J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 May;57(5):379-385. 10.3340/jkns.2015.57.5.379.
Infrequent Hemorrhagic Complications Following Surgical Drainage of Chronic Subdural Hematomas
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Life Sciences, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy. angelo.rusconi@hotmail.com
- 2Neurosurgical Unit, Ospedale di Circolo, Varese, Italy.
- KMID: 1881738
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.5.379
Abstract
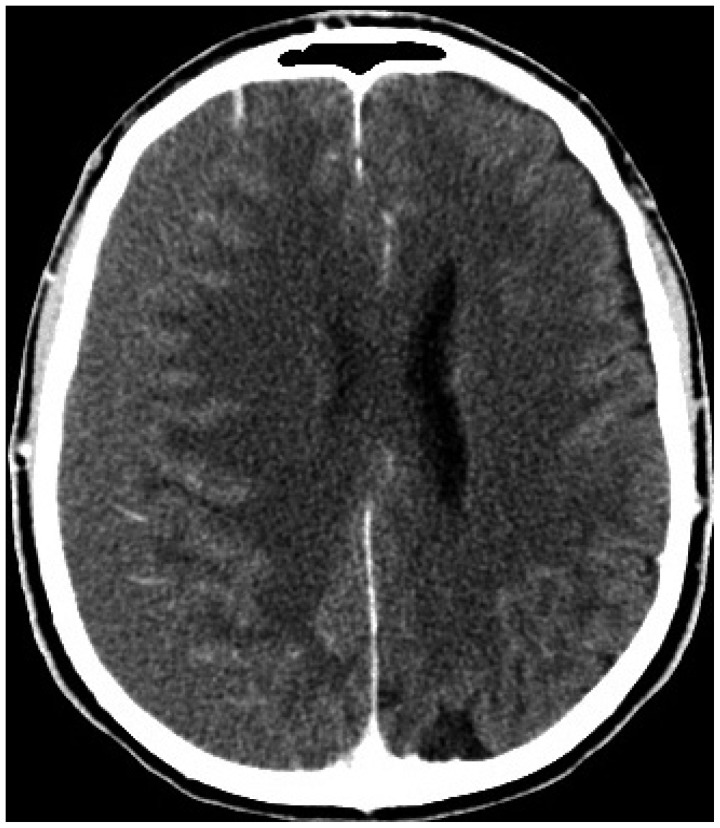
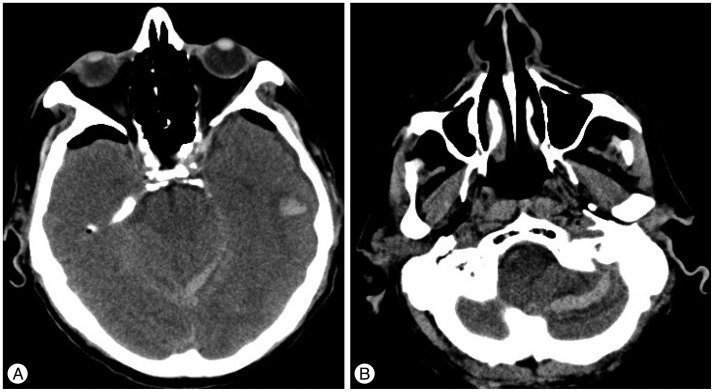
- Chronic subdural hematomas mainly occur amongst elderly people and usually develop after minor head injuries. In younger patients, subdural collections may be related to hypertension, coagulopathies, vascular abnormalities, and substance abuse. Different techniques can be used for the surgical treatment of symptomatic chronic subdural hematomas : single or double burr-hole evacuation, with or without subdural drainage, twist-drill craniostomies and classical craniotomies. Failure of the brain to re-expand, pneumocephalus, incomplete evacuation, and recurrence of the fluid collection are common complications following these procedures. Acute subdural hematomas may also occur. Rarely reported hemorrhagic complications include subarachnoid, intracerebral, intraventricular, and remote cerebellar hemorrhages. The causes of such uncommon complications are difficult to explain and remain poorly understood. Overdrainage and intracranial hypotension, rapid brain decompression and shift of the intracranial contents, cerebrospinal fluid loss, vascular dysregulation and impairment of venous outflow are the main mechanisms discussed in the literature. In this article we report three cases of different post-operative intracranial bleeding and review the related literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Postoperative Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Multipunctate Intracerebral Hemorrhages Following Evacuation of Bilateral Chronic Subdural Hematomas
Won-Bae Seung, Ju Ho Jeong
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017;13(2):149-152. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.2.149.Remote Hemorrhage after Burr Hole Drainage of Chronic Subdural Hematoma
Chang Hyeun Kim, Geun Sung Song, Young Ha Kim, Young Soo Kim, Soon Ki Sung, Dong Wuk Son, Sang Weon Lee
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2017;13(2):144-148. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.2.144.
Reference
-
1. Arpino L, Gravina M, Basile D, Franco A. Spontaneous chronic subdural hematoma in a young adult. J Neurosurg Sci. 2009; 53:55–57. PMID: 19546844.2. Brockmann MA, Groden C. Remote cerebellar hemorrhage : a review. Cerebellum. 2006; 5:64–68. PMID: 16527766.3. Brockmann MA, Nowak G, Reusche E, Russlies M, Petersen D. Zebra sign : cerebellar bleeding pattern characteristic of cerebrospinal fluid loss. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102:1159–1162. PMID: 16028781.
Article4. Chang SH, Yang SH, Son BC, Lee SW. Cerebellar hemorrhage after burr hole drainage of supratentorial chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:592–595. PMID: 20062580.
Article5. Cioffi F, Pasqualin A, Cavazzani P, Da Pian R. Subarachnoid haemorrhage of unknown origin : clinical and tomographical aspects. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1989; 97:31–39. PMID: 2718794.
Article6. Cohen-Gadol AA. Remote contralateral intraparenchymal hemorrhage after overdrainage of a chronic subdural hematoma. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2013; 4:834–836. PMID: 23959412.
Article7. de Noronha RJ, Sharrack B, Hadjivassiliou M, Romanowski CA. Subdural haematoma : a potentially serious consequence of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003; 74:752–755. PMID: 12754345.
Article8. Dinc C, Iplikcioglu AC, Bikmaz K, Navruz Y. Intracerebral haemorrhage occurring at remote site following evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2008; 150:497–499. discussion 499PMID: 18305890.
Article9. Dincer A, Özcan Ü, Kaya D, Usseli MI, Erzen C, Pamir MN. Asymptomatic remote cerebellar hemorrhage : CT and MRI findings. Cerebellum. 2012; 11:880–886. PMID: 22249914.
Article10. Drapkin AJ. Chronic subdural hematoma : pathophysiological basis for treatment. Br J Neurosurg. 1991; 5:467–473. PMID: 1764228.11. Fogelholm R, Heiskanen O, Waltimo O. Chronic subdural hematoma in adults. Influence of patient's age on symptoms, signs, and thickness of hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1975; 42:43–46. PMID: 1167376.12. Gelabert-González M, Iglesias-Pais M, García-Allut A, Martínez-Rumbo R. Chronic subdural haematoma : surgical treatment and outcome in 1000 cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2005; 107:223–229. PMID: 15823679.
Article13. Haykowsky MJ, Eves ND, R Warburton DE, Findlay MJ. Resistance exercise, the Valsalva maneuver, and cerebrovascular transmural pressure. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003; 35:65–68. PMID: 12544637.
Article14. Hellwig D, Kuhn TJ, Bauer BL, List-Hellwig E. Endoscopic treatment of septated chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1996; 45:272–277. PMID: 8638225.
Article15. Huang CY, Lee PH, Lin SH, Chuang MT, Sun YT, Hung YC, et al. Remote cerebellar hemorrhage following supratentorial craniotomy. Neurol Res. 2012; 34:422–429. PMID: 22664148.
Article16. Hyam JA, Turner J, Peterson D. Cerebellar haemorrhage after repeated burr hole evacuation for chronic subdural haematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2007; 14:83–86. PMID: 17071089.
Article17. Infuso L. [Subarachnoid hemorrhage of unknown origin]. Minerva Anestesiol. 1998; 64:149–153. PMID: 9773644.18. Keller TM, Chappell ET. Spontaneous acute subdural hematoma precipitated by cocaine abuse: case report. Surg Neurol. 1997; 47:12–14. discussion 14-15PMID: 8986158.
Article19. Kim JK, Kim SW, Kim SH. Intracerebral hemorrhage following evacuation of a chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013; 53:108–111. PMID: 23560175.
Article20. Korosue K, Kondoh T, Ishikawa Y, Nagao T, Tamaki N, Matsumoto S. Acute subdural hematoma associated with nontraumatic middle meningeal artery aneurysm : case report. Neurosurgery. 1988; 22:411–413. PMID: 3352892.
Article21. Missori P, Domenicucci M, Sassun TE, Tarantino R, Peschillo S. Alterations in the intracranial venous sinuses in spontaneous nontraumatic chronic subdural hematomas. J Clin Neurosci. 2013; 20:389–393. PMID: 23219821.
Article22. Miyazaki T, Matsumoto Y, Ohta F, Daisu M, Moritake K. A case of unknown origin subarachnoid hemorrhage immediately following drainage for chronic subdural hematoma. Kurume Med J. 2004; 51:163–167. PMID: 15373234.
Article23. Modesti LM, Hodge CJ, Barnwell ML. Intracerebral hematoma after evacuation of chronic extracerebral fluid collections. Neurosurgery. 1982; 10(6 Pt 1):689–693. PMID: 7110541.
Article24. Mori K, Maeda M. Surgical treatment of chronic subdural hematoma in 500 consecutive cases : clinical characteristics, surgical outcome, complications, and recurrence rate. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001; 41:371–381. PMID: 11561347.
Article25. Ogasawara K, Ogawa A, Okuguchi T, Kobayashi M, Suzuki M, Yoshimoto T. Postoperative hyperperfusion syndrome in elderly patients with chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 2000; 54:155–159. PMID: 11077097.
Article26. Park JS, Hwang JH, Park J, Hamm IS, Park YM. Remote cerebellar hemorrhage complicated after supratentorial surgery : retrospective study with review of articles. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:136–143. PMID: 19763216.
Article27. Sambasivan M. An overview of chronic subdural hematoma : experience with 2300 cases. Surg Neurol. 1997; 47:418–422. PMID: 9131021.28. Singla A, Jacobsen WP, Yusupov IR, Carter DA. Subdural evacuating port system (SEPS)--minimally invasive approach to the management of chronic/subacute subdural hematomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:425–431. PMID: 22763191.
Article29. Spetzler RF, Wilson CB, Weinstein P, Mehdorn M, Townsend J, Telles D. Normal perfusion pressure breakthrough theory. Clin Neurosurg. 1978; 25:651–672. PMID: 710017.
Article30. Tindall GT, Payne NS 2nd, O'Brien MS. Complications of surgery for subdural hematoma. Clin Neurosurg. 1976; 23:465–482. PMID: 975697.
Article31. Toledo E, Eynan N, Shalit M. Intracranial hypotension--an iatrogenic complication of vacuum drainage systems. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1980; 52:55–59. PMID: 7376946.
Article32. Van Roost D, Thees C, Brenke C, Oppel F, Winkler PA, Schramm J. Pseudohypoxic brain swelling : a newly defined complication after uneventful brain surgery, probably related to suction drainage. Neurosurgery. 2003; 53:1315–1326. discussion 1326-1327PMID: 14633298.33. Vogels RL, Verstegen MJ, van Furth WR. Cerebellar haemorrhage after non-traumatic evacuation of supratentorial chronic subdural haematoma : report of two cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006; 148(Wien):993–996. PMID: 16804644.
Article34. Wasnick JD, Lien CA, Rubin LA, Fraser RA. Unexplained bradycardia during craniotomy closure : the role of intracranial hypotension. Anesth Analg. 1993; 76:432–433. PMID: 7818607.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Burr Hole Drainage versus Small Craniotomy of Chronic Subdural Hematomas
- Evolution of Chronic Subdural Hematoma based on Brain CT findings and Appropriate Treatment Methods
- Bilateral Acute Subdural Hematoma Following Evacuation of Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Twist-Drill or Burr Hole Craniostomy for Draining Chronic Subdural Hematomas: How to Choose It for Chronic Subdural Hematoma Drainage
- Complications Following Burr Hole Craniostomy and Closed-System Drainage for Subdural Lesions