Trends in Deceased Organ Donation and Utilization in Korea: 2000-2009
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwhamd@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Transplantation Research Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1714030
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.8.1122
Abstract
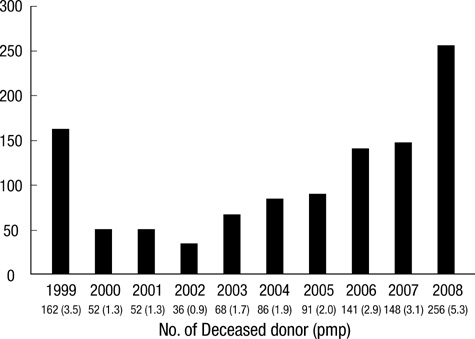
- Continuous efforts have been made by the organ donation and transplantation community in Korea to increase organ donation by the deceased. The authors detailed trends of organ donation and utilization over the past 10 yr using data provided by the KONOS. The yearly number of deceased donors has grown gradually since 2003. The number and percentage of old donors (> or =50 yr) and donors dying from intracranial hemorrhage has increased continuously. Therefore, the percentage of standard criteria donors (SCD) has been declining significantly, from 94% in 2000 to 79.2% in 2009. The number of organs transplanted per donor (OTPD) has also declined slightly since 2007, from 3.28 in 2007 to 2.95 in 2009. This decline may be attributable to increases in the number and percentage of extended criteria donors (ECD) and donors after cardiac death (DCD), since the OTPD was 2.25 for DCD, 2.5 for ECD, and 3.09 for SCD in 2009. In summary, the makeup of donors has changed significantly. There is an urgent need for establishment of an institutional framework including an independent organ procurement organization and for improvement for the National Transplant Act to increase deceased donor pool and to optimize management of ECD and DCD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Kidney Transplantation from Expanded Criteria Donor in Korea: It's Time to Have Our Own Criteria Based on Our Experiences
Shin-Seok Yang, Jae Berm Park
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2017;31(1):16-24. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2017.31.1.16.Optimal System for Deceased Organ Donation and Procurement in Korea
Sang-Il Min, Hyun Ahn Sang, Hyun Cho Won, Curie Ahn, Il Kim Soon, Jongwon Ha
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2011;25(1):1-7. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2011.25.1.1.Operational and Regulatory System Requirements for Pursuing Self-sufficiency in Deceased Donor Organ Transplantation Program in Korea
Myung-Gyu Kim, Cheol Jeong Jong, Eun Jin Cho, Ha Huh Kyu, Jaeseok Yang, Im Byeon Nyeon, Sook Yu Jin, Tae Bang Ki, Heoung Soo Chung, Won Ha Jong, Il Kim Soon, Hyun Cho Won, Curie Ahn
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2010;24(3):147-158. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2010.24.3.147.Considerations regarding anesthesia for renal transplantation
Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung
Anesth Pain Med. 2024;19(1):5-11. doi: 10.17085/apm.23153.
Reference
-
1. Lee YK, Lim SK, Min BS, Chung WH, Kim SG, Lee YU, Kim IC, Kim HP. Renal transplantation in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 1969. 12:983–992.2. Kwak JY, Park CD, Lee KS, Won CK, Kang CM, Park HC, Lee TY, Woo YN. An analysis of 15 cases of cadaveric kidney transplantation. J Korean Surg Soc. 1979. 44:128–136.3. Organ transplantation statistics. Korean Network for Organ Sharing. accessed on 7 October 2009. Available at http://konos.go.kr.4. Manyalich M, Costa AN, Paez G. IRODaT 2008 international donation and transplantation activity. Organs, Tissues & Cell. 2009. 12:85–88.5. Measures to improve organ donation. 2005. 10. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea Government.6. Cho WH, Kim HT, Lee HJ, Seo YM, Lee SD, Son EI, Kim IS, Choi SY, Park HJ, Joo SH. Development of Korean model for independent organ procurement organization. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2008. 22:109–119.7. Park YJ, Kang H, Kim EM, Shin WY, Yi NJ, Suh KS, Ahn C, Yoon BY, Park YH, Lee JN, Kim JH, Min SK, Kim SJ, Ha J. Establishment of active identification and management system for potential brain dead donors in life-link center. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2009. 23:43–51.8. Kim MS, Kim SI, Kim YS. Current status of deceased organ recovery and sharing in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008. 51:685–691.9. Port FK, Bragg-Gresham J, Metzger RA, Dykstra DM, Gillespie BW, Young EW, Delmonico FL, Wynn JJ, Merion RM, Wolfe RA, Held PJ. Donor characteristics associated with reduced graft survival: an approach to expanding the donor of kidney donors. Transplantation. 2002. 74:1281–1286.10. Feng S, Goodrich NP, Bragg-Gresham JL, Dykstra DM, Punch JD, DebRoy MA, Greenstein SM, Merion RM. Characteristics associated with liver graft failure: the concept of a donor risk index. Am J Transplant. 2006. 6:783–790.
Article11. Marks WH, Wagner D, Pearson TC, Orlowski JP, Nelson PW, McGowan JJ, Guidinger MK, Burdick J. Organ donation and utilization, 1995-2004: Entering the collaborative era. Am J Transplant. 2006. 6:1101–1110.
Article12. Tuttle-Newhall JE, Krishnan SM, Levy MF, McBride V, Orlowski JP, Sung RS. Organ donation and utilization in the United States: 1998-2007. Am J Transplant. 2009. 9:879–893.
Article13. OPTN/SRTR 2008 Annual Report. United Network for Organ Sharing. accessed on 12 October 2009. Available at http://www.ustransplant.org/annual_reports/current/201_dc.pdf.14. Chang GJ, Mahanty HD, Ascher NL, Roberts JP. Expanding the donor pool: can the Spanish Model work in the United States? Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:1259–1263.
Article15. Miranda B, Fernandez Lucas M, de Felipe C, Naya M, Gonzalez-Posada JM, Matesanz R. Organ donation in Spain. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999. 14:Suppl 3. 15–21.16. Steering Committee of the Istanbul Summit. Organ trafficking and transplant tourism and commercialism: the Declaration of Istanbul. Lancet. 2008. 372:5–6.17. Han YJ, Hwang YS, Lee SK, Koh EN, Lee NH. A report on the establishment and management of organ procurement organization. 2006. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea Government.18. Prottas JM. The organization of organ procurement. J Health Polit Policy Law. 1989. 14:41–55.
Article19. UNOS membership. United Network for Organ Sharing. accessed on 14 October 2009. Available at http://www.unos.org/whoWeAre/membership.asp.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trends in Deceased Organ Donation and Utilization in Korea: 2000-2009
- Assessment of hospital deceased organ donation potential at St. Luke’s Medical Center–Quezon City
- Analysis of Factors Affecting Emergency Physicians’ Attitudes toward Deceased Organ & Tissue Donation
- Determination of factors influencing family decision upon organ or tissue donation request in potential deceased organ donors in Malaysia: a 22-years national audit
- Willingness and attitude of the Arab world population towards solid organ