Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2009 Mar;2(1):13-19. 10.3342/ceo.2009.2.1.13.
Galectin-8 Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea. chosi@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1466555
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2009.2.1.13
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Despite the ongoing development of treatment protocols for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), the patients suffering with this malady have shown only a modestly improved outcome. This poor outcome has been attributed to the lack of therapy that's individualized to the tumor's biological properties. Various studies have showed that galectin-8 is widely expressed in tumor tissues as well as in normal tissues, and the level of the galectin-8 expression may correlate with the malignancy of human squamous cell carcinoma. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the expression of galectin-8 and to investigate its correlations with the primary stage, the nodal involvement, the clinical stage and the histologic grade of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx.
METHODS
The paraffin-embedded tissue specimens from 77 patients who were diagnosed as LSCC between 1993 and 2007 were immunohistochemically stained for galectin-8.
RESULTS
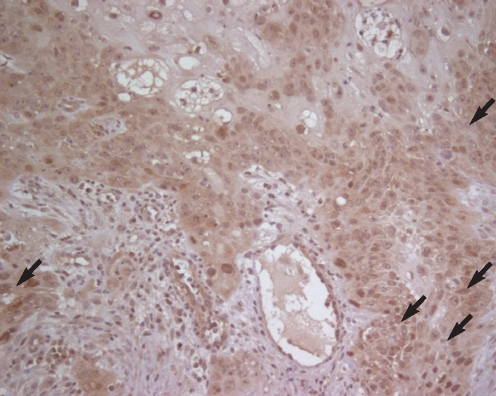
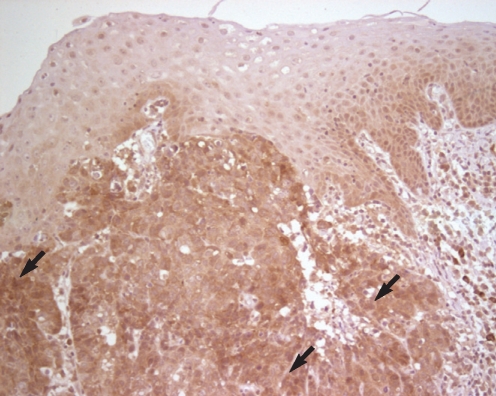
Immunohistochemical analysis showed that a strong positive expression of galectin-8 was correlated with the T-stages, the nodal stages and the clinical stages. However, the histopathologic grades were not correlated with the galectin-8 expression in LSCC.
CONCLUSION
The expression of galectin-8 protein can be used as a prognostic factor for patients with LSCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schantz SP, Harrison LB, Forastiere AA. DeVita V, Hellman S, Rosenberg S, editors. Tumors of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx, oral cavity, and oropharynx. Cancer: principles and practice of oncology. 1997. 5th ed. Philadelphia (PA): JB Lippincott;p. 741–847.2. Park IS, Kim SH, Jung YG, Rho YS, Kim HJ, Lim HJ. Clinical significance of the expression of TGF-a and TGF-β in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and hypopharynx. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1996; 6. 39(6):980–989.3. Hadari YR, Paz K, Dekel R, Mestrovic T, Accili D, Zick Y. Galectin-8: a new rat lectin, related to galectin-4. J Biol Chem. 1995; 2. 17. 270(7):3447–3453. PMID: 7852431.4. Hadari YR, Eisenstein M, Zakut R, Zick Y. Galectin-8: on the road from structure to function. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol. 1997; 1. 9(45):103–112.
Article5. Hadari YR, Arbel-Goren R, Levy Y, Amsterdam A, Alon R, Zakut R, et al. Galectin-8 binding to integrins inhibits cell adhesion and induces apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 2000; 7. 113(Pt 13):2385–2397. PMID: 10852818.
Article6. Zick Y, Eisenstein M, Goren RA, Hadari YR, Levy Y, Ronen D. Role of galectin-8 as a modulator of cell adhesion and cell growth. Glycoconj J. 2004; 19(7-9):517–526. PMID: 14758075.
Article7. Shin DH, Lee CH, Kang HJ, Sol MY, Lee MK. Significance of galectin-3 expression in pulmonary non-small cell carcinoma. Korean J Pathol. 2006; 10. 40(5):326–332.8. Kim HJ, Kim KH, Jang YD, Cho SH, Koh YW, Kim DW, et al. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and survivin in squamous cell carcinoma of larynx. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2006; 12. 49(12):1188–1193.9. Jung KY, Choi JO. Clinical significance of the expression of oncosuppressor gene protein and epidermal growth factor receptor in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1993; 36(5):990–1004.10. Lee DY, Im DM, Do NY, Na HJ, Choi JS, Kim SH, et al. Study on immunohistochemical expression of p53, epidermal growth factor and c-erbB-2 in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2001; 4. 44(4):412–447.11. Barondes SH, Castronovo V, Cooper DN, Cummings RD, Drickamer K, Feizi T, et al. Galectins: a family of animal beta-galactoside-binding lectins. Cell. 1994; 2. 25. 76(4):597–598. PMID: 8124704.12. Hirabayashi J, Hashidate T, Arata Y, Nishi N, Nakamura T, Hirashima M, et al. Oligosaccharide specificity of galectins: a search by frontal affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002; 9. 1572(2-3):232–254. PMID: 12223272.
Article13. Leffler H. Introduction to galectins. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol. 1997; 1. 9(45):9–19.14. Hirabayashi J, Kasai K. The family of metazoan metal-independent β-galactoside-binding lectins: structure, function and molecular evolution. Glycobiology. 1993; 8. 3(4):297–304. PMID: 8400545.
Article15. Liu FT, Patterson RJ, Wang JL. Intracellular functions of galectins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002; 9. 19. 1572(2-3):263–273. PMID: 12223274.
Article16. Perillo NL, Marcus ME, Baum LG. Galectins: versatile modulators of cell adhesion, cell proliferation, and cell death. J Mol Med. 1998; 5. 76(6):402–412. PMID: 9625297.
Article17. Danguy A, Camby I, Kiss R. Galectins and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002; 9. 19. 1572(2-3):285–293. PMID: 12223276.
Article18. Haugen BR, Woodmansee WW, McDermott MT. Towards improving the utility of fine-needle aspiration biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid tumours. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002; 3. 56(3):281–290. PMID: 11940037.
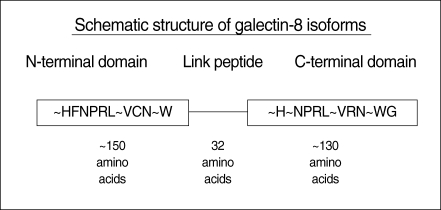
Article19. Bidon-Wagner N, Le Pennec JP. Human galectin-8 isoforms and cancer. Glycoconj J. 2004; 19(7-9):557–563. PMID: 14758080.
Article20. Rechreche H, Mallo GV, Montalto G, Dagorn JC, Iovanna JL. Cloning and expression of the mRNA of human galectin-4, an S-type lectin down-regulated in colorectal cancer. Eur J Biochem. 1997; 8. 15. 248(1):225–230. PMID: 9310382.
Article21. Nagy N, Legendre H, Engels O, Andre S, Kaltner H, Wasano K, et al. Refined prognostic evaluation in colon carcinoma using immunohistochemical galectin fingerprinting. Cancer. 2003; 4. 15. 97(8):1849–1858. PMID: 12673710.
Article22. Levy Y, Arbel-Goren R, Hadari YR, Eshhar S, Ronen D, Elhanany E, et al. Galectin-8 functions as a matricellular modulator of cell adhesion. J Biol Chem. 2001; 8. 17. 276(33):31285–31295. PMID: 11371555.
Article23. Bidon N, Brichory F, Bourguet P, Le Pennec JP, Dazord L. Galectin-8: a complex sub-family of galectins (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2001; 9. 8(3):245–250. PMID: 11494049.
Article24. Danguy A, Rorive S, Decaestecker C, Bronckart Y, Kaltner H, Hadari YR, et al. Immunohistochemical profile of galectin-8 expression in benign and malignant tumors of epithelial, mesenchymatous and adipous origins, and of the nervous system. Histol Histopathol. 2001; 7. 16(3):861–868. PMID: 11510978.25. Nagy N, Bronckart Y, Camby I, Legendre H, Lahm H, Kaltner H, et al. Galectin-8 expression decreases in cancer compared with normal and dysplastic human colon tissue and acts significantly on human colon cancer cell migration as a suppressor. Gut. 2002; 3. 50(3):392–401. PMID: 11839721.
Article26. Camby I, Belot N, Rorive S, Lefranc F, Maurage CA, Lahm H, et al. Galectins are differentially expressed in supratentorial pilocytic astrocytomas, astrocytomas, anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas, and significantly modulate tumor astrocyte migration. Brain Pathol. 2001; 1. 11(1):12–26. PMID: 11145198.
Article27. Bidon N, Brichory F, Hanash S, Bourguet P, Dazord L, Le Pennec JP. Two messenger RNAs and five isoforms for Po66-CBP, a galectin-8 homolog in a human lung carcinoma cell line. Gene. 2001; 8. 22. 274(1-2):253–262. PMID: 11675018.
Article28. Bassen R, Brichory F, Caulet-Maugendre S, Bidon N, Delaval P, Desrues B, et al. Expression of Po66-CBP, a type-8 galectin, in different healthy, tumoral and peritumoral tissues. Anticancer Res. 1999; Nov–Dec. 19(6B):5429–5433. PMID: 10697573.29. Henno S, Brichory F, Langanay T, Desrues B, Bidon N, Delaval P, et al. Expression of Po66-CBP, a galectin-8, in different types of primary and secondary broncho-pulmonary tumors. Oncol Rep. 2002; Jan–Feb. 9(1):177–180. PMID: 11748478.
Article30. Caulet-Maugendre S, Birolleau S, Corbineau H, Bassen R, Desrues B, Bidon N, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of the intracellular component of galectin-8 in squamous cell metaplasia of the bronchial epithelium in neoplastic and benign processes. Pathol Res Pract. 2001; 197(12):797–801. PMID: 11795826.31. Su ZZ, Lin J, Shen R, Fisher PE, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB. Surface-epitope masking and expression cloning identifies the human prostate carcinoma tumor antigen gene PCTA-1 a member of the galectin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996; 7. 09. 93(14):7252–7257. PMID: 8692978.
Article32. Wollina U, Graefe T, Feldrappe S, Andre S, Wasano K, Kaltner H, et al. Galectin fingerprinting by immuno- and lectin histochemistry in cutaneous lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002; 2. 128(2):103–110. PMID: 11862481.33. Simon P, Decaestecker C, Choufani G, Delbrouck C, Danguy A, Salmon I, et al. The levels of retinoid RARbeta receptors correlate with galectin-1, -3 and -8 expression in human cholesteatomas. Hear Res. 2001; 6. 156(1-2):1–9. PMID: 11377877.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Galectin-3 Expression in Pulmonary Non-Small Cell Carcinoma
- Expression of Cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Expression of bFGF and CD-31 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Decreased expression of galectin-3 is associated with the progression of cervical neoplasia
- Expression of p53 and MHC Class I According to HPV Infection in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas