J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Mar;27(3):332-334. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.3.332.
Positive Rates of 2009 Novel Influenza A (H1N1) was High in School-Aged Individuals: Significance in Pandemic Control
- Affiliations
-
- 1Greencross Reference Laboratory, Yongin, Korea. seonghomed@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chosun University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1793009
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.3.332
Abstract
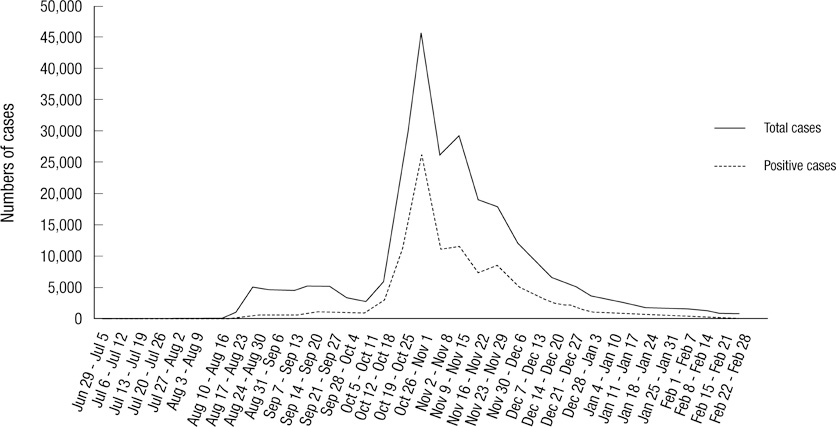
- In this study, data from a pandemic H1N1 outbreak in Korea were analyzed according to time, geography (districts), and age. A total of 252,271 samples collected nationwide were referred to the Greencross Reference Laboratory from June 2009 to February 2010 for H1N1 confirmation testing. Of these samples, 105,300 (41.7%) were H1N1-positive. With time, positivity was highest (57.0%) from October 26 - November 1 (4 weeks after Chuseok). The positive rates among districts show the highest value in Ulsan City (63.1%) and the lowest in Gyeongnam Province (32.8%). The positive rates for ages 0-2, 3-5, 6-11, 12-17, 18-20, 21-30, 31-40, 41-50, 51-60, and > 60 yr were 17.0%, 33.1%, 56.2%, 55.5%, 55.3%, 41.5%, 28.2%, 30.5%, 31.1%, and 16.8%, respectively, indirectly indicating propagation of H1N1 through schools. Pandemic control should involve school-targeted strategies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Incidence and Epidemiological Characteristics of 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Among School-Based Populations in Korea
Hyun Jung Kim, Byung Chul Chun, Hoo Jae Hann, Jang Wook Sohn, Sae Yoon Kee, Si Hyun Kim, Myoung Youn Jo, Kyung Young Lee, Seok Hyeon Lee, Min Ja Kim, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(6):431-438. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.6.431.
Reference
-
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Swine infleunza A (H1N1) infection in two children: Southern California, March-April 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009. 58:400–402.2. Current WHO phase of pandemic alert. World Health Organization. accessed on 30 Dec 2009. Available at http://www.who.int/meidacentre/news/statements/2009/h1n1_pandemic_phase6_20090611/en/index.htm.3. Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. accessed on 14 Feb 2010. Available at http://flu.cdc.go.kr.4. Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Analysis of reported pandemic infleunza (A/H1N1 2009) virus infections in Korea. Pub Health Wly Rep. 2010. 3:637–642.5. Kim HS, Kim JH, Shin SY, Kang YA, Lee HG, Kim JS, Lee JK, Cho B. Fatal cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. 26:22–27.6. Park SI, Kim MJ, Hwang HY, Oh CE, Lee JH, Park JS. Clinical characteristics of children with 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) admitted in a single institution. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:886–891.7. Shin SY, Kim JH, Kim HS, Kang YA, Lee HG, Kim JS, Lee JK, Kim WK. Clinical characteristics of Korean pediatric patients critically ill with influenza A (H1N1) virus. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2010. 45:1014–1020.8. Kim JH, Yoo HS, Lee JS, Lee EG, Park HK, Sung YH, Kim S, Kim HS, Shin SY, Lee JK. The spread of pandemic H1N1 2009 by age and region and the comparison among monitoring tools. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1109–1112.9. World Health Organization. New influenza A (H1N1) virus: global epidemiological situation, June 2009. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2009. 84:249–257.10. World Health Organization. Epidemiological summary of pandemic infleunza A (H1N1) 2009 virus: Ontario, Canada, June 2009. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2009. 84:485–491.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The 2009 H1N1 Pandemic Influenza in Korea
- A Case of Oseltamivir-Resistant Pandemic Influenza (H1N1 2009)
- A Case of Pandemic 2009 H1N1 Influenza A Manifestation as Apical Ballooning Syndrome
- Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of pandemic novel Influenza A (H1N1)
- Novel Influenza A/H1N1 Pandemic: Current Status and Prospects