID: 1490662.20. Hebert RL, Jacobson HR, Breyer MD. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct by increasing intracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1991; 87:1992–1998. PMID: 1645747.21. Hebert RL, Jacobson HR, Fredin D, Breyer MD. Evidence that separate PGE2 receptors modulate water and sodium transport in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1993; 265:F643–F650. PMID: 8238544.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Drug Induced Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus and Hyperprolactinemia in Schizophrenia Simultaneously
- A Case of Lithium-Induced Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus and Rhabdomyolysis
- A Case of Lithium-Induced Upper Extremity Peripheral Polyneuropathy and Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
- A Case of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Associated with Hydronephrosis
- A case of membranous glomerulonephritis induced by lithium