Korean J Gastroenterol.
2010 May;55(5):340-343. 10.4166/kjg.2010.55.5.340.
Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Combination Chemotherapy of Oxaliplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Sun General Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. cnu4169@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1718341
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2010.55.5.340
Abstract
- Oxaliplatin with 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin (FOLFOX) has become the standard treatment in patients with colorectal cancer. Among known toxicities induced by oxaliplatin, hematological, gastrointestinal and neurological toxicities are common. However, acute pulmonary toxicity associated with oxaliplatin is unusual. One case of interstitial lung disease associated with the FOLFOX protocol is reported here.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Antineoplastic Agents/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Antineoplastic Combined Chemotherapy Protocols
Colorectal Neoplasms/drug therapy
Fluorouracil/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Humans
Leucovorin/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Lung Diseases, Interstitial/chemically induced/*etiology/radiography
Male
Organoplatinum Compounds/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
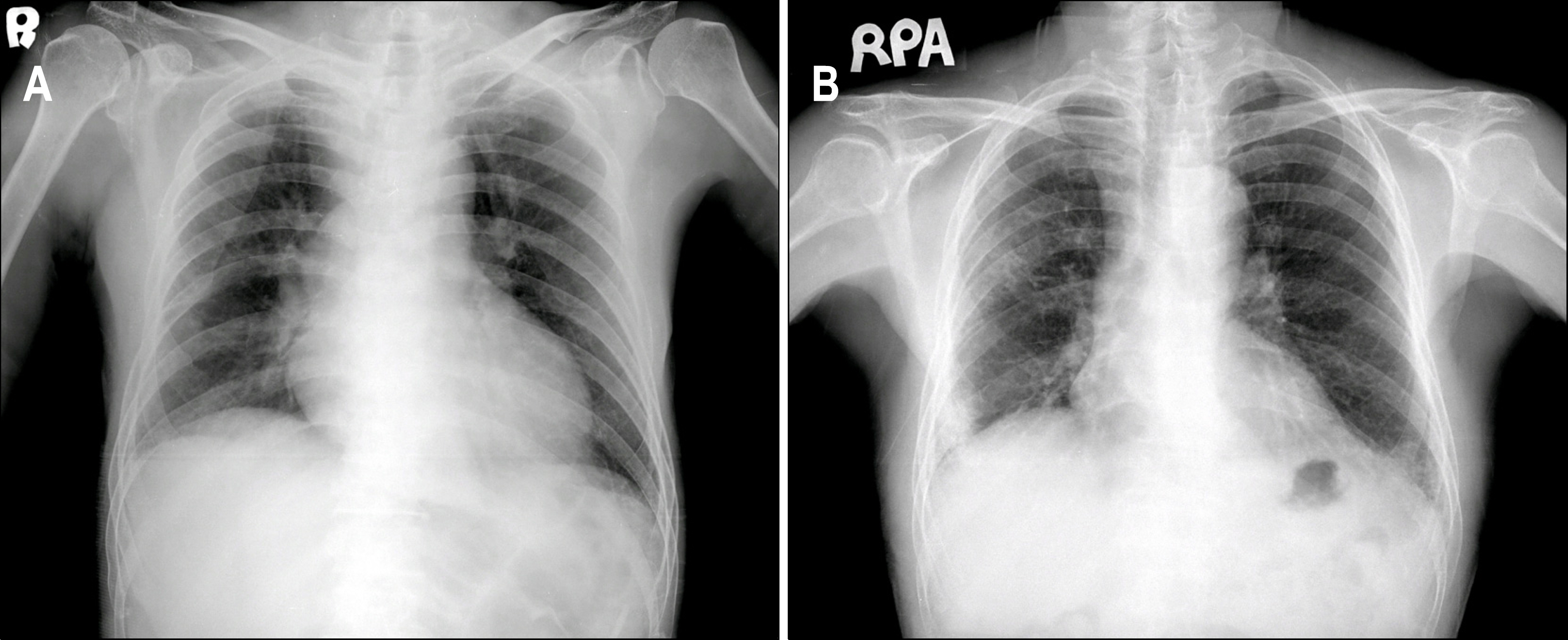
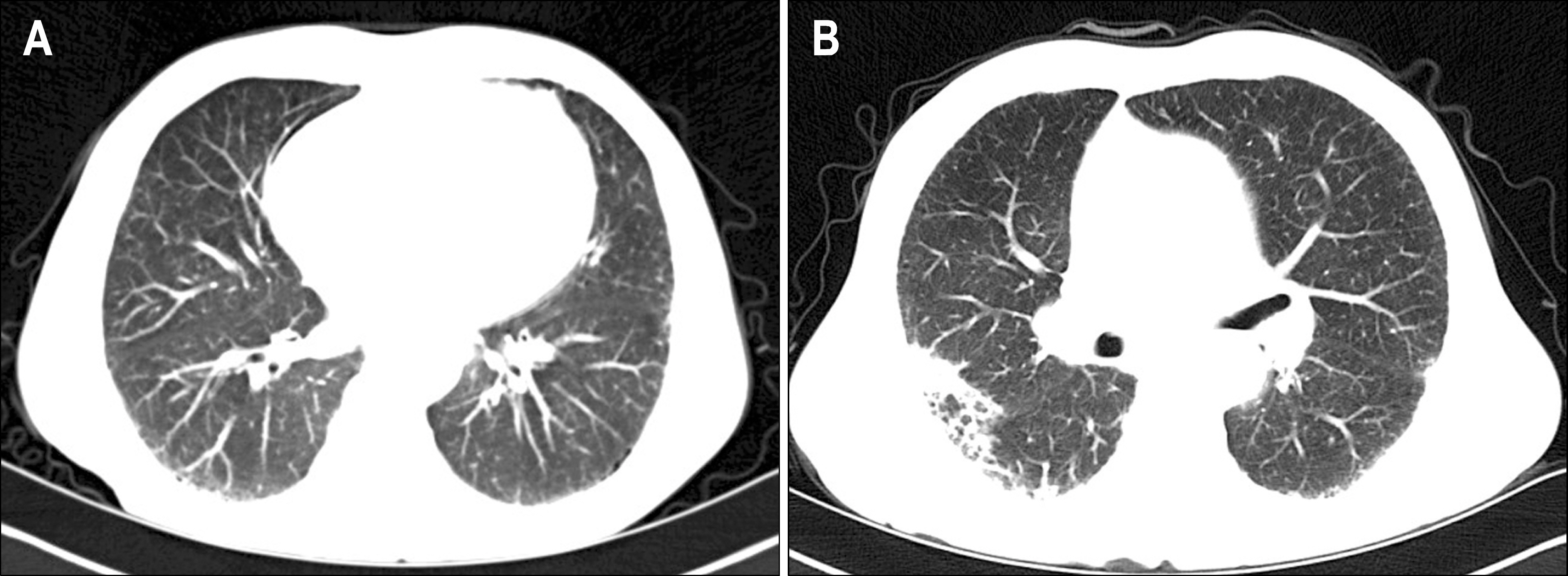
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, et al. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:23–30.
Article2. André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2343–2351.
Article3. Hausheer FH, Schilsky RL, Bain S, Berghorn EJ, Lieberman F. Diagnosis, management and evaluation of chemotherapy- induced peripheral neuropathy. Semin Oncol. 2006; 33:15–49.4. Jung KH, Kil SY, Choi IK, et al. Interstitial lung diseases in patients treated with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (FOLFOX). Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006; 10:1181–1182.5. Ruiz-Casado A, Garcí a MD, Racionero MA. Pulmonary toxicity of 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin. Clin Transl Oncol. 2006; 8:624.6. Pasetto LM, Monfardini S. Is acute dyspnea related to oxaliplatin administration? World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:5907–5908.
Article7. Gagnadoux F, Roiron C, Carrie E, Monnier-Cholley L, Lebeau B. Eosinophilic lung disease under chemotherapy with oxaliplatin for colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002; 25:388–390.
Article8. Trisolini R, Lazzeri Agli L, Tassinari D, et al. Acute lung injury associated with 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatinum combined chemotherapy. Eur Respir J. 2001; 18:243–245.9. Raymond E, Faivre S, Chaney S, Woynarowski J, Cvitkovic E. Cellular and molecular pharmacology of oxaliplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002; 1:227–235.10. Ramanathan RK, Clark JW, Kemeny NE, et al. Safety and toxicity analysis of oxaliplatin combined with fluorouracil or as a single agent in patients with previously treated advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 15:2904–2911.
Article11. Yague XH, Soy E, Merino BQ, Puig J, Fabregat MB, Colo-mer R. Interstitial pneumonitis after oxaliplatin treatment in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2005; 7:515–517.12. Rubbia-Brandt L, Audard V, Sartoretti P, et al. Severe hepatic sinusoidal obstruction associated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:460–466.
Article13. Kinnula VL, Vuorinen K, Ilumets H, Rytilä P, Myllä rniemi M. Thiol proteins, redox modulation and parenchymal lung disease. Curr Med Chem. 2007; 14:213–222.
Article14. Demedts M, Costabel U. ATS/ERS international multidis-ciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur Respir J. 2002; 19:794–796.
Article15. Wells AU. High-resolution computed tomography in the diagnosis of diffuse lung disease: a clinical perspective. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2003; 24:347–356.16. Ryu JH, Daniels CE, Hartman TE, Yi ES. Diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007; 82:976–986.
Article17. Akira M, Kozuka T, Yamamoto S, Sakatani M. Computed tomography findings in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 178:372–378.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diffuse alveolar damage during chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin
- Multiple Cancers in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis and Aggravated Interstitial Lung Disease by Chemotherapy
- Pulmonary Fibrosis Under Chemotherapy with Oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and Leucovorin
- Leucovorin-induced Hypersensitivity Reaction in a Patient with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated with Cetuximab Plus FOLFOX Chemotherapy: A Case Report
- A case of eosinophilic pneumonia under chemotherapy with the combination of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin for colon cancer