J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Sep;28(9):1382-1387. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.9.1382.
Incidence of Deep Vein Thrombosis after Spinal Cord Injury in Korean Patients at Acute Rehabilitation Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yays.sung@samsung.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1793057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.9.1382
Abstract
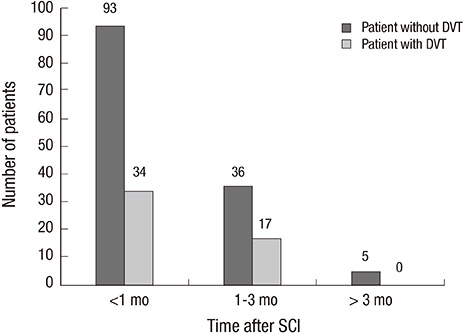
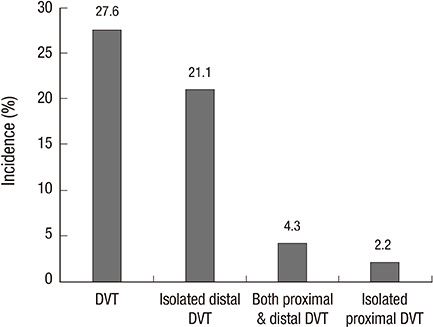
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and subsequent pulmonary embolism (PE) remain significant causes of morbidity, mortality in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI). Since incidence of DVT after SCI in Korean population has not been much studied, we retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 185 SCI patients admitted for acute rehabilitation unit to investigate the incidence of DVT. Color Doppler ultrasonography was performed to screen for the occurrence of DVT at the time of initial presentation to acute rehabilitation unit. Primary study outcome was the incidence of DVT. Possible risk factors for DVT including the epidemiologic characteristics, completeness of motor paralysis, cause of injury, spasticity, surgery, and active cancer were analyzed. The incidence of DVT after SCI was 27.6%. In multiple logistic regression analysis, absence of spasticity was a significant independent risk factor (P<0.05) for occurrence of DVT. Symptomatic pulmonary embolism was evident in 7 patients without an episode of sudden death. Therefore, it is concluded that the incidence of DVT after SCI in Korean patients is comparable with that in Western populations. This result suggests that pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis should be considered in Korean patients with SCI.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Female
Humans
Incidence
Logistic Models
Male
Middle Aged
Paralysis/etiology
Pulmonary Embolism/epidemiology/etiology
Rehabilitation Centers
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Spinal Cord Injuries/*complications
Venous Thrombosis/*epidemiology/etiology/ultrasonography
Young Adult
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Prophylaxis and Management of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Trauma Patients
Yong-Cheol Yoon, Jae-Ang Sim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2015;28(1):82-92. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.82.Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism after spinal cord disease at a rehabilitation unit: a retrospective study
Yoonhee Kim, Minjae Jeong, Myung Woo Park, Hyun Iee Shin, Byung Chan Lee, Du Hwan Kim
J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(Suppl):S56-S64. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2023.00689.
Reference
-
1. Waring WP, Karunas RS. Acute spinal cord injuries and the incidence of clinically occurring thromboembolic disease. Paraplegia. 1991; 29:8–16.2. White RH, Zhou H, Romano PS. Incidence of idiopathic deep venous thrombosis and secondary thromboembolism among ethnic groups in California. Ann Intern Med. 1998; 128:737–740.3. Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, Heit JA, Samama CM, Lassen MR, Colwell CW. American College of Chest Physicians. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008; 133:381S–453S.4. Chung SB, Lee SH, Kim ES, Eoh W. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after spinal cord injury: a prospective study in 37 consecutive patients with traumatic or nontraumatic spinal cord injury treated by mechanical prophylaxis. J Trauma. 2011; 71:867–870.5. Piovella F, Wang CJ, Lu H, Lee K, Lee LH, Lee WC, Turpie AG, Gallus AS, Planès A, Passera R, et al. Deep-vein thrombosis rates after major orthopedic surgery in Asia: an epidemiological study based on postoperative screening with centrally adjudicated bilateral venography. J Thromb Haemost. 2005; 3:2664–2670.6. Leizorovicz A. SMART Venography Study Steering Committee. Epidemiology of post-operative venous thromboembolism in Asian patients: results of the SMART venography study. Haematologica. 2007; 92:1194–1200.7. Todd JW, Frisbie JH, Rossier AB, Adams DF, Als AV, Armenia RJ, Sasahara AA, Tow DE. Deep venous thrombosis in acute spinal cord injury: a comparison of 125I fibrinogen leg scanning, impedance plethysmography and venography. Paraplegia. 1976; 14:50–57.8. Perkash A, Prakash V, Perkash I. Experience with the management of thromboembolism in patients with spinal cord injury: part I. incidence, diagnosis and role of some risk factors. Paraplegia. 1978; 16:322–331.9. Watson N. Anti-coagulant therapy in the prevention of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in the spinal cord injury. Paraplegia. 1978; 16:265–269.10. Merli GJ, Herbison GJ, Ditunno JF, Weitz HH, Henzes JH, Park CH, Jaweed MM. Deep vein thrombosis: prophylaxis in acute spinal cord injured patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988; 69:661–664.11. Agarwal NK, Mathur N. Deep vein thrombosis in acute spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2009; 47:769–772.12. Sugimoto Y, Ito Y, Tomioka M, Tanaka M, Hasegawa Y, Nakago K, Yagata Y. Deep venous thrombosis in patients with acute cervical spinal cord injury in a Japanese population: assessment with Doppler ultrasonography. J Orthop Sci. 2009; 14:374–376.13. Rathore MF, Hanif S, New PW, Butt AW, Aasi MH, Khan SU. The prevalence of deep vein thrombosis in a cohort of patients with spinal cord injury following the Pakistan earthquake of October 2005. Spinal Cord. 2008; 46:523–526.14. Ko HY, Shin YB, Jho SK. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis in spinal cord injury. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:359–364.15. Riklin C, Baumberger M, Wick L, Michel D, Sauter B, Knecht H. Deep vein thrombosis and heterotopic ossification in spinal cord injury: a 3 year experience at the Swiss Paraplegic Centre Nottwil. Spinal Cord. 2003; 41:192–198.16. Powell M, Kirshblum S, O'Connor KC. Duplex ultrasound screening for deep vein thrombosis in spinal cord injured patients at rehabilitation admission. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999; 80:1044–1046.17. Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration. The burden of overweight and obesity in the Asia-Pacific region. Obes Rev. 2007; 8:191–196.18. Khoo KL, Tan H, Liew YM, Deslypere JP, Janus E. Lipids and coronary heart disease in Asia. Atherosclerosis. 2003; 169:1–10.19. Perkash A, Sullivan G, Toth L, Bradleigh LH, Linder SH, Perkash I. Persistent hypercoagulation associated with heterotopic ossification in patients with spinal cord injury long after injury has occurred. Paraplegia. 1993; 31:653–659.20. Germing A, Schakrouf M, Lindstaedt M, Grewe P, Meindl R, Mügge A. Do not forget the distal lower limb veins in screening patients with spinal cord injuries for deep venous thromboses. Angiology. 2010; 61:78–81.21. Furlan JC, Fehlings MG. Role of screening tests for deep venous thrombosis in asymptomatic adults with acute spinal cord injury: an evidence-based analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:1908–1916.22. Gündüz S, Oğur E, Möhür H, Somuncu I, Açjksöz E, Ustünsöz B. Deep vein thrombosis in spinal cord injured patients. Paraplegia. 1993; 31:606–610.23. Green D, Lee MY, Lim AC, Chmiel JS, Vetter M, Pang T, Chen D, Fenton L, Yarkony GM, Meyer PR Jr. Prevention of thromboembolism after spinal cord injury using low-molecular-weight heparin. Ann Intern Med. 1990; 113:571–574.24. Yelnik A, Dizien O, Bussel B, Schouman-Claeys E, Frija G, Pannier S, Held JP. Systematic lower limb phlebography in acute spinal cord injury in 147 patients. Paraplegia. 1991; 29:253–260.25. Green D, Hartwig D, Chen D, Soltysik RC, Yarnold PR. Spinal Cord Injury Risk Assessment for Thromboembolism (SPIRATE Study). Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2003; 82:950–956.26. Bors E, Conrad CA, Massell TB. Venous occlusion of lower extremities in paraplegic patients. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1954; 99:451–454.27. Kadyan V, Clinchot DM, Colachis SC. Cost-effectiveness of duplex ultrasound surveillance in spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:191–197.28. Zierler BK. Ultrasonography and diagnosis of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2004; 109:I9–I14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep Venous Thrombosis and Heterotopic Ossification in the Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury
- Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism after spinal cord disease at a rehabilitation unit: a retrospective study
- Incidence of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Spinal Cord Injury
- Thromboembolism in the Sub-Acute Phase of Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review of the Literature
- The Incidence of Deep Vein Thrombosis in the Lower Extremity