Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korea: a multicenter retrospective case study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. cwkim1805@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2262961
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.203
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the causes, clinical features and characteristics of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (FDEIA) in Korea.
METHODS
A retrospective medical chart review was performed on the patients diagnosed with anaphylaxis between 2007 and 2011 in 14 hospitals in Korea. Cases with FDEIA were subsequently identified among anaphylaxis patients, and subgroup analyses were done to assess clinical characteristics of FDEIA.
RESULTS
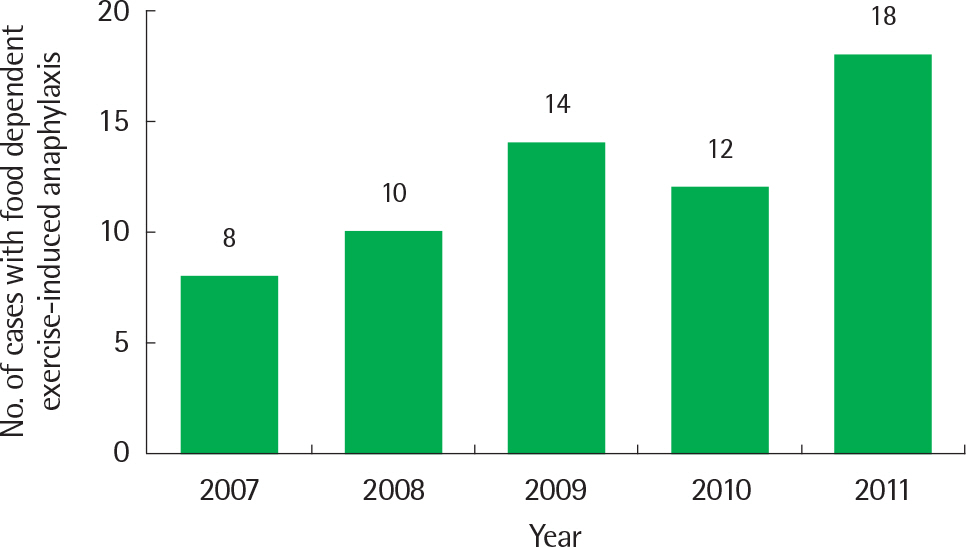
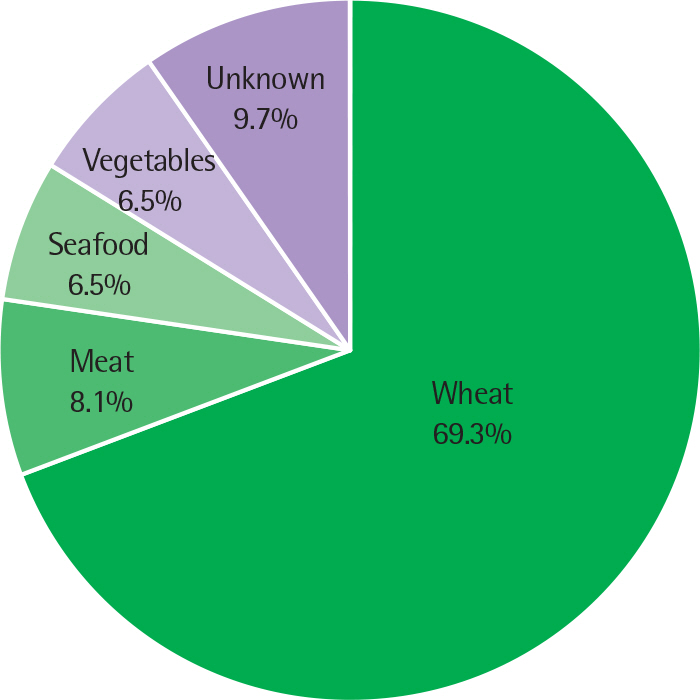
A total of 62 subjects with FDEIA (male, 72.6%; aged 16 to 70 years) were enrolled in 10 hospitals. Wheat (69.3%) was the most common cause of FDEIA, followed by meat (8.1%), seafood (6.5%), and vegetables (6.5%). The clinical manifestations were cutaneous (100%), respiratory (64.5%), cardiovascular (61.3%), and gastrointestinal (9.7%), respectively. In severity assessment, approximately 40% of FDEIA were classified as severe anaphylaxis. Portable epinephrine auto-injector was prescribed to 17.2% of patients, and about one fifth of the patients experienced redevelopment of anaphylactic symptoms during follow-up period. There was no significant difference of age, gender, latent period, total immunoglobulin E, and past history of allergic disease between patients with severe anaphylaxis group and patients with mild-to-moderate group.
CONCLUSION
Wheat is the most common cause of FDEIA in Korea. Because significant number of patients with FDEIA experienced anaphylactic symptoms after diagnosis of FDEIA, more comprehensive therapeutic and educational approaches will be required to prevent recurrent development of anaphylaxis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Epidemiologic study on food-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis
Min-Suk Yang
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):179-180. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.179.Hymenoptera venom anaphylaxis in adult Korean: a multicenter retrospective case study
Su-Kyoung Lee, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park, Gwang Cheon Jang, Young-Koo Jee, Hye-Kyung Park, Young-Il Koh, Joo-Hee Kim, Cheol-Woo Kim, Gyu-Young Hur, Mi Kyoung Kim, Tae-Bum Kim, Gil-Soon Choi, Sang-Heon Kim, Seong-Wook Sohn,
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014;2(5):344-351. doi: 10.4168/aard.2014.2.5.344.Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Korean children: a single-center retrospective case study
Eun Lee, Min-Ju Kim, Song-I Yang, Jinho Yu, Soo-Jong Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(3):194-199. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.3.194.Apple-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis
Dong Hyun Kim, Kyung Hee Park, Young Joo Kim, Jun Ho Kim, Hee Jae Han, Hye Jung Park, Jung-Won Park, Jae-Hyun Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(3):224-227. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.3.224.Analysis of clinical characteristics of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis at a single tertiary hospital
Soo Jie Chung, Jisu Shim, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kyoung-Hee Sohn, Sung-Yoon Kang, Min-Gyu Kang, Han-Ki Park, Hye-Ryun Kang
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2016;4(6):436-441. doi: 10.4168/aard.2016.4.6.436.A Case of Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis Presenting with Lower Lid Angioedema
Jung Ran You, Min Hee Kim, Youn Mi Sung, Suk Woo Yang
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(9):1459-1463. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.9.1459.
Reference
-
1. Ben-Shoshan M, Clarke AE. Anaphylaxis: past, present and future. Allergy. 2011; 66:1–14.
Article2. Morita E, Kunie K, Matsuo H. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J Dermatol Sci. 2007; 47:109–17.
Article3. Barg W, Medrala W, Wolanczyk-Medrala A. Exercise-induced anaphylaxis: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011; 11:45–51.
Article4. Maulitz RM, Pratt DS, Schocket AL. Exercise-induced anaphylactic reaction to shellfish. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:433–4.
Article5. Lee BJ, Ban JW, Kim YK, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. Three cases of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Korean J Med. 1998; 54:718–22.6. Kim MK, Lee KS, Kim MS. Food (wheat flour) dependent exerclse - induced anaphylaxis in asthmatics: related with the amont of wheat flour and exercise. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 19:724–9.7. Shin YS, Youn SH, Kim MC, Choi JH, Suh YJ, Suh CH, et al. A case of wheat-induced anaphylaxis in an adult. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 23:539–43.8. Kim JH, Lee JI, Yang BY, Ahn SJ, Park SJ, Kim S, et al. A case of food-de-pendent exercise-induced anaphylaxis developed only in winter. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:331–5.9. Choi JH, Lee HB, Ahn IS, Park CW, Lee CH. Wheat-dependent, exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: a successful case of prevention with ketotifen. Ann Dermatol. 2009; 21:203–5.
Article10. Lee HB, Ahn IS, Choi JH, Park CW. A case of wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Ann Dermatol. 2009; 21:447–9.
Article11. Jeon KW, Kim C, Kim YK, Kang MS, Bong JD, Ki SY, et al. A case of parsely dependent sxercise-induced anaphylaxsis. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998; 18:728–32.12. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim KM, Kwon HS, Kim DI, Park CH, et al. A Case report of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis to apples. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 26:242–5.13. Yoon TY, Choi KH, Lee KM, Ahn JY, Kim MK. Crown daisy-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in a patient with mugwort-sensitized polli-nosis. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:63–6.14. Kim SM, Yoo SH, Kim MK. A case of squash-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:140–3.15. Pang SJ, No SJ, Kim DW, Lee SM, Lee EJ, Kim CH, et al. A case report of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in a patient who was sen-sitive to pork. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012; 22:116–21.
Article16. Gelincik A, Demirturk M, Yılmaz E, Ertek B, Erdogdu D, Colakoglu B, et al. Anaphylaxis in a tertiary adult allergy clinic: a retrospective review of 516 patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 110:96–100.17. Ye YM, Kim MK, Kang HR, Kim TB, Sohn SW, Koh YI, et al. Anaphylaxis in Korean adults: a multicenter retrospective case study. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 32(S2):S226.18. Sampson HA, Munoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, Adkinson NF Jr, Bock SA, Branum A, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report–Second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:391–7.
Article19. Brown SG. Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:371–6.
Article20. Romano A, Di Fonso M, Giuffreda F, Papa G, Artesani MC, Viola M, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: clinical and laboratory findings in 54 subjects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2001; 125:264–72.
Article21. Aihara Y, Takahashi Y, Kotoyori T, Mitsuda T, Ito R, Aihara M, et al. Fre-quency of food-dependent, exercise-induced anaphylaxis in Japanese ju-nior-high-school students. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:1035–9.
Article22. Morita E, Matsuo H, Chinuki Y, Takahashi H, Dahlstrom J, Tanaka A. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis -importance of omega-5 gliadin and HMW-glutenin as causative antigens for wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis-. Allergol Int. 2009; 58:493–8.23. Koh YI, Choi IS, Chung SU, Cho S. Clinical features of adult patients with anaphylaxis associated with food in Gwangju and Chonnam area. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 24:217–23.24. Kim MJ, Choi GS, Um SJ, Sung JM, Shin YS, Park HJ, et al. Anaphylaxis; 10 years' experience at a university hospital in Suwon. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 28:298–304.25. Yang MS, Lee SH, Kim TW, Kwon JW, Lee SM, Kim SH, et al. Epidemio-logic and clinical features of anaphylaxis in Korea. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:31–6.
Article26. Palosuo K, Varjonen E, Kekki OM, Klemola T, Kalkkinen N, Alenius H, et al. Wheat omega-5 gliadin is a major allergen in children with immediate allergy to ingested wheat. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:634–8.27. Park HJ, Kim JH, Kim JE, Jin HJ, Choi GS, Ye YM, et al. Diagnostic value of the serum-specific IgE ratio of ω-5 gliadin to wheat in adult patients with wheat-induced anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012; 157:147–50.
Article28. Shadick NA, Liang MH, Partridge AJ, Bingham C, Wright E, Fossel AH, et al. The natural history of exercise-induced anaphylaxis: survey results from a 10-year follow-up study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 104:123–7.
Article29. Tanaka S. An epidemiological survey on food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis in kindergartners, schoolchildren and junior high school students. Asia Pac J Public Health. 1994; 7:26–30.
Article30. Matsuo H, Morimoto K, Akaki T, Kaneko S, Kusatake K, Kuroda T, et al. Exercise and aspirin increase levels of circulating gliadin peptides in patients with wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:461–6.
Article31. Aihara M, Miyazawa M, Osuna H, Tsubaki K, Ikebe T, Aihara Y, et al. Food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis: influence of concurrent aspirin administration on skin testing and provocation. Br J Dermatol. 2002; 146:466–72.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis
- Food allergies and food-induced anaphylaxis: role of cofactors
- Wheat-dependent, Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis: A Successful Case of Prevention with Ketotifen
- Three Cases of Food-dependent Exercise-induced Anaphylaxis
- A case of food-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis developed only in winter