J Korean Soc Radiol.
2014 Apr;70(4):307-311. 10.3348/jksr.2014.70.4.307.
Radiologic Features of Proteus Syndrome: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. okkimmd@hanafos.com
- KMID: 2041943
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.70.4.307
Abstract
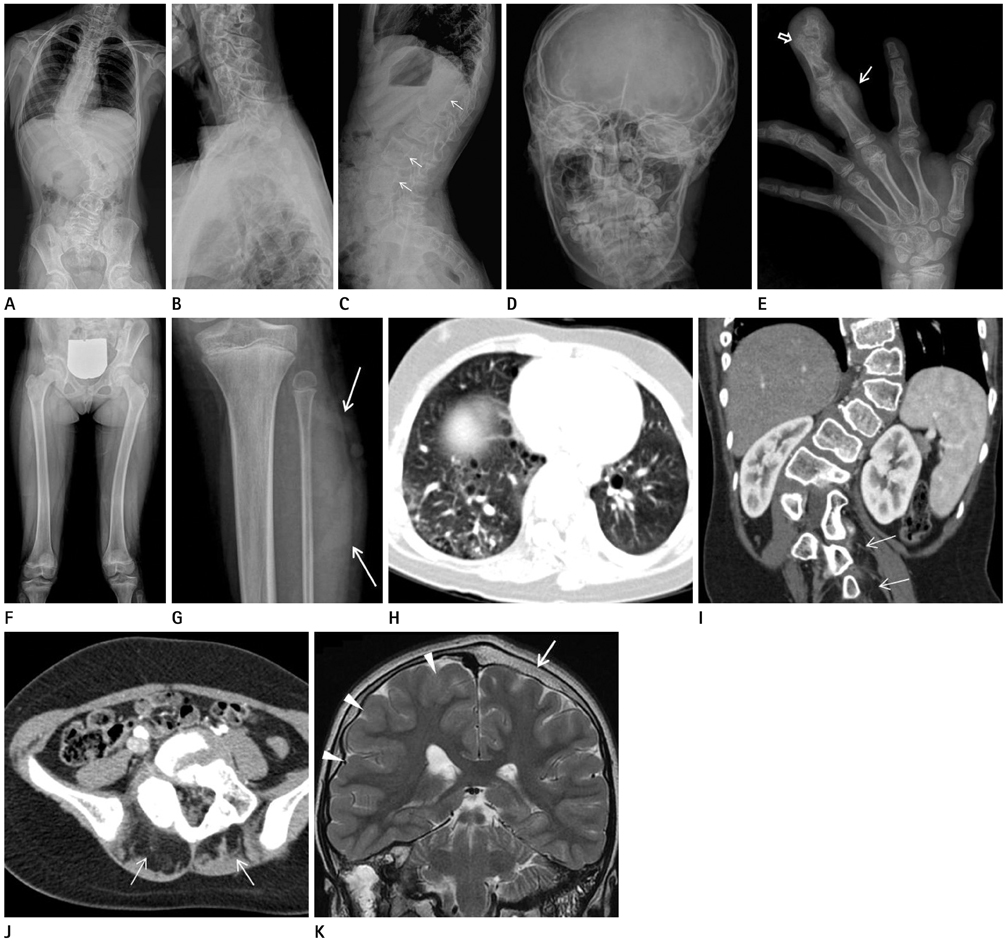
- Proteus syndrome is a rare congenital hamartomatous condition that is characterized by a wide range of malformations with overgrowth of various tissues. The author reports the case of a Proteus syndrome in a 14-year-old girl who had the unique features of this syndrome including megaspondylodysplasia with resultant scoliosis, leg discrepancy, macrodactyly, clinodactyly, hyperostosis in external auditory meatus, asymmetric megalencephaly, splenomegaly, cystic lung changes, asymmetric soft tissue fat infiltrations and a long, asymmetric face, with descriptions of the radiological features.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cohen MM Jr, Hayden PW. A newly recognized hamartomatous syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1979; 15:291–296.2. Wiedemann HR, Burgio GR, Aldenhoff P, Kunze J, Kaufmann HJ, Schirg E. The proteus syndrome. Partial gigantism of the hands and/or feet, nevi, hemihypertrophy, subcutaneous tumors, macrocephaly or other skull anomalies and possible accelerated growth and visceral affections. Eur J Pediatr. 1983; 140:5–12.3. Lindhurst MJ, Sapp JC, Teer JK, Johnston JJ, Finn EM, Peters K, et al. A mosaic activating mutation in AKT1 associated with the Proteus syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:611–619.4. Cohen MM Jr. Proteus syndrome review: molecular, clinical, and pathologic features. Clin Genet. 2013; [Epub ahead of print].5. Cohen MM Jr. Causes of premature death in Proteus syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 2001; 101:1–3.6. Biesecker LG, Happle R, Mulliken JB, Weksberg R, Graham JM Jr, Viljoen DL, et al. Proteus syndrome: diagnostic criteria, differential diagnosis, and patient evaluation. Am J Med Genet. 1999; 84:389–395.7. Jamis-Dow CA, Turner J, Biesecker LG, Choyke PL. Radiologic manifestations of Proteus syndrome. Radiographics. 2004; 24:1051–1068.8. Lim GY, Kim OH, Kim HW, Lee KS, Kang KH, Song HR, et al. Pulmonary manifestations in Proteus syndrome: pulmonary varicosities and bullous lung disease. Am J Med Genet A. 2011; 155A:865–869.9. Bastos H, da Silva PF, de Albuquerque MA, Mattos A, Riesgo RS, Ohlweiler L, et al. Proteus syndrome associated with hemimegalencephaly and Ohtahara syndrome: report of two cases. Seizure. 2008; 17:378–382.10. Demir MK. Case 131: Proteus syndrome. Radiology. 2008; 246:974–979.