Yonsei Med J.
2009 Aug;50(4):512-516. 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.512.
Molecular Epidemiology of Hepatitis A Virus in the South-East Area of Gyeonggi-do in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Pochon CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. sghwang@cha.ac.kr
- 2Institute for Clinical Research, College of Medicine, Pochon CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1758609
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2009.50.4.512
Abstract
- PURPOSE
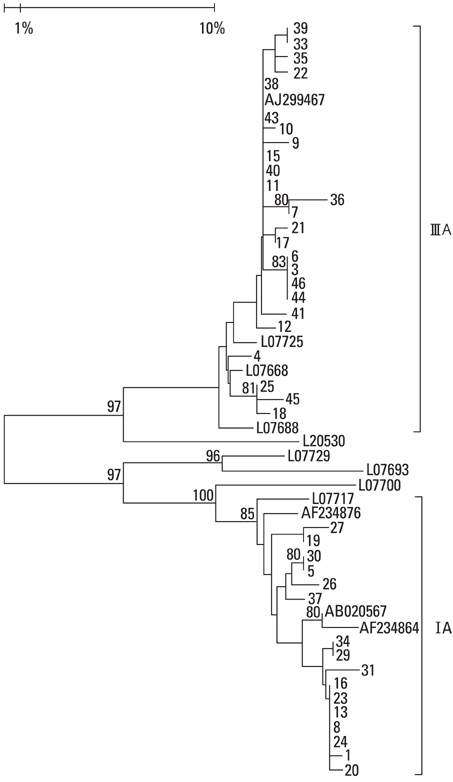
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) has been a leading cause of acute hepatitis in Korea. The reported genotypes of acute hepatitis A in Korea are the subgenotype IA and IB. The aim of the present study is to investigate HAV genotypes in the south-east area of Gyeonggi-do in Korea. MATERIALS AND METHODS: From June 2004 to June 2006, 46 acute hepatitis A patients were enrolled prospectively. All had sporadic acute hepatitis A patients. All suspected cases of acute hepatitis A were tested for IgM anti-HAV antibodies. We sequenced 168 bp of nucleotides of the putative VP1/P2A junction and determined the HAV genotype with reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. The clinical and laboratory results of all patients were recorded. RESULTS: HAV-ribonucleic acid (RNA) was detected in 41 samples out of 46 samples. Among the 41 samples, 25 (60%) were shown to have subgenotype IIIA and the other 16 (40%) were subgenotype IA. Several amino acid substitutions were found. CONCLUSION: In these HAV sporadic cases, IIIA and IA were identified, and this may reflect co-circulation of various genotypes in Korea. This study provides valuable new data on the genetic distribution of HAV and important information to help design appropriate public health measures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Molecular and Clinical Characterization of Hepatitis A Virus in Gwangju and Jeonnam Province
Du Young Noh, Sung Bum Cho, Yeon Joo Kim, Wan Sik Lee, Chang Hwan Park, Young Eun Joo, Hyen Soo Kim, Jong Sun Rew, Sung Kyu Choi
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011;57(6):346-351. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.6.346.Comparative Genotype Analysis of Hepatitis A Virus: Two One-Year Studies in South Korea in 2002 and 2011
In Hyuk Baek, Hyun Woong Lee, Hyung Joon Kim, Mi-Ok Song, Seung-Kew Yoon, Jong-Hwa Park, In Sik Chung, Wonyong Kim
J Bacteriol Virol. 2014;44(3):252-260. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2014.44.3.252.
Reference
-
1. Melnick JL. Properties and classification of hepatitis A virus. Vaccine. 1992. 10:Suppl 1. S24–S26.
Article2. Martin A, Lemon SM. Hepatitis A virus: from discovery to vaccines. Hepatology. 2006. 43:S164–S172.
Article3. Robertson BH, Jansen RW, Khanna B, Totsuka A, Nainan OV, Siegl G, et al. Genetic relatedness of hepatitis A virus strains recovered from different geographical regions. J Gen Virol. 1992. 73:1365–1377.
Article4. Jansen RW, Siegl G, Lemon SM. Molecular epidemiology of human hepatitis A virus defined by an antigen-capture polymerase chain reaction method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990. 87:2867–2871.
Article5. Gust ID. Epidemiological patterns of hepatitis A in different parts of the world. Vaccine. 1992. 10:Suppl 1. S56–S58.
Article6. Koff RS. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of hepatitis A virus infection. Vaccine. 1992. 10:Suppl 1. S15–S17.
Article7. Byun KS, Kim JH, Song KJ, Baek LJ, Song JW, Park SH, et al. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis A virus in Korea. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001. 16:519–524.
Article8. Lee TH, Kim SM, Lee GS, Im EH, Huh KC, Choi YW, et al. [Clinical features of acute hepatitis A in the Western part of Daejeon and Chungnam province: single center experience]. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006. 47:136–143.9. Kang CI, Choi CM, Park TS, Lee DJ, Oh MD, Choe KW. Incidence and seroprevalence of Hepatitis A virus infections among young Korean soldiers. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:546–548.
Article10. Park JY, Lee JB, Jeong SY, Lee SH, Lee MA, Choi HJ. Molecular characterization of an acute hepatitis A outbreak among healthcare workers at a Korean hospital. J Hosp Infect. 2007. 67:175–181.
Article11. Costa-Mattioli M, Di Napoli A, Ferré V, Billaudel S, Perez-Bercoff R, Cristina J. Genetic variability of hepatitis A virus. J Gen Virol. 2003. 84:3191–3201.12. Poovorawan Y, Theamboonlers A, Chongsrisawat V, Jantaradsamee P, Chutsirimongkol S, Tangkijvanich P. Clinical features and molecular characterization of hepatitis A virus outbreak in a child care center in Thailand. J Clin Virol. 2005. 32:24–28.13. Khanna B, Spelbring JE, Innis BL, Robertson BH. Characterization of a genetic variant of human hepatitis A virus. J Med Virol. 1992. 36:118–124.
Article14. Hussain Z, Das BC, Husain SA, Asim M, Chattopadhyay S, Malik A, et al. Hepatitis A viral genotypes and clinical relevance: Clinical and molecular characterization of hepatitis A virus isolates from northern India. Hepatol Res. 2005. 32:16–24.15. Arankalle VA, Sarada Devi KL, Lole KS, Shenoy KT, Verma V, Haneephabi M. Molecular characterization of hepatitis A virus from a large outbreak from Kerala, India. Indian J Med Res. 2006. 123:760–769.16. Spada E, Genovese D, Tosti ME, Mariano A, Cuccuini M, Proietti L, et al. An outbreak of hepatitis A virus infection with a high case-fatality rate among injecting drug users. J Hepatol. 2005. 43:958–964.
Article17. Tjon GM, Götz H, Koek AG, de Zwart O, Mertens PL, Coutinho RA, et al. An outbreak of hepatitis A among homeless drug users in Rotterdam, The Netherlands. J Med Virol. 2005. 77:360–366.18. Wells R, Fisher D, Fenaughty A, Cagle H, Jaffe A. Hepatitis A prevalence among injection drug users. Clin Lab Sci. 2006. 19:12–17.19. Jee YM, Go U, Cheon D, Kang Y, Yoon JD, Lee SW, et al. Detection of hepatitis A virus from clotting factors implicated as a source of HAV infection among haemophilia patients in Korea. Epidemiol Infect. 2006. 134:87–93.
Article20. Stene-Johansen K, Jonassen Tø, Skaug K. Characterization and genetic variability of Hepatitis A virus genotype IIIA. J Gen Virol. 2005. 86:2739–2745.
Article21. Cuthbert JA. Hepatitis A: old and new. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001. 14:38–58.22. Yokosuka O. Does genotype of hepatitis A virus relate to clinical characteristics of hepatitis A? Hepatol Res. 2005. 32:14–15.
Article23. Rezende G, Roque-Afonso AM, Samuel D, Gigou M, Nicand E, Ferre V, et al. Viral and clinical factors associated with the fulminant course of hepatitis A infection. Hepatology. 2003. 38:613–618.
Article24. Fujiwara K, Yokosuka O, Ehata T, Saisho H, Saotome N, Suzuki K, et al. Association between severity of type A hepatitis and nucleotide variations in the 5' non-translated region of hepatitis A virus RNA: strains from fulminant hepatitis have fewer nucleotide substitutions. Gut. 2002. 51:82–88.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Epidemiology of Hepatitis A Virus in the South-East Area of Gyeonggi-do in Korea
- Clinical Significance of Outbreak of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in Endemic Area with Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination
- A study on the relationship between HBeAg and hepatitis B virus DNAamong healthy HBsAg carries
- History and future of hepatitis B virus control in South Korea