Immune Netw.
2009 Oct;9(5):153-157. 10.4110/in.2009.9.5.153.
Inhibition of Leukocyte Adhesion by Developmental Endothelial Locus-1 (Del-1)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Experimental Immunology Branch, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. choieun@mail.nih.gov
- KMID: 1474576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2009.9.5.153
Abstract
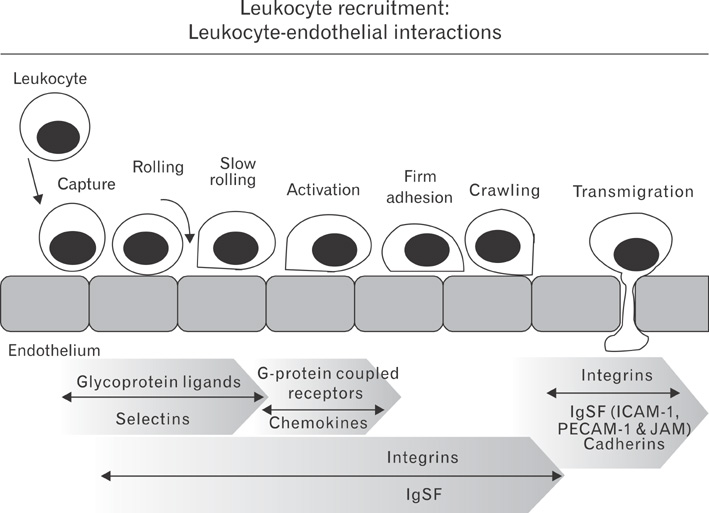
- The leukocyte adhesion to endothelium is pivotal in leukocyte recruitment which takes place during inflammatory, autoimmune and infectious conditions. The interaction between leukocytes and endothelium requires an array of adhesion molecules expressed on leukocytes and endothelial cells, thereby promoting leukocyte recruitment into sites of inflammation and tissue injury. Intervention with the adhesion molecules provides a platform for development of anti-inflammatory therapeutics. This review will focus on developmental endothelial locus-1 (Del-1), an endogenous inhibitor of leukocyte adhesion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. von Andrian UH, Mackay CR. T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N Engl J Med. 2000. 343:1020–1034.
Article2. Luster AD, Alon R, von Andrian UH. Immune cell migration in inflammation: present and future therapeutic targets. Nat Immunol. 2005. 6:1182–1190.
Article3. Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. 7:678–689.
Article4. Zarbock A, Ley K. New insights into leukocyte recruitment by intravital microscopy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. 334:129–152.
Article5. McEver RP, Cummings RD. Perspectives series; cell adhesion in vascular biology. Role of PSGL-1 binding to selectins in leukocyte recruitment. J Clin Invest. 1997. 100:485–491.
Article6. Alon R, Feizi T, Yuen CT, Fuhlbrigge RC, Springer TA. Glycolipid ligands for selectins support leukocyte tethering and rolling under physiologic flow conditions. J Immunol. 1995. 154:5356–5366.7. Berlin C, Bargatze RF, Campbell JJ, von Andrian UH, Szabo MC, Hasslen SR, Nelson RD, Berg EL, Erlandsen SL, Butcher EC. Alpha 4 integrins mediate lymphocyte attachment and rolling under physiologic flow. Cell. 1995. 80:413–422.
Article8. Sigal A, Bleijs DA, Grabovsky V, van Vliet SJ, Dwir O, Figdor CG, van Kooyk Y, Alon R. The LFA-1 integrin supports rolling adhesions on ICAM-1 under physiological shear flow in a permissive cellular environment. J Immunol. 2000. 165:442–452.
Article9. Marshall BT, Long M, Piper JW, Yago T, McEver RP, Zhu C. Direct observation of catch bonds involving cell-adhesion molecules. Nature. 2003. 423:190–193.
Article10. Adams DH, Lloyd AR. Chemokines: leucocyte recruitment and activation cytokines. Lancet. 1997. 349:490–495.
Article11. Campbell JJ, Qin S, Bacon KB, Mackay CR, Butcher EC. Biology of chemokine and classical chemoattractant receptors: differential requirements for adhesion-triggering versus chemotactic responses in lymphoid cells. J Cell Biol. 1996. 134:255–266.
Article12. Johnson Z, Proudfoot AE, Handel TM. Interaction of chemokines and glycosaminoglycans: a new twist in the regulation of chemokine function with opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005. 16:625–636.
Article13. Campbell JJ, Hedrick J, Zlotnik A, Siani MA, Thompson DA, Butcher EC. Chemokines and the arrest of lymphocytes rolling under flow conditions. Science. 1998. 279:381–384.
Article14. Tanaka Y, Adams DH, Shaw S. Regulation of leukocyte recruitment by proadhesive cytokines immobilized on endothelial proteoglycan. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1993. 184:99–106.
Article15. Dunne JL, Ballantyne CM, Beaudet AL, Ley K. Control of leukocyte rolling velocity in TNF-alpha-induced inflammation by LFA-1 and Mac-1. Blood. 2002. 99:336–341.
Article16. Phillipson M, Heit B, Colarusso P, Liu L, Ballantyne CM, Kubes P. Intraluminal crawling of neutrophils to emigration sites; a molecularly distinct process from adhesion in the recruitment cascade. J Exp Med. 2006. 203:2569–2575.
Article17. Schenkel AR, Mamdouh Z, Muller WA. Locomotion of monocytes on endothelium is a critical step during extravasation. Nat Immunol. 2004. 5:393–400.
Article18. Barreiro O, Yanez-Mo M, Serrador JM, Montoya MC, Vicente-Manzanares M, Tejedor R, Furthmayr H, Sanchez-Madrid F. Dynamic interaction of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 with moesin and ezrin in a novel endothelial docking structure for adherent leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 2002. 157:1233–1245.
Article19. Carman CV, Springer TA. A transmigratory cup in leukocyte diapedesis both through individual vascular endothelial cells and between them. J Cell Biol. 2004. 167:377–388.
Article20. Huang AJ, Manning JE, Bandak TM, Ratau MC, Hanser KR, Silverstein SC. Endothelial cell cytosolic free calcium regulates neutrophil migration across monolayers of endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1993. 120:1371–1380.
Article21. Millan J, Ridley AJ. Rho GTPases and leucocyte-induced endothelial remodelling. Biochem J. 2005. 385:329–337.
Article22. Wee H, Oh HM, Jo JH, Jun CD. ICAM-1/LFA-1 interaction contributes to the induction of endothelial cell-cell separation; implication for enhanced leukocyte diapedesis. Exp Mol Med. 2009. 41:341–348.
Article23. Wittchen ES. Endothelial signaling in paracellular and transcellular leukocyte transmigration. Front Biosci. 2009. 14:2522–2545.
Article24. Lou O, Alcaide P, Luscinskas FW, Muller WA. CD99 is a key mediator of the transendothelial migration of neutrophils. J Immunol. 2007. 178:1136–1143.
Article25. Bixel MG, Petri B, Khandoga AG, Khandoga A, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Wolburg H, März S, Krombach F, Vestweber D. A CD99-related antigen on endothelial cells mediates neutrophil but not lymphocyte extravasation in vivo. Blood. 2007. 109:5327–5336.
Article26. Wakelin MW, Sanz MJ, Dewar A, Albelda SM, Larkin SW, Boughton-Smith N, Williams TJ, Nourshargh S. An anti-platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 antibody inhibits leukocyte extravasation from mesenteric microvessels in vivo by blocking the passage through the basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1996. 184:229–239.
Article27. Schenkel AR, Mamdouh Z, Chen X, Liebman RM, Muller WA. CD99 plays a major role in the migration of monocytes through endothelial junctions. Nat Immunol. 2002. 3:143–150.
Article28. Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Imhof BA, Dejana E, Engelhardt B, Nourshargh S. Endothelial cell activation leads to neutrophil transmigration as supported by the sequential roles of ICAM-2, JAM-A, and PECAM-1. Blood. 2009. 113:6246–6257.
Article29. Garrido-Urbani S, Bradfield PF, Lee BP, Imhof BA. Vascular and epithelial junctions: a barrier for leucocyte migration. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. 36:203–211.
Article30. Pfeiffer F, Kumar V, Butz S, Vestweber D, Imhof BA, Stein JV, Engelhardt B. Distinct molecular composition of blood and lymphatic vascular endothelial cell junctions establishes specific functional barriers within the peripheral lymph node. Eur J Immunol. 2008. 38:2142–2155.
Article31. Wegmann F, Petri B, Khandoga AG, Moser C, Khandoga A, Volkery S, Li H, Nasdala I, Brandau O, Fässler R, Butz S, Krombach F, Vestweber D. ESAM supports neutrophil extravasation, activation of Rho, and VEGF-induced vascular permeability. J Exp Med. 2006. 203:1671–1677.
Article32. Butcher EC, Picker LJ. Lymphocyte homing and homeostasis. Science. 1996. 272:60–66.
Article33. Lalor PF, Adams DH. The liver: a model of organ-specific lymphocyte recruitment. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2002. 4:1–16.
Article34. Robert C, Kupper TS. Inflammatory skin diseases, T cells, and immune surveillance. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1817–1828.
Article35. Shetty S, Lalor PF, Adams DH. Lymphocyte recruitment to the liver: molecular insights into the pathogenesis of liver injury and hepatitis. Toxicology. 2008. 254:136–146.
Article36. Lee WY, Kubes P. Leukocyte adhesion in the liver: distinct adhesion paradigm from other organs. J Hepatol. 2008. 48:504–512.
Article37. Wong J, Johnston B, Lee SS, Bullard DC, Smith CW, Beaudet AL, Kubes P. A minimal role for selectins in the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed liver microvasculature. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:2782–2790.
Article38. Choi EY, Chavakis E, Czabanka MA, Langer HF, Fraemohs L, Economopoulou M, Kundu RK, Orlandi A, Zheng YY, Prieto DA, Ballantyne CM, Constant SL, Aird WC, Papayannopoulou T, Gahmberg CG, Udey MC, Vajkoczy P, Quertermous T, Dimmeler S, Weber C, Chavakis T. Del-1, an endogenous leukocyte-endothelial adhesion inhibitor, limits inflammatory cell recruitment. Science. 2008. 322:1101–1104.
Article39. Hidai C, Kawana M, Kitano H, Kokubun S. Discoidin domain of Del1 protein contributes to its deposition in the extracellular matrix. Cell Tissue Res. 2007. 330:83–95.
Article40. Hidai C, Zupancic T, Penta K, Mikhail A, Kawana M, Quertermous EE, Aoka Y, Fukagawa M, Matsui Y, Platika D, Auerbach R, Hogan BL, Snodgrass R, Quertermous T. Cloning and characterization of developmental endothelial locus-1: an embryonic endothelial cell protein that binds the alphavbeta3 integrin receptor. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:21–33.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resveratrol blunts tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced monocyte adhesion and transmigration
- Allicin Reduces Adhesion Molecules and NO Production Induced by gamma irradiation in Human Endothelial Cells
- Leukocyte-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Induced by Ischemia and Reperfusion Observed with in vivo Videomicroscopy
- ICAM-1/LFA-1 interaction contributes to the induction of endothelial cell-cell separation: implication for enhanced leukocyte diapedesis
- Effect of VCAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells by proinflammatory cytokines