J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Dec;65(6):577-583. 10.3348/jksr.2011.65.6.577.
Pulmonary Lipiodol Accumulation after Transarterial Chemoembolization: CT Findings and Its Radiologic Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chung-Ang University Medical Center, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. j3mn@chol.com
- KMID: 2002925
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.65.6.577
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate CT findings and radiologic outcomes of pulmonary lipiodol accumulation (PLA) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective study involved 488 TACEs for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (n = 160) and hepatic metastasis for non-hepatic malignancies (n = 7) in 167 patients. We reviewed the patient clinicoradiologic findings before and after TACE and calculated the incidence of PLA and PLA resolution time after initial CT and after TACE.
RESULTS
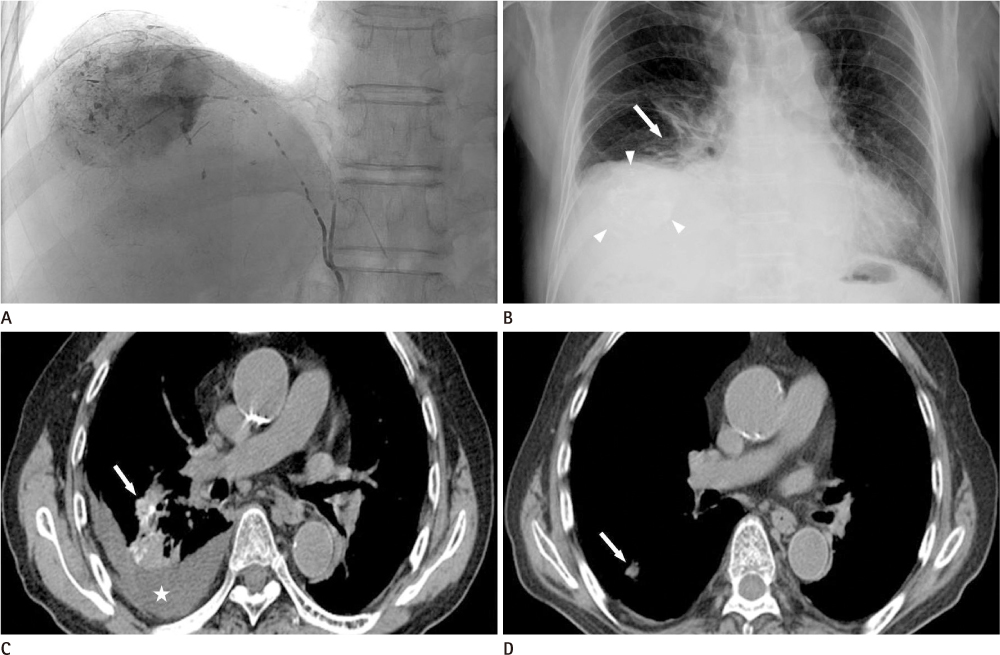
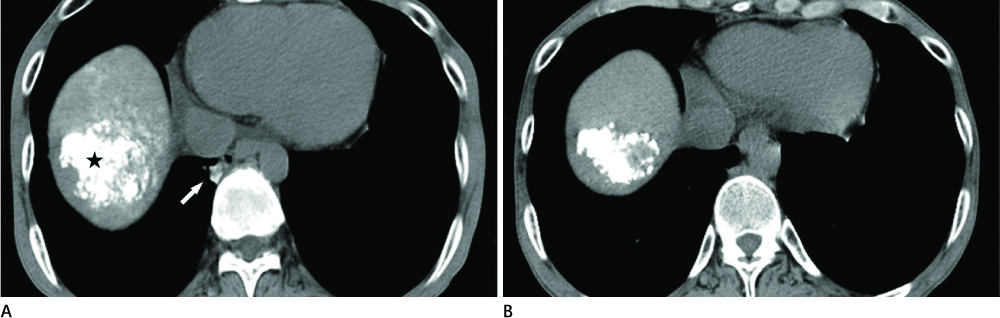
Lipiodol accumulation in the lungs was seen under CT after TACE in seven patients (M : F = 6 : 1, mean age 61 years). The incidence of PLA at CT was 4.1% (7/167 patients). In five patients, associated intrathoracic abnormalities including pleural effusion with (n = 3) or without consolidation (n = 2) were revealed at CT scans. The CT resolution time and PLA recovery time were 56 +/- 54 days and 66 +/- 52 days, respectively.
CONCLUSION
The recovery time for lipiodol accumulation was 66 days. It is believed that the clinical and radiologic outcome of PLA without respiratory failure is promising, and conservative treatment will suffice when lipiodol accumulation in the lungs is seen in CT images after TACE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Lipiodol-induced Pneumonitis Following Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Heechul Nam
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022;80(5):233-236. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.119.
Reference
-
1. Xia J, Ren Z, Ye S, Sharma D, Lin Z, Gan Y, et al. Study of severe and rare complications of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for liver cancer. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 59:407–412.2. Lee KH, Sung KB, Lee DY, Park SJ, Kim KW, Yu JS. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: anatomic and hemodynamic considerations in the hepatic artery and portal vein. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1077–1091.3. Chung JW, Park JH, Im JG, Han JK, Han MC. Pulmonary oil embolism after transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 1993; 187:689–693.4. Tajima T, Honda H, Kuroiwa T, Yabuuchi H, Okafuji T, Yosimitsu K, et al. Pulmonary complications after hepatic artery chemoembolization or infusion via the inferior phrenic artery for primary liver cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:893–900.5. Choi SY, Goo JM, Chun HJ, Han DH. Lipiodol can simulate cement embolism in patients having undergone vertebroplasty due to metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:E2–E3.6. Wu GC, Perng WC, Chen CW, Chian CF, Peng CK, Su WL. Acute respiratory distress syndrome after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinomas. Am J Med Sci. 2009; 338:357–360.7. Raoul JL, Bourguet P, Bretagne JF, Duvauferrier R, Coornaert S, Darnault P, et al. Hepatic artery injection of I-131-labeled lipiodol. Part I. Biodistribution study results in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases. Radiology. 1988; 168:541–545.8. Lin MT, Kuo PH. Pulmonary lipiodol embolism after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. JRSM Short Rep. 2010; 1:6.9. Fraimow W, Wallace S, Lewis P, Greening RR, Cathcart RT. Changes in pulmonary function due to lymphangiography. Radiology. 1965; 85:231–241.10. Samejima M, Tamura S, Kodama T, Yuuki Y, Takasaki J, Sekiva R, et al. [Pulmonary complication following intra-arterial infusion of lipiodol-adriamycin emulsion for hepatocellular carcinoma, report of a case]. Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1990; 50:24–28.11. Lörcher U, Peters J, Kollath J. [Changes in the lungs and pleura following chemoembolization of liver tumors with mitomycin-lipiodol]. Rofo. 1990; 152:569–573.12. Charnsangavej C, Chuang VP, Wallace S, Soo CS, Bowers T. Angiographic classification of hepatic arterial collaterals. Radiology. 1982; 144:485–494.13. Koehler RE, Korobkin M, Lewis F. Arteriographic demonstration of collateral arterial supply to the liver after hepatic artery ligation. Radiology. 1975; 117:49–54.14. Han D, Lee KS, Franquet T, Müller NL, Kim TS, Kim H, et al. Thrombotic and nonthrombotic pulmonary arterial embolism: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003; 23:1521–1539.15. Rossi SE, Goodman PC, Franquet T. Nonthrombotic pulmonary emboli. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:1499–1508.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An A to Z of Lipiodol Beyond the Clinical Practice in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Diagnostic Value of Immediate CT after Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison with 2-3 Week Delayed CT
- Transarterial chemoembolization using drug eluting beads for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Now and future
- A Case of Lipiodol Pneumonitis After Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Therapeutic effect of transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma