Healthc Inform Res.
2012 Mar;18(1):74-83. 10.4258/hir.2012.18.1.74.
Smart Information System for Gachon University Gil Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1u-HealthCare Center, Incheon, Korea. pdk66@gilhospital.com
- 2IT Division, Gachon University Gil Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 3MCC Inc., Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Information Technology, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2166620
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2012.18.1.74
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
In this research, the hospital information system of Gachon University Gil hospital is introduced and a future strategy for hospital information systems is proposed.
METHODS
This research introduces the development conditions of hospital information system at Gachon University Gil hospital, information about the development of the enterprise resource planning (ERP), a medical service process improvement system, and the personal health record (PHR) system.
RESULTS
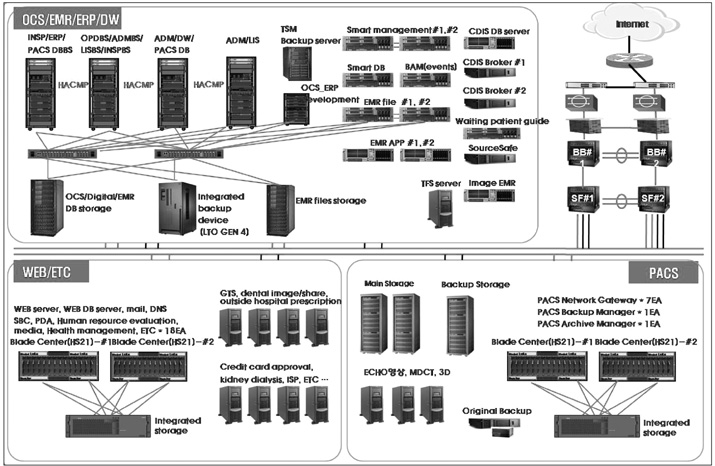
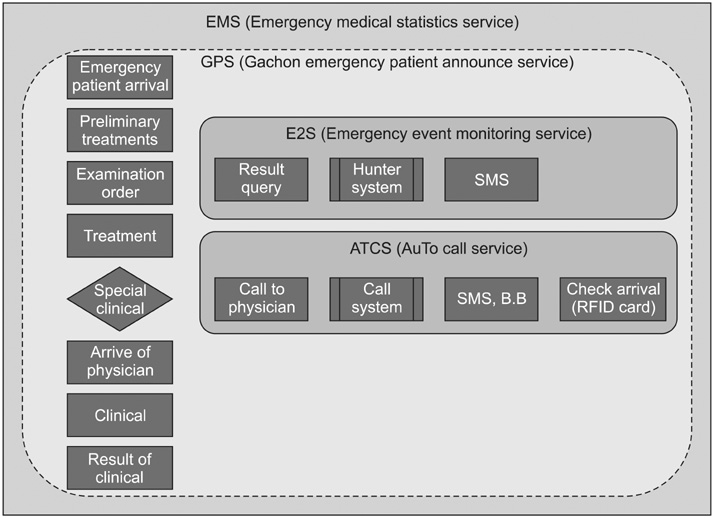
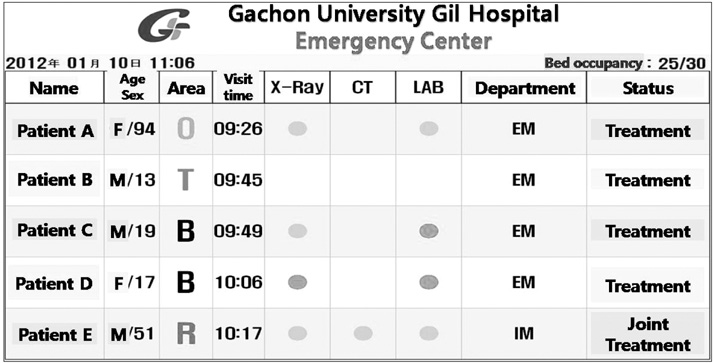
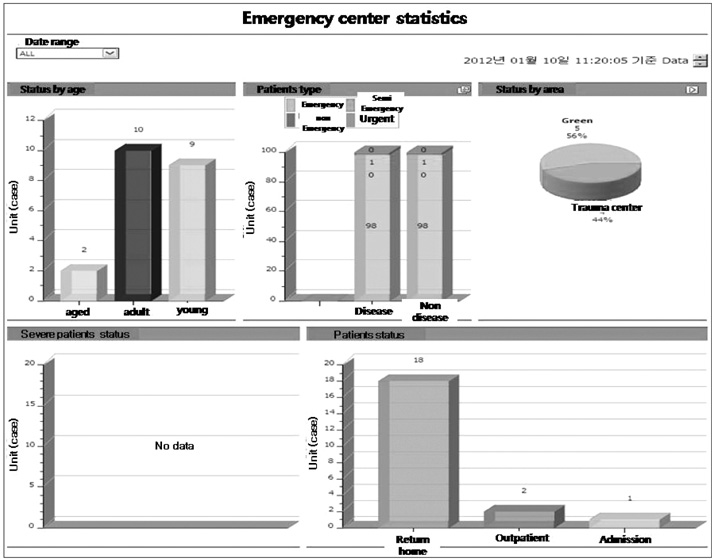
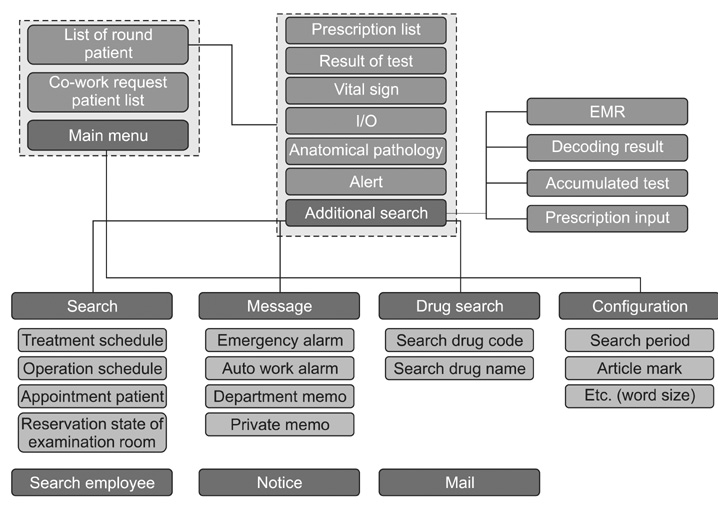
The medical service process and work efficiency were improved through the medical service process improvement system, which is the most common hospital information system at Gachon University Gil hospital and which includes an emergency medical service system, an online evaluation system and a round support system.
CONCLUSIONS
Gachon University Gil hospital developed medical service improvement systems to increase work efficiency of medical team and optimized the systems to prove the availability of high-quality medical services for patients and their families. The PHR-based personalized health care solution is under development and will provide higher quality medical service for more patients in the future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
XDS-I Gateway Development for HIE Connectivity with Legacy PACS at Gil Hospital
Mikael Fernandus Simalango, Youngchul Kim, Young Tae Seo, Young Hwan Choi, Yong Kyun Cho
Healthc Inform Res. 2013;19(4):293-300. doi: 10.4258/hir.2013.19.4.293.Healthcare Decision Support System for Administration of Chronic Diseases
Ji-In Woo, Jung-Gi Yang, Young-Ho Lee, Un-Gu Kang
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(3):173-182. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.173.
Reference
-
1. Lee TK. Status of present medical information system and future strategies. Korean Soc Comput Inf Rev. 2011. 19:1–11.2. Shin JW. Gachon University Gil hospital, leading medical and IT convergence. Korea Inf Sci Soc Rev. 2010. 28:106–109.3. Chung DG, Kim KH, Kim MG. The study on computer network for medical application. Annu Bull Inst Hosp Manage. 1995. 1:51–75.4. Park YM, Oh YH. A Study on the integration of healthcare information system based on SOA for PHR services. J Korean Inst Electron Eng. 2011. 48:136–142.5. Reti SR, Feldman HJ, Safran C. Governance for personal health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2009. 16:14–17.
Article6. Kim MI, Johnson KB. Personal health records: evaluation of functionality and utility. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2002. 9:171–180.
Article7. DesRoches CM, Campbell EG, Rao SR, Donelan K, Ferris TG, Jha A, Kaushal R, Levy DE, Rosenbaum S, Shields AE, Blumenthal D. Electronic health records in ambulatory care: a national survey of physicians. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:50–60.
Article8. Lee SW, Lee KB, Kang JW, Choi JC, Oh JH. Trends in personalized medicine research. Korea Inf Sci Soc Rev. 2011. 29:19–25.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Smart Information System for Gachon University Gil Hospital
- Development of Personalized Urination Recognition Technology Using Smart Bands
- The Prospect of a New Smart Healthcare System: A Wearable Device-Based Complex Structure of Position Detecting and Location Recognition System
- Smartphone Addiction of Adolescents, Not a Smart Choice
- Is Dynamic Left Ventricular Dyssynchrony a Novel Surrogate Marker in the Patient with Hypertension?