Cancer Res Treat.
2009 Dec;41(4):237-240.
Pseudoaneurysm Due to Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung: Two Cases of Spontaneous Resolution after Chemotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. kshryj@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
Abstract
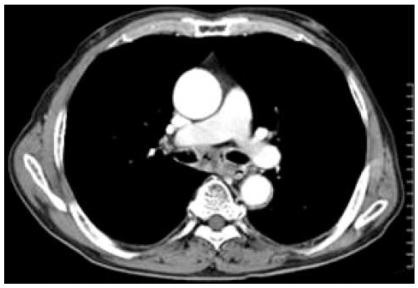
- Pseudoaneurysm due to cancer is uncommon generally and is extremely rare in lung cancer. We report two cases of false aneurysms due to lung cancer that spontaneously regressed upon chemotherapy without intervention. Both patients had squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and the diagnosis of a pseudoaneurysm was made using computed tomography. There was no evidence of severe bronchial hemorrhage and the psuedoaneurysms were small and well-encased. Chemotherapy was performed and the pseudoaneurysms resolved.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shaaban H, Sharma H, Rao J, Clark S. A pulmonary artery false aneurysm after right middle lobectomy: a case report. J Med Case Reports. 2007; 1:70. PMID: 17718925.
Article2. Gomez-Jorge J, Mitchell SE. Embolization of a pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm due to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1999; 10:1127–1130. PMID: 10496719.
Article3. Oliver TB, Stevenson AJ, Gillespie IN. Pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm due to bronchial carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 1997; 70:950–951. PMID: 9486073.
Article4. Akpinar E, Turkbey B, Canyigit M, Peynircioglu B, Hazirolan T, Pamuk AG, et al. Bleeding pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to squamous cell lung cancer: computed tomography findings and endovascular management. Acta Radiol. 2006; 47:944–946. PMID: 17077046.
Article5. Lönn L, Olmarker A, Geterud K, Risberg B. Prospective randomized study comparing ultrasound-guided thrombin injection to compression in the treatment of femoral pseudoaneurysms. J Endovasc Ther. 2004; 11:570–576. PMID: 15482031.
Article6. Hwang KW, Chun KJ, An SG, Kim KY, Kim CW, Hong TJ, et al. A case of ultrasound-guided thrombin injection therapy for pseudoaneurysm caused by the hemostatic puncture closure device angio-seal. Korean J Intern Med. 2007; 72:181–185.7. Remy J, Lemaitre L, Lafitte JJ, Vilain MO, Saint Michel J, Steenhouwer F. Massive hemoptysis of pulmonary arterial origin: diagnosis and treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984; 143:963–969. PMID: 6333165.
Article8. DeLima LG, Wynands JE, Bourke ME, Walley VM. Catheter-induced pulmonary artery false aneurysm and rupture: case report and review. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 1994; 8:70–75. PMID: 8167290.
Article9. You CK, Whatley GS. Swan-Ganz catheter-induced pulmonary artery pseudoaneurysm: a case of complete resolution without intervention. Can J Surg. 1994; 37:420–424. PMID: 7922906.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung: Two Case Reports with CT Imaging Findings
- A Case of Spontaneous Regression of Non-small-cell Lung Cancer
- Multiple primary lung cancer: Synchronous small cell lung carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- p40 Immunohistochemistry Is an Excellent Marker in Primary Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- A Case of Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma Similar with Herpetic Keratitis