Yonsei Med J.
2012 Nov;53(6):1220-1223. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1220.
Arterial Occlusive Disease Complicating Radiation Therapy of Cervical Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital Cardiovascular Center, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cdhlyj@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1414268
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.6.1220
Abstract
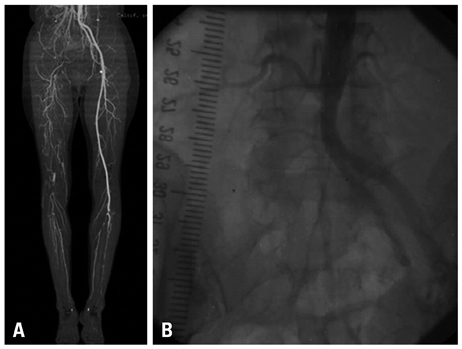
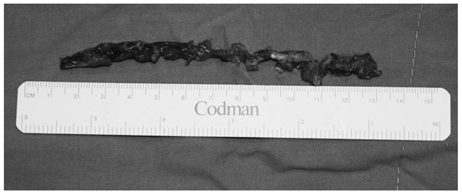
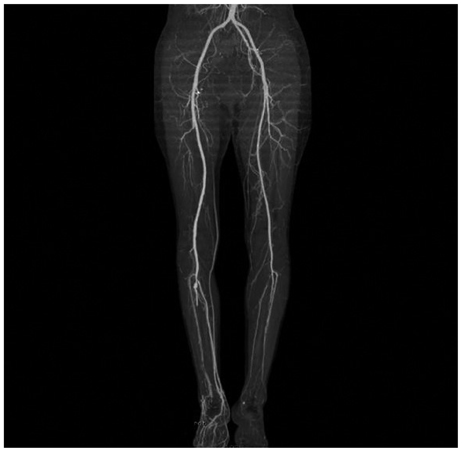
- Radiation-induced arterial disease is caused by significant atherosclerosis in the circumjacent vessels being irradiated. Even though this has been recognized as survival of cancer patients treated with radiotherapy improves, it is a problem that is often under-reported. We present a case of chronic thromboembolic occlusion of right common iliac artery in a 53-year-old woman who was treated with radiation therapy for cervical cancer 13 years ago. We initially performed percutaneous transluminal angioplasty with thrombolytic therapy, but had to cease thrombolytic therapy due to upper gastrointestinal bleeding of Dieulafoy's lesion, nevertheless, achieved good results after revascularization by Fogarty embolectomy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McCready RA, Hyde GL, Bivins BA, Mattingly SS, Griffen WO Jr. Radiation-induced arterial injuries. Surgery. 1983. 93:306–312.2. Hughes WF, Carson CL, Laffaye HA. Subclavian artery occlusion 42 years after mastectomy and radiotherapy. Am J Surg. 1984. 147:698–700.
Article3. Har-Shai Y, Schein M, Molek AD, Peled IJ, Best LA. Ruptured mycotic aneurysm of the subclavian artery after irradiation. A case report. Eur J Surg. 1993. 159:59–60.4. Ross HB, Sales JE. Post-irradiation femoral aneurysm treated by iliopopliteal by-pass via the obturator foramen. Br J Surg. 1972. 59:400–405.
Article5. de Baere T, Ousehal A, Kuoch V, Sapoval M, Lagrange C, Roche A. Endovascular management of bleeding iliac artery pseudoaneurysms complicating radiation therapy for pelvic malignancies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 170:349–353.
Article6. Pettersson F, Swedenborg J. Atherosclerotic occlusive disease after radiation for pelvic malignancies. Acta Chir Scand. 1990. 156:367–371.7. Mellière D, Becquemin JP, Berrahal D, Desgranges P, Cavillon A. Management of radiation-induced occlusive arterial disease: a reassessment. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1997. 38:261–269.8. Katras T, Baltazar U, Colvett K, Rush D, Dunn J, Stanton P Jr. Radiation-related arterial disease. Am Surg. 1999. 65:1176–1179.9. Butler MJ, Lane RH, Webster JH. Irradiation injury to large arteries. Br J Surg. 1980. 67:341–343.
Article10. Modrall JG, Sadjadi J. Early and late presentations of radiation arteritis. Semin Vasc Surg. 2003. 16:209–214.
Article11. Jurado JA, Bashir R, Burket MW. Radiation-induced peripheral artery disease. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008. 72:563–568.
Article12. Levenback C, Burke TW, Rubin SC, Curtin JP, Wharton JT. Arterial occlusion complicating treatment of gynecologic cancer: a case series. Gynecol Oncol. 1996. 63:40–46.
Article13. Andros G, Schneider PA, Harris RW, Dulawa LB, Oblath RW, Salles-Cunha SX. Management of arterial occlusive disease following radiation therapy. Cardiovasc Surg. 1996. 4:135–142.14. Farrugia M, Gowda KM, Cheatle TR, Ashok TP. Radiotherapy-related axillary artery occlusive disease: percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting. Two case reports and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006. 29:1144–1147.
Article15. Pherwani AD, Reid JA, Keane PF, Hannon RJ, Soong CV, Lee B. Synergism between radiotherapy and vascular risk factors in the accelerated development of atherosclerosis: a report of three cases. Ann Vasc Surg. 2002. 16:671–675.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Arterial Occlusive Disease
- Radiation sigmoiditis mimicking sigmoid colon cancer after radiation therapy for cervical cancer: the implications of three-dimensional image-based brachytherapy planning
- Angiographic Evaluation of Occlusive Coronary Arterial Disease
- Recent Management of FIGO stage IB2 Cervical Cancer
- Peripheral Arterial Occlusion in Young Adult: 2 cases