J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Feb;23(1):138-141. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.138.
Transient Acquired Hemophilia Associated with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics and the Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, School of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea. hwaph@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Division of Translational Research, International Vaccine Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1786861
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.138
Abstract
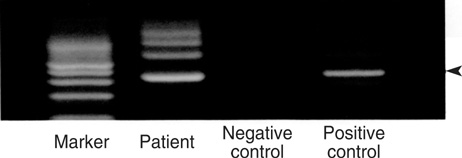
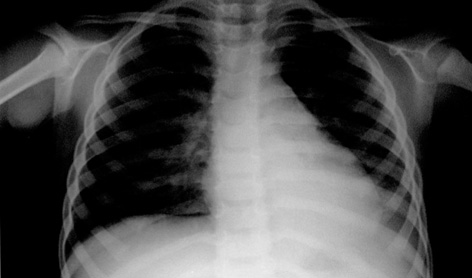
- Acquired hemophilia is a rare disorder caused by autoantibodies to factor VIII (FVIII) (also referred to as factor VIII inhibitors or anti-FVIII) and may be associated with pregnancy, underlying malignancy, or autoimmune disorders. A 33-month-old girl who presented with hematochezia and ecchymotic skin lesions was diagnosed with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia by serology and polymerase chain reaction. Hematologic studies showed a prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), partially corrected mixing test for aPTT, reduced levels of FVIII, and the presence of antibodies against FVIII. She was treated conservatively with prednisone and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) without FVIII transfusion and recovered without sequelae. This report provides the first description of acquired hemophilia due to anti-FVIII in association with M. pneumoniae in Korea. We discuss this case in the context of the current literature on acquired hemophilia in children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Acute Hepatitis with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection and Transient Depression of Multiple Coagulation Factors
Joo Hee Chang, Young Se Kwon, Bok Ki Kim, Byong Kwan Son, Jee Eun Lee, Dae Hyun Lim, Soon Ki Kim, Joon Mi Kim, Sung Kil Kang
Yonsei Med J. 2008;49(6):1055-1059. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.6.1055.
Reference
-
1. Kessler CM. An introduction to factor VIII inhibitors: the detection and quantitation. Am J Med. 1991. 91:1S–5S.
Article2. Grunewald M, Beneke H, Guthner C, Germowitz A, Brommer A, Griesshammer M. Acquired haemophilia: experiences with a standardized approach. Haemophilia. 2001. 7:164–169.3. Shwaiki A, Lara L, Ahmed F, Crock R, Rutecki GW, Whittier FC. Acquired inhibitor to factor VIII in small cell lung cancer: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Hematol. 2001. 80:124–126.
Article4. Moraca RJ, Ragni MV. Acquired anti-FVIII inhibitors in children. Haemophilia. 2002. 8:28–32.
Article5. Ferwerda A, Moll HA, de Groot R. Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J Pediatr. 2001. 160:483–491.
Article6. Collazos J, Egurbide MV, Atucha K, Esteban P, de Miguel J. Transient acquired factor II deficiency with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Infect Dis. 1991. 164:434–435.
Article7. Kim KY, Yang CH, Cho MJ, Lee M. Comprehensive clinical and statistical analysis of hemophilia in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 1988. 3:107–115.
Article8. Green D, Lechner K. A survey of 215 non-hemophilic patients with inhibitors to Factor VIII. Thromb Haemost. 1981. 45:200–203.
Article9. Klukowska A, Laguna P, Obitko-Pludowska A, Niedzielska K, Malinowska I, Rokicka-Milewska R. Acquired factor VIII inhibitor in a non-haemophilic boy. Haemophilia. 2003. 9:642–645.
Article10. Boggio LN, Green D. Acquired hemophilia. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2001. 5:389–404.
Article11. Aledort LM, Green D, Teitel JM. Unexpected bleeding disorders. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2001. 306–321.
Article12. Bouvry P, Recloux P. Acquired hemophilia. Haematologica. 1994. 79:550–556.13. Delgado J, Jimenez-Yuste V, Hernandez-Navarro F, Villar A. Acquired haemophilia: review and meta-analysis focused on therapy and prognostic factors. Br J Haematol. 2003. 121:21–35.
Article14. Bossi P, Cabane J, Ninet J, Dhote R, Hanslik T, Chosidow O, Jouan-Flahault C, Horellou MH, Leynadier F, Liozon E, Pouchot J, Robin JP, Sanderson F, Schaeffer A, Sicard D, Staikowsky F, Wechsler B, Zittoun R. Acquired hemophilia due to factor VIII inhibitors in 34 patients. Am J Med. 1998. 105:400–408.
Article15. Dykes AC, Walker ID, Lowe GD, Tait RC. Combined prednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for acquired factor VIII inhibitors: a 2-year review. Haemophilia. 2001. 7:160–163.
Article16. Ferri GM, Vaccaro F, Caccavo D, Imperato G, Bonomo L. Development of factor VIII: C inhibitors following vaccination. Acta Haematol. 1996. 96:110–111.17. Waites KB. New concepts of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2003. 36:267–278.18. Baseman JB, Tully JG. Mycoplasmas: sophisticated, reemerging, and burdened by their notoriety. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997. 3:21–32.
Article19. Zakarija A, Green D. Acquired hemophilia: diagnosis and management. Curr Hematol Rep. 2002. 1:27–33.20. Buwitt-Beckmann U, Heine H, Wiesmuller KH, Jung G, Brock R, Akira S, Ulmer AJ. Toll-like receptor 6-independent signaling by diacylated lipopeptides. Eur J Immunol. 2005. 35:282–289.
Article21. Shimizu T, Kida Y, Kuwano K. Lipid-associated membrane proteins of Mycoplasma fermentans and M. penetrans activate human immunodeficiency virus long-terminal repeats through Toll-like receptors. Immunology. 2004. 113:121–129.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transient Acquired Hemophilia Associated with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
- Clinical Observation on Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children
- A clinical study of mycoplasma pneumonia in children during recent 5 years
- Clinical Consideration on Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children