Standardization of Weed Pollen Extracts, Japanese Hop and Mugwort, in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. parkjw@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2374046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.2.399
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Japanese hop (Humulus spp.) and mugwort (Artemisia spp.) are notable causes of autumn pollinosis in East Asia. However, Japanese hop and mugwort pollen extracts, which are widely used for the diagnosis, have not been standardized. This study was performed to standardize Japanese hop and mugwort pollen extracts.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Allergen extracts were prepared in a standardized way using locally collected Humulus japonicus and purchased Artemisia vulgaris pollens. The immunoglobulin E (IgE) reactivities of prepared extracts were compared with commercial extracts via IgE immunoblotting and inhibition analyses. Intradermal skin tests were performed to determine the bioequivalent allergy unit (BAU).
RESULTS
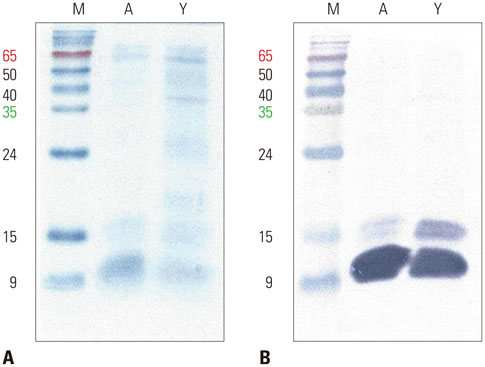
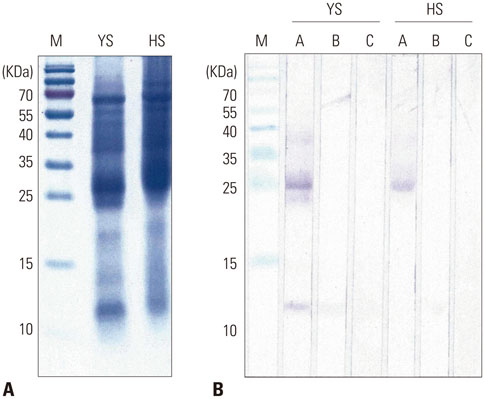
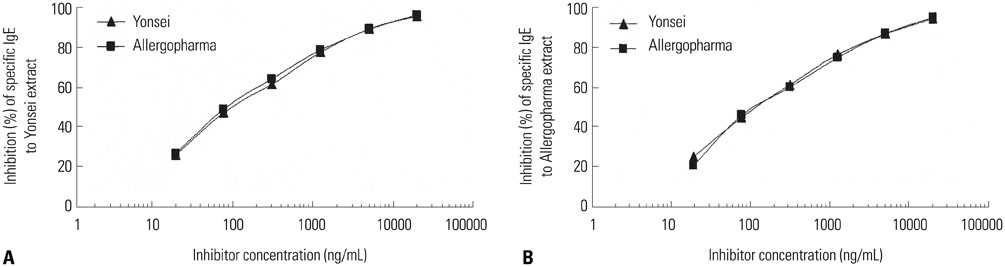
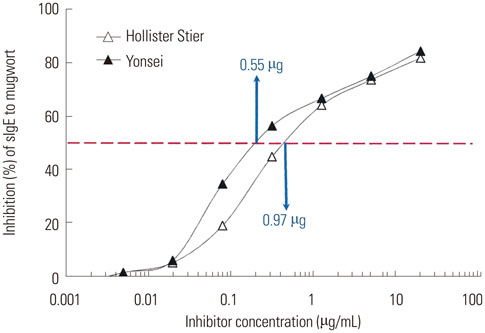
The IgE reactive components of the extracts via IgE immunoblotting were similar to those of commercial extracts. A 11-kDa allergen showed the strongest IgE reactivity in Japanese hop, as did a 28-kDa allergen in mugwort pollen extracts. Allergenic potencies of the investigatory Japanese hop and mugwort extracts were essentially indistinguishable from the commercial ones. Sums of erythema of 50 mm by the intradermal skin test (SigmaED50) were calculated to be 14.4th and 13.6th three-fold dilutions for Japanese hop and mugwort extracts, respectively. Therefore, the allergenic activity of the prepared extracts was 90827.4 BAU/mg for Japanese hop and 34412 BAU/mg for mugwort.
CONCLUSION
We produced Japanese hop and mugwort pollen extracts using a standardized method. Standardized Japanese hop and mugwort pollen extracts will facilitate the production of improved diagnostic and immunotherapeutic reagents.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens/*analysis/*immunology
Antibody Specificity
*Artemisia
Bronchial Hyperreactivity/blood/immunology
Cross Reactions
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Humans
Immunoblotting
Immunoglobulin E/blood/*immunology
Pollen/*chemistry/*immunology
Reference Standards
Republic of Korea
Rhinitis, Allergic, Seasonal
Allergens
Immunoglobulin E
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Comparison between Newly Developed and Commercial Inhalant Skin Prick Test Reagents Using In Vivo and In Vitro Methods
Sang Chul Lee, Da Woon Sim, Jongsun Lee, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Kyung Hee Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung Dong Kim, Jung-Won Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(13):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e101.Comparison of the ImmunoCAP Assay and AdvanSure™ AlloScreen Advanced Multiplex Specific IgE Detection Assay
Kyung Hee Park, Jongsun Lee, Sang Chul Lee, Young Woong Son, Da Woon Sim, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(4):786-792. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.786.Validation of PROTIA™ Allergy-Q 64 Atopy® as a Specific IgE Measurement Assay for 10 Major Allergen Components
Sung Ryeol Kim, Kyung Hee Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Bum Joon Kim, Jae Hwan Hwang, Kook Jin Lim, Jung-Won Park
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(3):422-432. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.3.422.IgE Cross-Reactivity between
Humulus japonicus andHumulus lupulus
Kyoung Yong Jeong, Jongsun Lee, Gianni Mistrello, Kyung Hee Park, Jung-Won Park
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(7):852-856. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.852.Evaluation of the allergenic relationship between
Humulus japonicus andHumulus lupulus pollen allergens
Chang-Gyu Jung, Eun-Mi Yang, Ji-Ho Lee, Hyun Mi Kim, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(4):217-222. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.217.Allergen standardization
Jung-Won Park, Kyoung Yong Jeong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(4):191-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.4.191.
Reference
-
1. Park HS, Coi SY, Nahm DH, Kim HY. Revival of Hop Japanese pollinosis in asthmatic subjects in Kyungki area. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998; 18:52–60.2. Weber RW. On the cover. Hop. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 100:A4.3. Hong CS, Hwang Y, Oh SH, Kim HJ, Huh KB, Lee SY. Survey of the airborne pollens in Seoul, Korea. Yonsei Med J. 1986; 27:114–120.
Article4. Park HS, Nahm DH, Suh CH, Lee SM, Choi SY, Jung KS, et al. Evidence of Hop Japanese pollinosis in Korea: IgE sensitization and identification of allergenic components. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 100:475–479.
Article5. Yoon YW, Lee MK, Park HS, Park SS, Hong CS. The skin test reactivity and the level of the total IgE in the allergic patients. Allergy. 1989; 9:385–398.6. Lee JW, Choi GS, Kim JE, Jin HJ, Kim JH, Ye YM, et al. Changes in sensitization rates to pollen allergens in allergic patients in the southern part of Gyeonggi province over the last 10 years. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 31:33–40.7. Kim TB, Kim KM, Kim SH, Kang HR, Chang YS, Kim CW, et al. Sensitization rates for inhalant allergens in Korea; a multi-center study. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 23:483–493.8. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Ann HW, Jin MN, Choi SY, et al. A nationwide survey of inhalant allergens sensitization and levels of indoor major allergens in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:222–227.
Article9. Jeong KY, Hong CS, Lee JS, Park JW. Optimization of allergen standardization. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:393–400.
Article10. Cox L, Nelson H, Lockey R, Calabria C, Chacko T, Finegold I, et al. Allergen immunotherapy: a practice parameter third update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1 Suppl. S1–S55.11. Ingemann L, Formgren H, Løwenstein H, Ipsen H. The use of a reference allergenic extract in the evaluation of allergen products. Allergy. 1985; 40:273–281.
Article12. Ipsen H, Formgren H, Løwenstein H, Ingemann L. Immunochemical and biological characterization of a mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris) pollen extract. Allergy. 1985; 40:289–294.
Article13. Park HS, Hong CS, Choi HJ, Hahm KS. Identification and partial purification of pollen allergens from Artemisia princeps. Yonsei Med J. 1989; 30:346–354.
Article14. Brandys J, Grimsøen A, Nilsen BM, Paulsen BS, Park HS, Hong CS. Cross-reactivity between pollen extracts from six Artemisia species. Planta Med. 1993; 59:221–228.
Article15. Katial RK, Lin FL, Stafford WW, Ledoux RA, Westley CR, Weber RW. Mugwort and sage (Artemisia) pollen cross-reactivity: ELISA inhibition and immunoblot evaluation. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 79:340–346.
Article16. Lee YW, Choi SY, Lee EK, Sohn JH, Park JW, Hong CS. Cross-allergenicity of pollens from the Compositae family: Artemisia vulgaris, Dendranthema grandiflorum, and Taraxacum officinale. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007; 99:526–533.
Article17. van Ree R. Indoor allergens: relevance of major allergen measurements and standardization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:270–277.
Article18. Tao AL, He SH. Cloning, expression, and characterization of pollen allergens from Humulus scandens (Lour) Merr and Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005; 26:1225–1232.
Article19. Jeong KY, Han IS, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee JS, Hong CS, et al. Allergenicity of recombinant profilins from Japanese hop, Humulus japonicus. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2013; 23:345–350.20. Turkeltaub PC, Rastogi SC, Baer H, Anderson MC, Norman PS. A standardized quantitative skin-test assay of allergen potency and stability: studies on the allergen dose-response curve and effect of wheal, erythema, and patient selection on assay results. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982; 70:343–352.
Article21. May JC, Sih JT, Miller JR, Seligmann EB Jr. Optimization of parameters in protein nitrogen unit precipitation procedure for allergenic extracts. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979; 63:87–97.
Article22. Himly M, Jahn-Schmid B, Dedic A, Kelemen P, Wopfner N, Altmann F, et al. Art v 1, the major allergen of mugwort pollen, is a modular glycoprotein with a defensin-like and a hydroxyprolinerich domain. FASEB J. 2003; 17:106–108.
Article23. Jimeno L, Duffort O, Serrano C, Barber D, Polo F. Monoclonal antibody-based ELISA to quantify the major allergen of Artemisia vulgaris pollen, Art v 1. Allergy. 2004; 59:995–1001.
Article24. Dreborg S, Einarsson R. The major allergen content of allergenic preparations reflect their biological activity. Allergy. 1992; 47(4 Pt 2):418–423.
Article25. Jeong KY, Lee JH, Kim EJ, Lee JS, Cho SH, Hong SJ, et al. Current status of standardization of inhalant allergen extracts in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:196–200.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Standardization of Weed Pollen Extracts, Japanese Hop and Mugwort, in Korea
- Cross - reactivity between pollens in patients sensitlzed to multiple pollens
- Cross-allergenicity between dandelion and major weed pollens
- IgE Cross-Reactivity between Humulus japonicus and Humulus lupulus
- Antigenic relationship between mugwort and ragweed pollens by crossed immunoelectrophoresis