J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Oct;26(10):1265-1269. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.10.1265.
Exhaled Nitric Oxide is Associated with Allergic Inflammation in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Good Gangan Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics and Institute of Allergy, Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Sciences, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mhsohn@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1785981
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.10.1265
Abstract
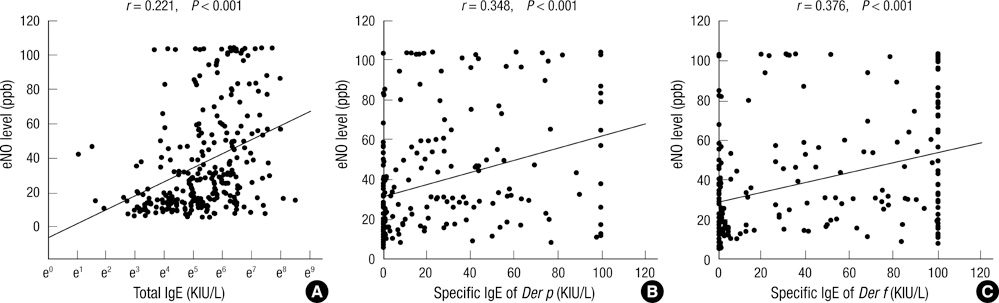
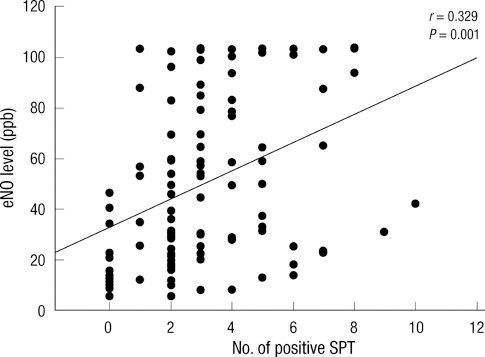
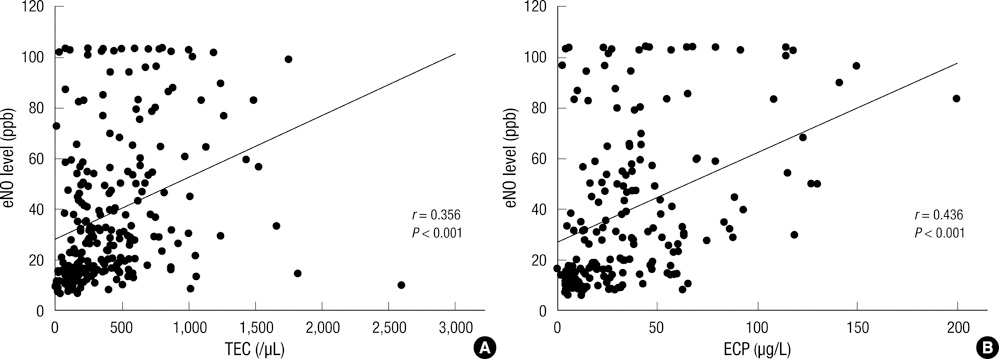
- Exhaled nitric oxide (eNO) has been proposed as a noninvasive marker of airway inflammation in asthma. In asthmatic patients, exhaled NO levels have been shown to relate with other markers of eosinophilic recruitment, which are detected in blood, sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and bronchial biopsy samples. The purpose of this study was to assess the possible relationship between eNO and allergic inflammation or sensitization in childhood asthma and allergic rhinitis. Subjects consisted of 118 asthmatic children, 79 patients with allergic rhinitis, and 74 controls. Their age ranged from 6 to 15 yr old. eNO level, peripheral blood eosinophil count, eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), serum total IgE level and specific IgE levels were measured. Methacholine challenge test and allergic skin prick test for common allergens were performed in all subjects. Atopic group (n = 206, 44.48 +/- 30.45 ppb) had higher eNO values than non-atopic group (n = 65, 20.54 +/- 16.57 ppb, P < 0.001). eNO level was significantly higher in patients with asthma (42.84 +/- 31.92 ppb) and in those with allergic rhinitis (43.59 +/- 29.84 ppb) than in healthy controls (27.01 +/- 21.34 ppb, P < 0.001) but there was no difference between asthma and allergic rhinitis group. eNO also had significant positive correlations with Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus IgE level (r = 0.348, P < 0.001), Dermatophagoides farinae IgE level (r = 0.376, P < 0.001), and the number of positive allergens in skin prick test (r = 0.329, P = 0.001). eNO had significant positive correlations with peripheral blood eosinophil count (r = 0.356, P < 0.001), serum total IgE level (r = 0.221, P < 0.001), and ECP (r = 0.436, P < 0.001). This study reveals that eNO level is associated with allergic inflammation and the degree of allergic sensitization.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Allergens/immunology
Animals
Asthma/*immunology
*Breath Tests
Bronchial Provocation Tests
Child
Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus/immunology
Eosinophil Cationic Protein/analysis/blood/immunology
Eosinophils
Exhalation
Female
Humans
Hypersensitivity, Immediate/*immunology
Immunoglobulin E/blood
Leukocyte Count
Male
Nitric Oxide/*analysis
Rhinitis, Allergic, Seasonal/*immunology
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Relationships between Fraction of Nitric Oxide, Airway Hyperresponsiveness, Blood Eoshinophil Counts and Serum Eosinophil Cationic Protein in Asthmatic Children
Hyeon Seok Seo, Bo Hyun Chung, Ha Neul Park, Sung Chul Seo, Bauer Siegfried, Dae Jin Song, Ji Tae Choung, Young Yoo
Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012;22(3):282-291. doi: 10.7581/pard.2012.22.3.282.Exhaled nitric oxide and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in atopic asthmatic children with and without allergic rhinitis
Junsung Park, Eun Lee, Song-I Yang, Jisun Yoon, Hyun-Ju Cho, Soo-Jong Hong, Jinho Yu
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(6):425-431. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.6.425.
Reference
-
1. Yunginger JW, Reed CE, O'Connell EJ, Melton LJ 3rd, O'Fallon WM, Silverstein MD. A community-based study of the epidemiology of asthma. Incidence rates, 1964-1983. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992. 146:888–894.2. Kay AB. The role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. Trends Mol Med. 2005. 11:148–152.3. Kim ES, Kim SH, Kim KW, Park JW, Kim YS, Sohn MH, Kim KE. Basement membrane thickening and clinical features of children with asthma. Allergy. 2007. 62:635–640.4. Baraldi E, Azzolin NM, Zanconato S, Dario C, Zacchello F. Corticosteroids decrease exhaled nitric oxide in children with acute asthma. J Pediatr. 1997. 131:381–385.5. Hamid Q, Springall DR, Riveros-Moreno V, Chanez P, Howarth P, Redington A, Bousquet J, Godard P, Holgate S, Polak JM. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in asthma. Lancet. 1993. 342:1510–1513.6. Cieslewicz G, Tomkinson A, Adler A, Duez C, Schwarze J, Takeda K, Larson KA, Lee JJ, Irvin CG, Gelfand EW. The late, but not early, asthmatic response is dependent on IL-5 and correlates with eosinophil infiltration. J Clin Invest. 1999. 104:301–308.7. Roberts G, Hurley C, Bush A, Lack G. Longitudinal study of grass pollen exposure, symptoms, and exhaled nitric oxide in childhood seasonal allergic asthma. Thorax. 2004. 59:752–756.8. de Kluijver J, Evertse CE, Schrumpf JA, van der Veen H, Zwinderman AH, Hiemstra PS, Rabe KF, Sterk PJ. Asymptomatic worsening of airway inflammation during low-dose allergen exposure in asthma: protection by inhaled steroids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 166:294–300.9. Kharitonov SA, Yates D, Robbins RA, Logan-Sinclair R, Shinebourne EA, Barnes PJ. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet. 1994. 343:133–135.10. Kharitonov SA, O'Connor BJ, Evans DJ, Barnes PJ. Allergen-induced late asthmatic reactions are associated with elevation of exhaled nitric oxide. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:1894–1899.11. Leung TF, Wong GW, Ko FW, Lam CW, Fok TF. Clinical and atopic parameters and airway inflammatory markers in childhood asthma: a factor analysis. Thorax. 2005. 60:822–826.12. American Thoracic Society. Medical Section of the American Lung Association. Guidelines for the evaluation of impairment/disability in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993. 147:1056–1061.13. American Thoracic Society. Medical Section of the American Lung Association. Recommendations for standardized procedures for the on-line and off-line measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in adults and children-1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 160:2104–2117.14. Brown WG, Halonen MJ, Kaltenborn WT, Barbee RA. The relationship of respiratory allergy, skin test reactivity, and serum IgE in a community population sample. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979. 63:328–335.15. Taylor DR, Pijnenburg MW, Smith AD, De Jongste JC. Exhaled nitric oxide measurements: clinical application and interpretation. Thorax. 2006. 61:817–827.16. Lex C, Ferreira F, Zacharasiewicz A, Nicholson AG, Haslam PL, Wilson NM, Hansel TT, Payne DN, Bush A. Airway eosinophilia in children with severe asthma: predictive values of noninvasive tests. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. 174:1286–1291.17. Payne DN, Adcock IM, Wilson NM, Oates T, Scallan M, Bush A. Relationship between exhaled nitric oxide and mucosal eosinophilic inflammation in children with difficult asthma, after treatment with oral prednisolone. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 164:1376–1381.18. Lemière C, Ernst P, Olivenstein R, Yamauchi Y, Govindaraju K, Ludwig MS, Martin JG, Hamid Q. Airway inflammation assessed by invasive and noninvasive means in severe asthma: eosinophilic and noneosinophilic phenotypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 118:1033–1039.19. Saito J, Inoue K, Sugawara A, Yoshikawa M, Watanabe K, Ishida T, Ohtsuka Y, Munakata M. Exhaled nitric oxide as a marker of airway inflammation for an epidemiologic study in schoolchildren. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 114:512–516.20. Franklin PJ, Turner SW, Le Souëf PN, Stick SM. Exhaled nitric oxide and asthma: complex interactions between atopy, airway responsiveness, and symptoms in a community population of children. Thorax. 2003. 58:1048–1052.21. Frank TL, Adisesh A, Pickering AC, Morrison JF, Wright T, Francis H, Fletcher A, Frank PI, Hannaford P. Relationship between exhaled nitric oxide and childhood asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:1032–1036.22. Persson MG, Zetterström O, Agrenius V, Ihre E, Gustafsson LE. Single-breath nitric oxide measurements in asthmatic patients and smokers. Lancet. 1994. 343:146–147.23. Massaro AF, Gaston B, Kita D, Fanta C, Stamler JS, Drazen JM. Expired nitric oxide levels during treatment of acute asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 152:800–803.24. Lee JH, Choi BS, Baek JY, Lee YJ, Kim KW, Sohn MH, Kim KE. Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide analysers in childhood asthma. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011. 21:17–23.25. Pavord ID, Shaw D. The use of exhaled nitric oxide in the management of asthma. J Asthma. 2008. 45:523–531.26. Travers J, Marsh S, Aldington S, Williams M, Shirtcliffe P, Pritchard A, Weatherall M, Beasley R. Reference ranges for exhaled nitric oxide derived from a random community survey of adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. 176:238–242.27. Hung CH, Hua YM, Hsu WT, Lai YS, Yang KD, Jong YJ, Chu YT. Montelukast decreased exhaled nitric oxide in children with perennial allergic rhinitis. Pediatr Int. 2007. 49:322–327.28. Togias A. Rhinitis and asthma: evidence for respiratory system integration. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:1171–1183.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurements of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in pediatric asthma
- Measurement and Interpretation of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide
- Exhaled NO: Determinants and Clinical Application in Children With Allergic Airway Disease
- Clinical application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in pediatric allergic rhinitis
- Nasal and Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Allergic Rhinitis