Ann Dermatol.
2011 Aug;23(3):329-337. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.3.329.
Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-cell Lymphoma: A Clinical and Pathologic Study of 14 Korean Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. miumiu@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2171924
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.3.329
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTL) is a distinctive skin lymphoma characterized by neoplastic T-cell infiltration of the subcutaneous tissue, mimicking panniculitis.
OBJECTIVE
To describe the clinical and pathologic features of SPTL in Korean patients.
METHODS
Fourteen SPTL patients evaluated over 15 years were retrospectively reviewed.
RESULTS
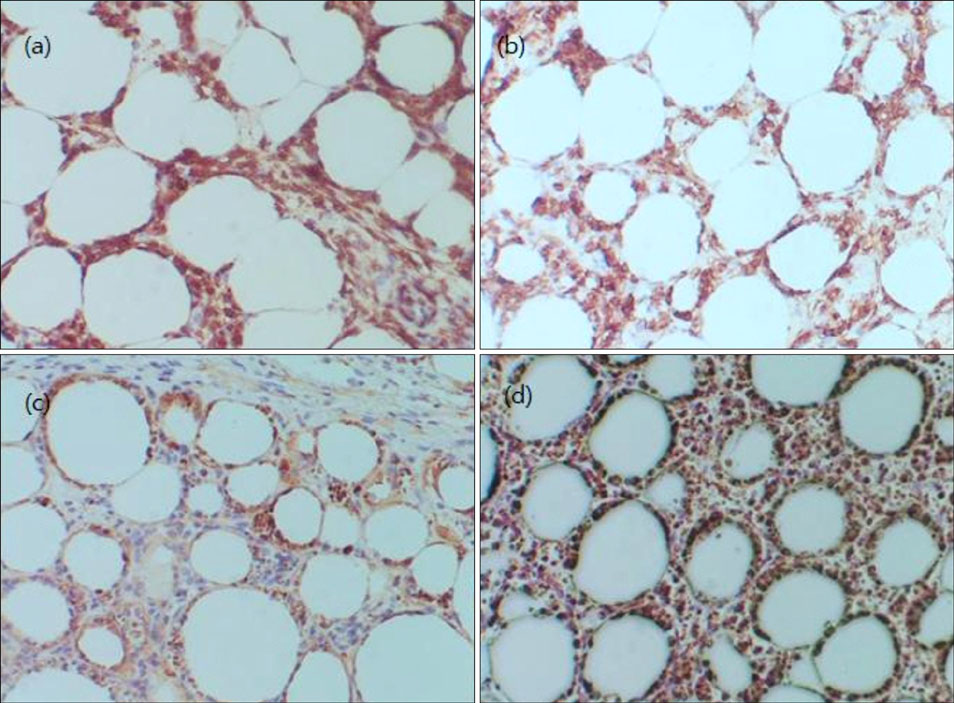
The mean patient age was 35 years (range: 7~73 years), with male predominance (2.5:1). Most patients presented with either nodules or plaques, occurring most commonly on the trunk, with two patients (14%) having hemophagocytic syndrome. Histopathologically, all patients showed infiltrates of small-to-medium pleomorphic cells mimicking panniculitis, with some also showing rimming, bean-bag cells, and fat necrosis. Most patients were positive for CD3 (14/14), CD8 (12/13), TIA-1 (9/9) and betaf1 (5/5), but were negative for CD4 (11/12), CD20 (8/8), CD56 (14/14) and Epstein-Barr virus (8/8). Ten patients (71%) received chemotherapy and 2 (14%) died due to the disease, with an average survival time of 4 months. Survival analysis did not reveal any significant prognostic factors.
CONCLUSION
This is the first series of patients with SPTL in Korea. Due to its indolent clinical course and relatively high survival rate, SPTL should be differentiated from cutaneous gammadelta T-cell lymphoma.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Inflammatory Nodules of the Leg
Kwang Hyun Cho
Ann Dermatol. 2012;24(4):383-392. doi: 10.5021/ad.2012.24.4.383.
Reference
-
1. Takeshita M, Okamura S, Oshiro Y, Imayama S, Okamoto S, Matsuki Y, et al. Clinicopathologic differences between 22 cases of CD56-negative and CD56-positive subcutaneous panniculitis-like lymphoma in Japan. Hum Pathol. 2004. 35:231–239.
Article2. Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, Cerroni L, Berti E, Swerdlow SH, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005. 105:3768–3785.
Article3. van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Brüggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL, et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia. 2003. 17:2257–2317.
Article4. Willemze R, Jansen PM, Cerroni L, Berti E, Santucci M, Assaf C, et al. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: definition, classification, and prognostic factors: an EORTC Cutaneous Lymphoma Group Study of 83 cases. Blood. 2008. 111:838–845.
Article5. Kong YY, Dai B, Kong JC, Zhou XY, Lu HF, Shen L, et al. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular study of 22 Asian cases according to WHO-EORTC classification. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008. 32:1495–1502.6. Hahtola S, Burghart E, Jeskanen L, Karenko L, Abdel-Rahman WM, Polzer B, et al. Clinicopathological characterization and genomic aberrations in subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. 128:2304–2309.
Article7. Massone C, Kodama K, Salmhofer W, Abe R, Shimizu H, Parodi A, et al. Lupus erythematosus panniculitis (lupus profundus): clinical, histopathological, and molecular analysis of nine cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2005. 32:396–404.
Article8. Magro CM, Crowson AN, Byrd JC, Soleymani AD, Shendrik I. Atypical lymphocytic lobular panniculitis. J Cutan Pathol. 2004. 31:300–306.
Article9. Pincus LB, LeBoit PE, McCalmont TH, Ricci R, Buzio C, Fox LP, et al. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma with overlapping clinicopathologic features of lupus erythematosus: coexistence of 2 entities? Am J Dermatopathol. 2009. 31:520–526.
Article10. Hoque SR, Child FJ, Whittaker SJ, Ferreira S, Orchard G, Jenner K, et al. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathological, immunophenotypic and molecular analysis of six patients. Br J Dermatol. 2003. 148:516–525.
Article11. Massone C, Chott A, Metze D, Kerl K, Citarella L, Vale E, et al. Subcutaneous, blastic natural killer (NK), NK/T-cell, and other cytotoxic lymphomas of the skin: a morphologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular study of 50 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. 28:719–735.
Article12. Gallardo F, Pujol RM. Subcutaneous panniculitic-like T-cell lymphoma and other primary cutaneous lymphomas with prominent subcutaneous tissue involvement. Dermatol Clin. 2008. 26:529–540. viii
Article13. Romero LS, Goltz RW, Nagi C, Shin SS, Ho AD. Subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma with associated hemophagocytic syndrome and terminal leukemic transformation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996. 34:904–910.
Article14. Magro CM, Crowson AN, Kovatich AJ, Burns F. Lupus profundus, indeterminate lymphocytic lobular panniculitis and subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a spectrum of subcuticular T-cell lymphoid dyscrasia. J Cutan Pathol. 2001. 28:235–247.
Article15. Reimer P, Rüdiger T, Müller J, Rose C, Wilhelm M, Weissinger F. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma during pregnancy with successful autologous stem cell transplantation. Ann Hematol. 2003. 82:305–309.
Article16. Mukai HY, Okoshi Y, Shimizu S, Katsura Y, Takei N, Hasegawa Y, et al. Successful treatment of a patient with subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma with high-dose chemotherapy and total body irradiation. Eur J Haematol. 2003. 70:413–416.
Article17. Weenig RH, Ng CS, Perniciaro C. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma: an elusive case presenting as lipomembranous panniculitis and a review of 72 cases in the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001. 23:206–215.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-cell Lymphoma: A Clinical and Pathologic Study of 14 Korean Patients
- Two Cases of Subcutaneous Panniculitis-like T-cell Lymphoma
- MR Findings of Subcutaneous Panniculitis-like T-Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report
- Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell Lymphoma with Hemophagocytic Syndrome in a Child: A Successful Treatment with the BFM-NHL-90 Protocol
- A Case of Subcutaneous Panniculitic T-cell Lymphoma-like Lesion Occurring in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus