J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Sep;22(Suppl):S38-S46. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S38.
Inhibition of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Growth by Toxoplasma gondii through Induction of Th1 Immune Responses and Inhibition of Angiogenesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department Infection Biology, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. yhalee@cnu.ac.kr
- 3Department Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Research Institute for Medical Science, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1785787
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S38
Abstract
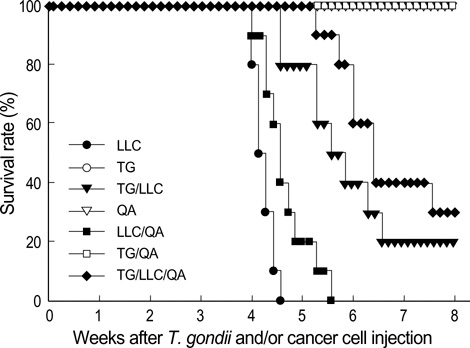
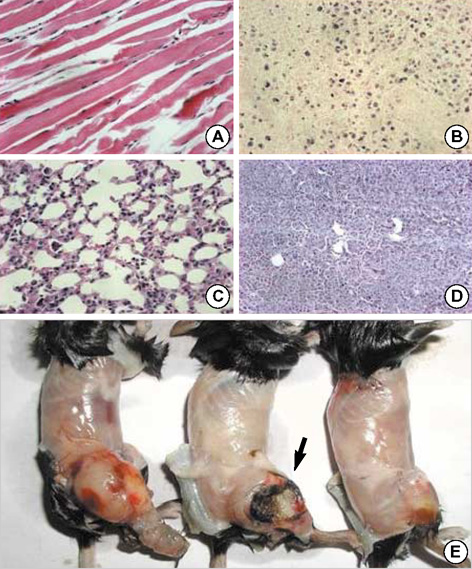
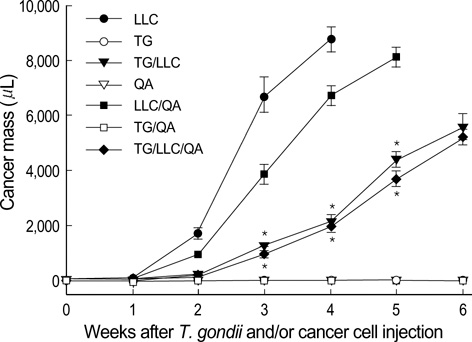
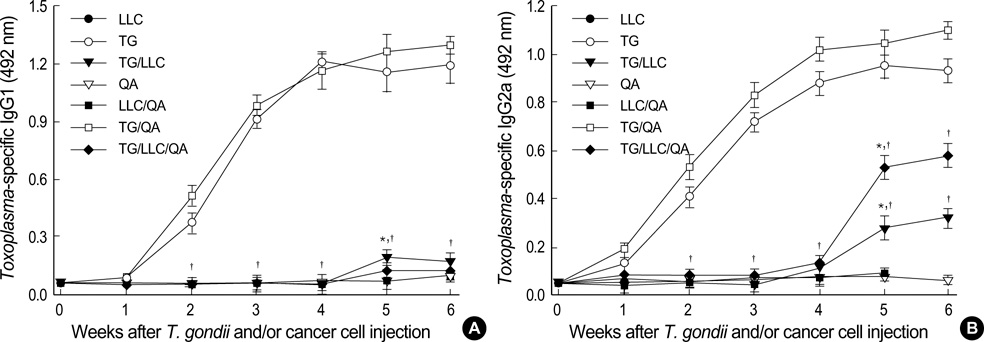
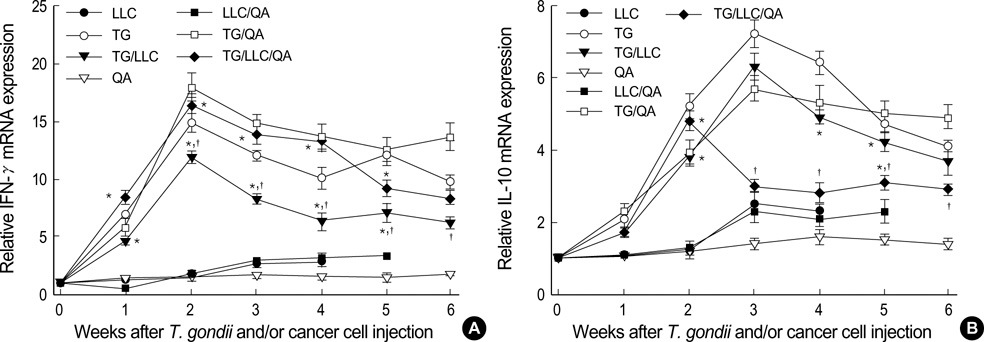
- Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite that induces antitumor activity against certain types of cancers. However, little information is available regarding the immunologic mechanisms that regulate these effects. For this purpose, C57BL/6 mice were administered either the T. gondii Me49 strain orally or Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells intramuscularly. Survival rates, tumor size, histopathology, and immune responses were determined for each group, and angiogenesis was evaluated by in vivo Matrigel plug assay. Toxoplasma-infected (TG-injected) mice survived the entire experimental period, whereas cancer cell-bearing (LLC-injected) mice died within six weeks. Mice injected with both T. gondii and cancer cells (TG/LLC-injected group) showed significantly increased survival rates, CD8+ T-cell percentages, IFN-gamma mRNA expression levels, serum IgG2a titers, and CTL responses as compared to the LLC-injected mice. In addition, angiogenesis in the TG/LLC-injected mice was notably inhibited. These effects in TG/LCC-injected mice were similar or were increased by the addition of an adjuvant, Quil-A. However, TG/LLC-injected mice showed decreased percentages of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, IFN-gamma mRNA expression levels, and serum IgG1 and IgG2a titers as compared to TG-injected mice. Taken together, our results demonstrate that T. gondii infection inhibits tumor growth in the Lewis lung carcinoma mouse model through the induction of Th1 immune responses and antiangiogenic activity.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Base Sequence
CD4-Positive T-Lymphocytes/immunology
CD8-Positive T-Lymphocytes/immunology
Carcinoma, Lewis Lung/blood supply/genetics/immunology/*therapy
Cell Line, Tumor
Cytotoxicity, Immunologic
DNA Primers/genetics
Female
Immunoglobulin G/blood
Immunotherapy/*methods
Interferon-gamma/genetics
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
Neovascularization, Pathologic
RNA, Messenger/genetics/metabolism
Th1 Cells/*immunology
Toxoplasma/*immunology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006. 56:106–130.
Article2. Collins LG, Haines C, Perkel R, Enck RE. Lung cancer: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2007. 75:56–63.3. Raez LE, Fein S, Podack ER. Lung cancer immunotherapy. Clin Med Res. 2005. 3:221–228.
Article4. Berzofsky JA, Terabe M, Oh S, Belyakov IM, Ahlers JD, Janik JE, Morris JC. Progress on new vaccine strategies for the immunotherapy and prevention of cancer. J Clin Invest. 2004. 113:1515–1525.
Article5. Blattman JN, Greenberg PD. Cancer immunotherapy: a treatment for the masses. Science. 2004. 305:200–205.
Article6. Petersen E. Toxoplasmosis. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007. 12:214–223.
Article7. Hibbs JB Jr, Lambert LH Jr, Remington JS. Resistance to murine tumors conferred by chronic infection with intracellular protozoa, Toxoplasma gondii and Besnoitia jellisoni. J Infect Dis. 1971. 124:587–592.
Article8. Miyahara K, Yokoo N, Sakurai H, Igarashi I, Sakata Y, Yoshida Y, Saito A, Hirose T, Suzuki N. Antitumor activity of Toxoplasma lysate antigen against methylcholanthrene-induced tumor-bearing rats. J Vet Med Sci. 1992. 54:221–228.
Article9. Varga A, Sokolowska-Kohler W, Presber W, Von Baehr V, Von Baehr R, Lucius R, Volk D, Nacsa J, Hever A. Toxoplasma infection and cell free extract of the parasites are able to reverse multidrug resistance of mouse lymphoma and human gastric cancer in vitro. Anticancer Res. 1999. 19:1317–1324.10. Suzuki Y, Kobayashi A. Antitumor effect of intralesional injection with formalin-fixed Toxoplasma gondii organisms on Lewis lung carcinoma in Toxoplasma-infected mice. Cancer Lett. 1985. 25:247–254.
Article11. Suzuki Y, Muto M, Kobayashi A. Antitumor effect of formalin-fixed Toxoplasma gondii organisms on EL4 lymphoma in Toxoplasma-infected mice. J Biol Response Mod. 1986. 5:288–293.12. Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Song GY, Li G, Lee JH, Lü J, Kim SH. 6-(1-Oxobutyl)-5,8-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone inhibits lewis lung cancer by antiangiogenesis and apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 2007. 120:2481–2490.
Article13. Lee EO, Lee HJ, Hwang HS, Ahn KS, Chae C, Kang KS, Lu J, Kim SH. Potent inhibition of Lewis lung cancer growth by heyneanol A from the roots of Vitis amurensis through apoptotic and anti-angiogenic activities. Carcinogenesis. 2006. 27:2059–2069.
Article14. Kimura Y, Kido T, Takaku T, Sumiyoshi M, Baba K. Isolation of an anti-angiogenic substance from Agaricus blazei Murill: its antitumor and antimetastatic actions. Cancer Sci. 2004. 95:758–764.
Article15. Lee YH, Kasper LH. Immune responses of different mouse strains after challenge with equivalent lethal doses of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasite. 2004. 11:89–97.16. Passaniti A, Taylor RM, Pili R, Guo Y, Long PV, Haney JA, Pauly RR, Grant DS, Martin GR. A simple, quantitative method for assessing angiogenesis and antiangiogenic agents using reconstituted basement membrane, heparin, and fibroblast growth factor. Lab Invest. 1992. 67:519–528.17. Tanaka M, Saijo Y, Sato G, Suzuki T, Tazawa R, Satoh K, Nukiwa T. Induction of antitumor immunity by combined immunogene therapy using IL-2 and IL-12 in low antigenic Lewis lung carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2000. 7:1481–1490.
Article18. Bertram JS, Janik P. Establishment of a cloned line of Lewis Lung Carcinoma cells adapted to cell culture. Cancer Lett. 1980. 11:63–73.
Article19. Denkers EY. T lymphocyte-dependent effector mechanisms of immunity to Toxoplasma gondii. Microbes Infect. 1999. 1:699–708.
Article20. Male DK, Brostoff J, Roth DB, Roitt I. Immunology. 2006. 7th ed. Canada: Mosby Elsevier.21. Sharma S, Stolina M, Luo J, Strieter RM, Burdick M, Zhu LX, Batra RK, Dubinett SM. Secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine mediates T cell-dependent antitumor responses in vivo. J Immunol. 2000. 164:4558–4563.
Article22. Dietrich A, Becherer L, Brinckmann U, Hauss J, Liebert UG, Gütz A, Aust G. Particle-mediated cytokine gene therapy leads to antitumor and antimetastatic effects in mouse carcinoma models. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2006. 21:333–341.
Article23. Komita H, Homma S, Saotome H, Zeniya M, Ohno T, Toda G. Interferon-gamma produced by interleukin-12-activated tumor infiltrating CD8+T cells directly induces apoptosis of mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2006. 45:662–672.
Article24. Choi Y, Jeon YH, Kang JH, Chung JK, Schmidt M, Kim AC. MIDGE/hNIS vaccination generates antigen-associated CD8+IFN-gamma+ T cells and enhances protective antitumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 2007. 120:1942–1950.25. Nguyen TD, Bigaignon G, Van Broeck J, Vercammen M, Nguyen TN, Delmee M, Turneer M, Wolf SF, Coutelier JP. Acute and chronic phases of Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice modulate the host immune responses. Infect Immun. 1998. 66:2991–2995.
Article26. Ramirez BS, Pestana ES, Hidalgo GG, Garcia TH, Rodriguez RP, Ullrich A, Fernandez LE. Active antimetastatic immunotherapy in Lewis lung carcinoma with self EGFR extracellular domain protein in VSSP adjuvant. Int J Cancer. 2006. 119:2190–2199.27. Lee YS, Yang HO, Shin KH, Choi HS, Jung SH, Kim YM, Oh DK, Linhardt RJ, Kim YS. Suppression of tumor growth by a new glycosaminoglycan isolated from the African giant snail Achatina fulica. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. 465:191–198.
Article28. Hunter CA, Yu D, Gee M, Ngo CV, Sevignani C, Goldschmidt M, Golovkina TV, Evans S, Lee WF, Thomas-Tikhonenko A. Cutting edge: systemic inhibition of angiogenesis underlies resistance to tumors during acute toxoplasmosis. J Immunol. 2001. 166:5878–5881.
Article29. Dumont AR, Kalfayan LH, Sekaly RP. Modulation of immune responses-strategies for optimising vaccines. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2004. 4:627–630.30. Behboudi S, Morein B, Villacres-Eriksson MC. Quillaja saponin formulations that stimulate proinflammatory cytokines elicit a potent acquired cell-mediated immunity. Scand J Immunol. 1999. 50:371–377.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antitumor and Antimetastatic Effects of Toxoplasma Gondii in Mice with Lewis Lung Carcinoma
- Cytokine and antibody responses of reactivated murine toxoplasmosis upon administration of dexamathasone
- Inhibition of entry of Toxoplasma gondii into MDCK cells by fetal bovine serum
- Gefitinib Inhibits the Growth of Toxoplasma gondii in HeLa Cells
- Evaluation of the anti-Toxoplasma gondii Activity of Hederagenin in vitro and in vivo