Korean J Radiol.
2005 Dec;6(4):267-277. 10.3348/kjr.2005.6.4.267.
Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Appendicitis: Evaluation by Meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine & Public Health, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. kimcb@wonju.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Institute for Health Services Research, Yonsei University, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Korea.
- 5Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Korea.
- 6Clinical Outcomes Research Center, University of Minnesota School of Public Health, USA.
- 7Transplant Information Services, University of Minnesota, USA.
- KMID: 1777285
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2005.6.4.267
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
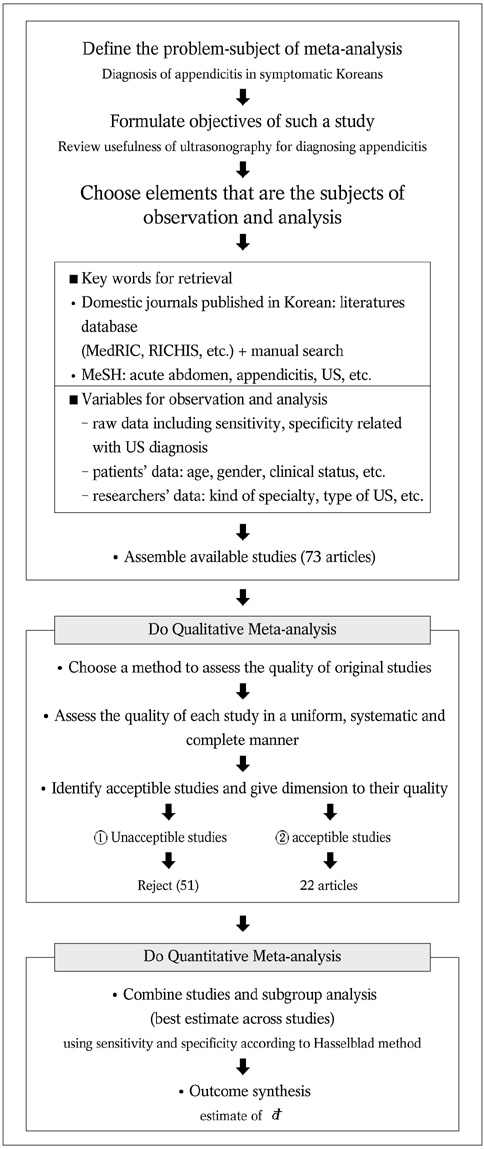
We wanted to review the usefulness of ultrasonography (US) for the diagnosis of appendicitis and to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of US according to patients' and researchers' characteristics. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The relevant Korean articles published between 1985 and 2003 were included in this study if the patients had clinical symptoms of acute appendicitis. The histopathologic findings were the reference standard and the data were presented for 2x2 tables. Articles were excluded if patients had no sonographic signs of appendicitis according to graded-compression US. Two reviewers independently extracted the data on study characteristics. The Hasselblad method was used to obtain the combined estimates of sensitivity and specificity for the performance of US. RESULTS: Twenty-two articles (2, 643 patients) fulfilled all inclusion criteria. The estimate of d calculated by combining the sensitivity and specificity was 2.0054 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.8553, 2.1554) by a random effects model. The overall sensitivity and specificity (95% CI) were 86.7% (85.4 to 88.0), and 90.0% (88.9 to 91.2), respectively. According to the subgroup meta-analysis by patients' characteristics, the d estimate (95% CI) of dominantly younger age, male, and highly clinical suggestive group for US was 2.2388 (1.8758 to 2.6019), 2.7131 (2.2493 to 3.1770), and 2.4582 (1.7387 to 3.1777), respectively. Also, according to subgroup meta-analysis by researchers' characteristics, the d value (95% CI) for US done by diagnostic radiologists and gray-scale was 2.0195 (1.7942 to 2.2447) and 2.2630 (1.8444 to 2.6815). CONCLUSION: This evidence suggests that US may be useful for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, especially when patients are younger age, male, and highly clinical suggestive.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Usefulness of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Peptic Ulcer Disease in Children
Eun Joo Lee, Yeoun Joo Lee, Jae Hong Park
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(1):57-62. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.1.57.
Reference
-
1. Deutsch A, Leopold GR. Ultrasonic demonstration of the inflamed appendix: Case report. Radiology. 1981. 140:163–164.2. Puylaert JBCM. Acute appendicitis: US evaluation using graded compression. Radiology. 1986. 158:355–360.3. Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Lewis FR. Acute appendicitis: High-resolution real-time US findings. Radiology. 1987. 163:11–14.4. Puylaert JB, Rutgers PH, Lalisang RI, de Vries BC, van der Werf SD, Dorr JP, et al. A prospective study of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of appendicitis. N Engl J Med. 1987. 317:666–669.5. Jeffrey RB Jr, Laing FC, Townsend RR. Acute appendicitis: Sonographic criteria based on 250 cases. Radiology. 1988. 167:327–329.6. Vignault F, Filiatrault D, Brandt ML, Garel L, Grignon A, Ouimet A. Acute appendicitis in children: Evaluation with US. Radiology. 1990. 176:501–504.7. Sivit CJ, Newman KD, Boenning DA, Nussbaum-Blask AR, Bulas DI, Bond SJ, et al. Appendicitis: Usefulness of US in diagnosis in a pediatric population. Radiology. 1992. 185:549–552.8. Crady SK, Jones JS, Wyn T, Luttenton CR. Clinical validity of ultrasound in children with suspected appendicitis. Ann Emerg Med. 1993. 22:1125–1129.9. Balthazar EJ, Birnbaum BA, Yee J, Megibow AJ, Roshkow J, Gray C. Acute appendicitis: CT and US correlation in 100 patients. Radiology. 1994. 190:31–35.10. Ramachandran P, Sivit CJ, Newman KD, Schwartz MZ. Ultrasonography as an adjunct in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis: A 4-year experience. J Pediatr Surg. 1996. 31:164–169.11. Puylaert JBCM, van der Zant FM, Rijke AM. Sonography and the acute abdomen: Practical considerations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 168:179–186.12. Birnbaum BA, Jeffrey RB Jr. CT and sonographic evaluation of acute right lower quadrant abdominal pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 170:361–371.13. Garcia Pena BM, Mandl KD, Kraus SJ, Fischer AC, Fleisher GR, Lund DP, et al. Ultrasonography and limited computed tomography in the diagnosis and management of appendicitis in children. JAMA. 1999. 282:1041–1046.14. Birnbaum BA, Wilson SR. Appendicitis at the millennium. Radiology. 2000. 215:337–348.15. Baldisserotto M, Marchiori E. Accuracy of noncompressive sonography of children with appendicitis according to the potential positions of the appendix. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 175:1387–1392.16. Jones PF. Suspected acute appendicitis: Trends in management over 30 years. Br J Surg. 2001. 88:1570–1577.17. Pena BM, Taylor GA, Fishman SJ, Mandl KD. Effect of an imaging protocol on clinical outcomes among pediatric patients with appendicitis. Pediatrics. 2002. 110:1088–1093.18. Rettenbacher T, Hollerweger A, Gritzmann N, Gotwald T, Schwamberger K, Ulmer H, et al. Appendicitis: Should diagnostic imaging be performed if the clinical presentation is highly suggestive of the disease? Gastroenterology. 2002. 123:992–998.19. Blebea JS, Meilstrup JW, Wise SW. Appendiceal imaging: Which test is best? Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2003. 24:91–95.20. Lee SL, Ho HS. Ultrasonography and computed tomography in suspected acute appendicitis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2003. 24:69–73.21. Sivit CJ. Imaging the child with right lower quadrant pain and suspected appendicitis: Current concepts. Pediatr Radiol. 2004. 34:447–453.22. Taylor GA. Suspected appendicitis in children: In search of the single best diagnostic test. Radiology. 2004. 231:293–295.23. Ziegler MM. The diagnosis of appendicitis: An evolving paradigm. Pediatrics. 2004. 113:130–132.24. Hernandez JA, Swischuk LE, Angel CA, Chung D, Chandler R, Lee S. Imaging of acute appendicitis: US as the primary imaging modality. Pediatr Radiol. 2005. 35:392–395.25. Wade DS, Marrow SE, Balsara ZN, Burkhard TK, Goff WB. Accuracy of ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis compared with the surgeon's clinical impression. Arch Surg. 1993. 128:1039–1046.26. Bendeck SE, Nino-Murcia M, Berry GJ, Jeffrey RB Jr. Imaging for suspected appendicitis: Negative appendectomy and perforation rates. Radiology. 2002. 225:131–136.27. McCallion J, Canning JP, Knight PV, McCallion JS. Acute appendicitis in the elderly: A 5-year retrospective study. Age Ageing. 1987. 16:256–260.28. Sivit CJ. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children: spectrum of sonographic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993. 161:147–152.29. Lim HK, Lee WJ, Lee SJ, Namgung S, Lim JH. Focal appendicitis confined to the tip: Diagnosis at US. Radiology. 1996. 200:799–801.30. Hormann M, Scharitzer M, Stadler A, Pokieser P, Puig S, Helbich T. Ultrasound of the appendix in children: Is the child too obese? Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:1428–1431.31. Guyatt GH, Tugwell PX, Feeny DH, Haynes RB, Drummond M. A framework for clinical evaluation of diagnostic technologies. CMAJ. 1986. 134:587–594.32. Irwig L, Tosteson AN, Gatsonis C, Lau J, Colditz G, Chalmers TC, et al. Guidelines for meta-analyses evaluating diagnostic tests. Ann Intern Med. 1994. 120:667–676.33. Orr RK, Porter D, Hartman D. Ultrasonography to evaluate adults for appendicitis: decision making based on meta-analysis and probabilistic reasoning. Acad Emerg Med. 1995. 2:644–650.34. Hallan S, Asberg A. The accuracy of C-reactive protein in diagnosing acute appendicitis-a meta-analysis-. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1997. 57:373–380.35. Obermaier R, Benz S, Asgharnia M, Kirchner R, Hopt UT. Value of ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis: Interesting aspects. Eur J Med Res. 2003. 8:451–456.36. Andersson REB. Meta-analysis of the clinical and laboratory diagnosis of appendicitis. Br J Surg. 2004. 91:28–37.37. Terasawa T, Blackmore CC, Bent S, Kohlwes RJ. Systematic review: Computed tomography and ultrasonography to detect acute appendicitis in adults and adolescents. Ann Intern Med. 2004. 141:537–546.38. Jenicek M, Feinstein AR. Epidemiology: The logic of modern medicine (IX. Meta-analysis in Medicine: Putting experiences together). 1995. 1st ed. Montreal EPIMED;269–295.39. Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH. Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997. 127:820–826.40. Bachmann LM, Bischof DB, Bischofberger SA, Bonani MG, Osann FM, Steurer J. Systematic quantitative overviews of the literature to determine the value of diagnostic tests for predicting acute appendicitis: Study protocol. BMC Surgery. 2002. 2:2.41. Middleton WD, Kurtz AB, Hertzberg BS. Ultrasound: The Requisites. 2004. 2nd ed. Mosby (An Affiliate of Elsevier Inc.);224–225.42. Quillin SP, Siegel MJ. Appendicitis in children: Color Doppler sonography. Radiology. 1992. 184:745–747.43. Hasselblad V, Hedges L. Meta-analysis of diagnostic and screening tests. Psychol Bull. 1995. 117:167–177.44. Song HH. Meta-analysis. 1998. 1st ed. Seoul: Chungmoonkak Press;55–57. 83–87.45. Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. A consumer's guide to subgroup analyses. Ann Intern Med. 1992. 116:78–84.46. Sackett DL, Haynes RB, Guyatt GH, Tugwell P. Clinical Epidemiology: A Basic Science for Clinical Medicine. 1991. 2nd ed. Boston/Toronto/London: Little, Brown and Company;119–139.47. Zielke A, Hasse C, Sitter H, Kisker O, Rothmund M. "Surgical" ultrasound in suspected acute appendicitis. Surg Endosc. 1997. 11:362–365.48. Allemann F, Cassina P, Rothlin M, Largiader F. Ultrasound scans done by surgeons for patients with acute abdominal pain: A prospective study. Eur J Surg. 1999. 165:966–970.49. Chen SC, Wang HP, Hsu HY, Huang PM, Lin FY. Accuracy of ED sonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Am J Emerg Med. 2000. 18:449–452.50. Emil S, Mikhail P, Laberge JM, Flageole H, Nguyen LT, Shaw KS, et al. Clinical versus sonographic evaluation of acute appendicitis in children: a comparison of patient characteristics and outcomes. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. 36:780–783.51. Kim SJ, Park CK, Yu SK, Park SH, Kim CY, Bahk YW, et al. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis using ultrasonograpy. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1987. 23:608–613.52. Suh HS, Chung MH, Kim KT. Ultrasonography for the acute appendicitis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1987. 23:998–1007.53. Lee JD, Lee JT, Cho JW, Yang JY. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis by ultrasonography. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1987. 6:158–167.54. Lee SH, Chang YD, Kim DH, Lee HK, Kwon KH, Kim KJ. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of acute appendicitis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1988. 24:306–311.55. Moon MJ, Lee HR, Oh EO. Ultrasonographic findings of acute appendicitis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1989. 25:273–280.56. Rhee JK, Park JC, Lim CY, Chae KM, Kim CG. Diagnostic significance of ultrasonography in appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1989. 37:93–96.57. Lim HK, Lee KW, Choo IW, Bae SH. A prospective study of ultrasonographic diagnosis of acute appendicitis. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1990. 9:31–36.58. Suh KH, Jung ID. Diagnostic significance of ultrasonography in acute appendicitis. J Pusan Surg Soc. 1992. 8:58–65.59. Sohn SH, Jung KS, Kim JS, Woo SK, Chung KY, Kim HJ. Value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1993. 29:249–254.60. Ko KH, Hwang JY, Song CH. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis using ultrasonography. J Korean Surg Soc. 1995. 49:398–401.61. Lee MK, Im CS, Ann SM, Kim CH, Lee DJ, Kwon JH. Ultrasonography for diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1996. 39:497–502.62. Lee HK, Ahn SI, Yang DH. The diagnostic value of ultrasonographic evaluation in acute appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1996. 50:574–582.63. Bae KH, Choi SY, Kim CS, Han HY, Song BJ, Park SH. Diagnostic accuracy and value of a preoperative ultrasonographic evaluation in acute appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1997. 53:1023–1030.64. Lee JC, Kim HS, Song KY, Yi JG, Park JH, Lee YJ, et al. Value of color doppler sonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1997. 16:141–146.65. Oh BY, Lim KS, Lee YJ, Kim W, Choi OK. Early diagnosis of acute appendicitis by use of ultrasonography in emergency department. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 1998. 9:586–594.66. Oh CH, Sung CK, Kim KH. Diagnostic efficacy of diagnostic scoring system and ultrasonographic examination in acute appendicitis: Retrospective and prospective study. J Korean Surg Soc. 1999. 57:72–80.67. Lee SC. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis: Comparison between gray scale, color doppler and power doppler US. Med J Red Cross Hospital. 1999. 26:255–261.68. Lee JM, Lee MS, Han HY, Yoon YG, Ym SH. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis in the community hospital: Validity and usefulness of sonography. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1999. 40:275–280.69. Lee SW, Lee JK, Baek SY, Kang BC, Lee SW. The diagnostic role of US in patients with right lower quadrant abdominal pain. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2000. 43:729–733.70. Chung HH, Kim YH, Kim HW, Park SC, Lee EJ, Chung KB, et al. Sonographic study about differential diagnosis between acute appendicitis and non-appendicitis in appendices of borderline diameter. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 2000. 19:257–263.71. Sim WS, Sim MS. Abdominal sonography of suspected appendicitis. J Korean Soc Coloproctology. 2001. 17:59–63.72. Lee JH, Choi PC, Shim MS, Song KJ, Jeong YK. Comparison of computer tomography and sonography in patients suspected of having appendicitis. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2001. 12:290–297.73. Kim SH. Realtime ultrasonography of acute appendicitis. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1985. 4:69–74.74. Kessler N, Cyteval C, Gallix B, Lesnik A, Blayac PM, Pujol J, et al. Appendicitis: Evaluation of sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of US, Doppler US, and laboratory findings. Radiology. 2004. 230:472–478.75. Rothrock SG, Skeoch G, Rush JJ, Johnson NE. Clinical features of misdiagnosed appendicitis in children. Ann Emerg Med. 1991. 20:45–50.76. Reynolds SL. Missed appendicitis in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1993. 9:1–3.77. Rothrock SG, Green SM, Dobson M, Colucciello SA, Simmons CM. Misdiagnosis of appendicitis in nonpregnant women of childbearing age. J Emerg Med. 1995. 13:1–8.78. Flum DR, Morris A, Koepsell T, Dellinger EP. Has misdiagnosis of appendicitis decreased over time? A population-based analysis. JAMA. 2001. 286:1748–1175.79. Flum DR, Koepsell T. The clinical and economic correlates of misdiagnosed appendicitis: Nationwide analysis. Arch Surg. 2002. 137:799–804.80. Schwartz SI, Shires GT, Spencer FC, Daly JM, Fischer JE, Galloway AC. Principles of Surgery. 1994. Vol. 2:7th ed (International ed.). McGraw-Hill Health Professions Division;1389–1391.81. Deeks JJ. Systematic reviews in health care: Systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening tests. BMJ. 2001. 323:157–162.82. Begg CB, Greenes RA. Assessment of diagnostic tests when disease verification is subject to selection bias. Biometrics. 1983. 39:207–215.83. Cochrane Methods Group on Systematic Review of Screening and Diagnostic Tests: Recommended Methods. Updated 1996. on 2002. Available at http://www.cochrane.org/cochrane/sadtdoc1.htm.84. National Health and Medical Research Council. How to Review the Evidence: Systemic Identification and Review of the Scientific Literature. 2000. Canberra: National Health and Medical Research Council.85. Kim YK, Lim HK, Bae SH, Oh YJ, Lee KW, Choo IW. Ultrasonographic findings in perforated appendicitis. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1990. 9:117–121.86. Lim CS, Lee KH, Lim HK, Seo GS, Bae SH. Detection of appendicoliths in patients with acute appendicitis: Comparative study with US and plain radiography. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1992. 11:123–129.87. Jeong HS, Kim KR, Oh ST, Kim KK. Ultrasonographic diagnosis in acute appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1992. 42:114–119.88. Kim CM, Kim SH, Huh SK. Ultrasonographic features of acute appendicitis: Comparison of the simple appendicitis and perforated appendicitis. J Maryknoll General Hospital. 1995. 5:153–158.89. Kim HS, Park JB, Yang HJ, Hwang SY, Park CW, Lee K. A clinical review of appendicitis and clinical validity of ultrasonography. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 1995. 6:371–380.90. Kim SH, Cha SH, Lee ES, Moon HY, Koo BH, Kim SM. Water-filled appendiceal sonography: New diagnostic modality for ambiguous appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1995. 48:867–872.91. An JH, Lee YH, Kim TH, Jung JJ, Yu PM, Choi YH, et al. Role of ultrasonography in acute abdomen. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 1996. 15:209–214.92. Bae JG, Lee YS, Jung YH, Kim JH, Lee WK, Lee TH. The US findings of acute nonperforated and perforated appendicitis in children. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1996. 34:671–674.93. Lee KS, Cho YU, Kim KR. The effect of combination of ultrasonography and a scoring system in the diagnosis of appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 1996. 51:714–721.94. Chung HH, Kim YH, Kim HW, Part SC, Lee EJ, Chung KB, et al. Sonographic study about differential diagnosis between acute appendicitis and non-appendicitis in appendices of borderline diameter. J Korean Soc Med Ultrasound. 2000. 19:257–264.95. Egger M, Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997. 315:629–634.96. Mulherin SA, Miller WC. Spectrum bias or spectrum effect? Subgroup variation in diagnostic test evaluation. Ann Intern Med. 2002. 137:598–560.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasonography of Appendicitis
- Ultrasonography Versus MRI for Diagnosing Acute Appendicitis During Pregnancy
- Value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
- A Case of Stump Appendicitis after Appendectomy
- Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis: Comparison between Gray Scale, Color Doppler and Power Doppler US