Korean J Radiol.
2006 Dec;7(4):275-280. 10.3348/kjr.2006.7.4.275.
Effect of Thin Overlapping Reconstruction on the Attenuation of Small (< or = 3 cm) Renal Cysts in the Nephrographic Phase of MDCT: a Phantom Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Center, Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kimsh@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1092551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2006.7.4.275
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
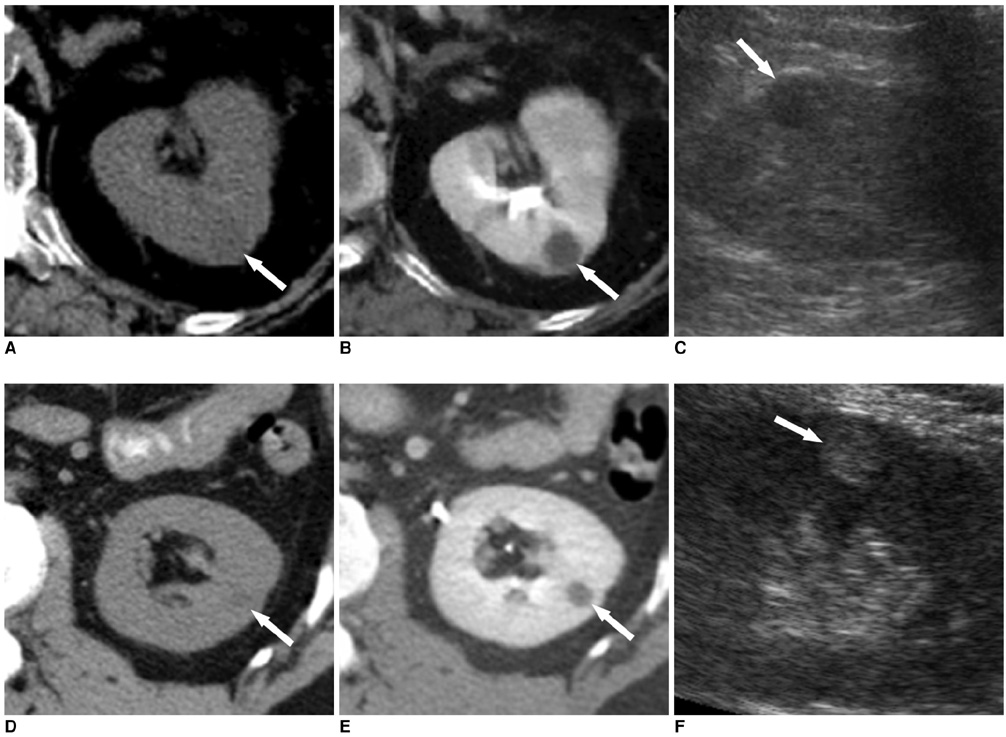
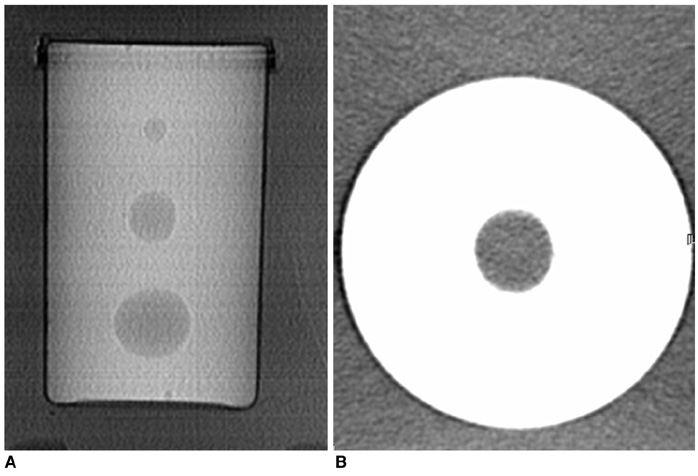
To evaluate the effect of thin overlapping reconstruction on the attenuation of small (< or = 3 cm) renal cysts in the nephrographic phase of multidetector CT (MDCT). MATERIALS AND METHODS: We scanned a phantom kidney containing spheres of various sizes (10, 20, and 30 mm) using both 4- and 16-channel MDCT scanners, and reconstructed images with various slice thickness (T, mm) and intervals (I, mm). The attenuation increase (AI) was measured for each sphere in 240-HU diluted solution of contrast material and compared with the attenuation in 35-HU solution. RESULTS: On the 4-channel MDCT, thin overlapping reconstruction (T/I = 3/1, compared with 5/5) lowered the AI as much as 17 HU in the 10 mm-sphere and 6 HU in the 20 mm-sphere (p < 0.05). Thin slicing alone was also effective; however overlapping alone was not. On the 16-channel MDCT, AI in the 10 mm-sphere was significantly lower than on the 4-channel MDCT with T/I = 5/5 (p < 0.05), however thinner slicing or overlapping did not affect the attenuation significantly in all of the spheres. CONCLUSION: The effect of thin overlapping reconstruction on minimizing falsely elevated attenuation in the nephrographic phase was significant only in cysts < or =20 mm on the 4-channel MDCT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bosniak MA. The current radiological approach to renal cysts. Radiology. 1986. 158:1–10.2. McClennan BL, Stanley RJ, Melson GL, Levitt RG, Sagel SS. CT of the renal cyst: is cyst aspiration necessary? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979. 133:671–675.3. Sagel SS, Stanley RJ, Levitt RG, Geisse G. Computed tomography of the kidney. Radiology. 1977. 124:359–370.4. Bosniak MA, Rofsky NM. Problems in the detection and characterization of small renal masses. Radiology. 1996. 198:638–641.5. Siegel CL, Fisher AJ, Bennett HF. Interobserver variability in determining enhancement of renal masses on helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:1207–1212.6. Maki DD, Birnbaum BA, Chakraborty DP, Jacobs JE, Carvalho BM, Herman GT. Renal cyst pseudoenhancement: beam-hardening effects on CT numbers. Radiology. 1999. 213:468–472.7. Coulam CH, Sheafor DH, Leder RA, Paulson EK, DeLong DM, Nelson RC. Evaluation of pseudoenhancement of renal cysts during contrast-enhanced CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:493–498.8. Birnbaum BA, Jacobs JE, Langlotz CP, Ramchandani P. Assessment of a bolus tracking technique in helical renal CT to optimize nephrographic phase imaging. Radiology. 1999. 211:87–94.9. Gokan T, Ohgiya Y, Munechika H, Nobusawa H, Hirose M. Renal cyst pseudoenhancement with beam hardening effect on CT attenuation. Radiat Med. 2002. 20:187–190.10. Birnbaum BA, Maki DD, Chakraborty DP, Jacobs JE, Babb JS. Renal cyst pseudoenhancement: evaluation with an anthropomorphic body CT phantom. Radiology. 2002. 225:83–90.11. Bae KT, Heiken JP, Siegel CL, Bennett HF. Renal cysts: is attenuation artifactually increased on contrast-enhanced CT images? Radiology. 2000. 216:792–796.12. Heneghan JP, Spielmann AL, Sheafor DH, Kliewer MA, DeLong DM, Nelson RC. Pseudoenhancement of simple renal cysts: a comparison of single and multidetector helical CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002. 26:90–94.13. Abdulla C, Kalra MK, Saini S, Maher MM, Ahmad A, Halpern E, et al. Pseudoenhancement of simulated renal cysts in a phantom using different multidetector CT scanners. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:1473–1476.14. Jinzaki M, McTavish JD, Zou KH, Judy PF, Silverman SG. Evaluation of small (3 cm) renal masses with MDCT: benefits of thin overlapping reconstructions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:223–228.15. Chung EP, Herts BR, Linnell G, Novick AC, Obuchowski N, Coll DM, et al. Analysis of changes in attenuation of proven renal cysts on different scanning phases of triphasic MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 182:405–410.16. Kalra MK, Maher MM, D'Souza R, Saini S. Multidetector computed tomography technology: current status and emerging developments. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2004. 28:S2–S6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characterization of Small Renal Masses Less than 4 cm with Quadriphasic Multidetector Helical Computed Tomography: Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Lesions
- Split-bolus CT urography with synchronous nephrographic and excretory phase in dogs: comparison of image quality with three-phase CT urography and optimal allocation ratio of contrast medium
- Multidetector CT Characteristics of Fumarate HydrataseDeficient Renal Cell Carcinoma and Papillary Type II Renal Cell Carcinoma
- The Difference of Nodule Detection Rates in the Liver According to the Pitch and Slice Thickness in Spiral CT: Experimental Study by Using Artificial Liver Phantom
- US and CT Findings of Small Renal Cell Carcinoma