Microorganisms Isolated from Blood Cultures and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns At a University Hospital During 1994-2003
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Colleage of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leekcp@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Colleage of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University Colleage of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University Colleage of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.4.265
Abstract
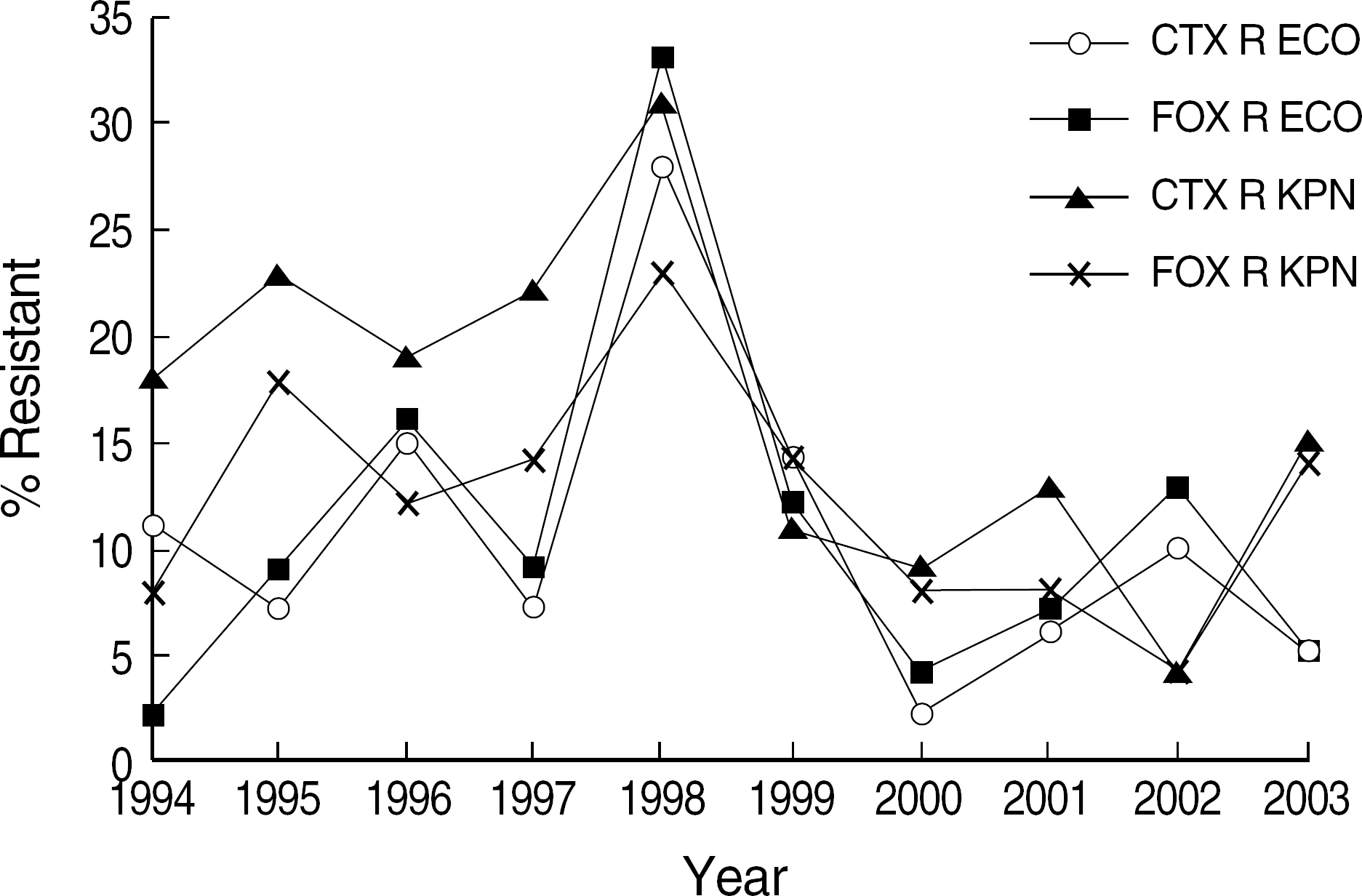
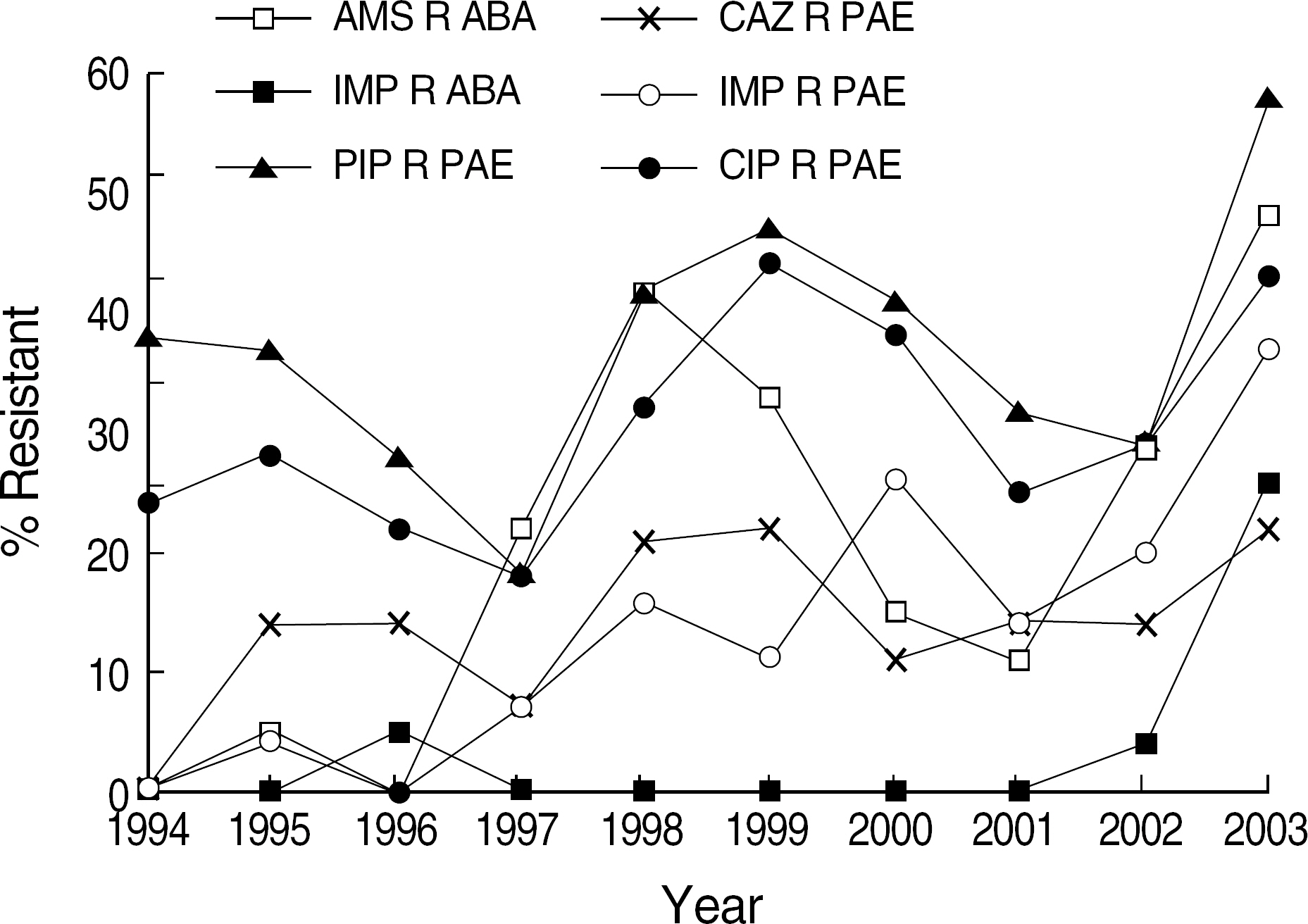
- BACKGROUND: Blood culture is important for the determination of the etiologic agent of bacteremia. Analysis of blood culture results and antimicrobial susceptibility trend can provide clinicians with relevant information for the empirical treatment of patients. METHODS: The species and antimicrobial susceptibility of the isolates from blood cultures at the Severance Hospital during 1994-2003 were analysed. Blood specimens were cultured for 7 days using tryptic soy broth and thioglycollate medium. Identification of organism was based on conventional methods or commercial kit systems. Antimicrobial susceptibility was tested by a disk diffusion method. RESULTS: Of 536,916 blood specimens cultured, 24,877 (4.6%) from 13,102 patients were positive. Among the isolates, 93.1% were aerobic or facultative anaerobic bacteria, 3.3% anaerobes, and 3.6% fungi. Escherichia coli was isolated most frequently, followed by Staphylococcus aureus, -hemolytic Streptococcus, Enterococcus spp., and Klebsiella pneumoniae. The proportion of patients with Enterococcus faecium and K. pneumoniae gradually increased during this study. Enterococcus, S. aureus and alpha-hemolytic Streptococcus were frequently isolated from the age group of less than 2 yr. E. coli, Enterococcus spp., K. pneumoniae and S. aureus from the age group of over 50 yr. Oxacillin-resistant S. aureus decreased, whereas vancomycin-resistant E. faecium and imipenemresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii increased. CONCLUSIONS: E. coli was the most common cause of bacteremia and S. aureus, -hemolytic Streptococcus, and K. pneumoniae were frequently isolated pathogens. The bacteremia due to Enterococcus, K. pneumoniae, fungi, vancomycin-resistant E. faecium, and imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii gradually increased during this period.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Bacteremia/epidemiology/*microbiology
Bacteria/drug effects/*isolation & purification
Child
Child, Preschool
*Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Drug Resistance, Fungal
Fungemia/epidemiology/microbiology
Hospitals, Teaching
Humans
Infant
Microbial Sensitivity Tests
Middle Aged
Retrospective Studies
Vancomycin/therapeutic use
Figure
Cited by 12 articles
-
In vitro Activities of Mecillinam Against Clinical Isolates of Enterobacteriaceae
Chang-Ki Kim, Jong Hwa Yum, Sang-Guk Lee, Yangsoon Lee, Jun Yong Choi, June Myung Kim, Kyungwon Lee, Yunsop Chong
Infect Chemother. 2009;41(3):174-180. doi: 10.3947/ic.2009.41.3.174.Recent Trends of Anaerobic Bacteria Isolated from Clinical Specimens and Clinical Characteristics of Anaerobic Bacteremia
Yongjung Park, Yangsoon Lee, Myungsook Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Dongeun Yong, Seok Hoon Jeong, June Myung Kim, Kyungwon Lee, Yunsop Chong
Infect Chemother. 2009;41(4):216-223. doi: 10.3947/ic.2009.41.4.216.Changes in Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Blood Isolates in a University Hospital in South Korea, 1998-2010
Nak-Hyun Kim, Jeong-Hwan Hwang, Kyoung-Ho Song, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Wan Beom Park, Eu Suk Kim, Sang-Won Park, Hong Bin Kim, Nam Joong Kim, Myoung-don Oh, Eui-Chong Kim
Infect Chemother. 2012;44(4):275-281. doi: 10.3947/ic.2012.44.4.275.Anaerobic Bacteremia: Impact of Inappropriate Therapy on Mortality
Jieun Kim, Yangsoon Lee, Yongjung Park, Myungsook Kim, Jun Yong Choi, Dongeun Yong, Seok Hoon Jeong, Kyungwon Lee
Infect Chemother. 2016;48(2):91-98. doi: 10.3947/ic.2016.48.2.91.Development of Blood Culture and Quality Improvement
Sunjoo Kim
Ann Clin Microbiol. 2013;16(4):153-161. doi: 10.5145/ACM.2013.16.4.153.Trends in Five-year Blood Cultures of Patients at a University Hospital (2003∼2007)
So Young Kim, Gayoung Lim, Min Jin Kim, Jin Tae Suh, Hee Joo Lee
Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2009;12(4):163-168. doi: 10.5145/KJCM.2009.12.4.163.Antimicrobial Resistance of Enterococcal Isolates from Blood and Risk Factors for Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcal Bacteremia in a Tertiary Care University Hospital from 2003 to 2007
Kyung Sun Park, Myeong Hee Kim, Tae Sung Park, Jin Tae Suh, Hee Joo Lee
Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2010;13(2):59-67. doi: 10.5145/KJCM.2010.13.2.59.Characteristics of Microorganisms Isolated from Blood Cultures at Nine University Hospitals in Korea during 2009
Hee-Jung Kim, Nam Yong Lee, Sunjoo Kim, Jeong Hwan Shin, Mi-Na Kim, Eui-Chong Kim, Sun Hoi Koo, Nam Hee Ryoo, Jae-Seok Kim, Ji-Hyun Cho
Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2011;14(2):48-54. doi: 10.5145/KJCM.2011.14.2.48.Characteristics of Microorganisms Isolated from Blood Cultures at a University Hospital Located in an Island Region During 2003∼2007
Sung Ha Kang, Young Ree Kim
Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2008;11(1):11-17. doi: 10.5145/kjcm.2008.11.1.11.Changes in Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Blood Isolates at a University Hospital in the Kyungnam area during 2005-2014
Dahae Yang, Woonhyoung Lee
Kosin Med J. 2018;33(1):29-40. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2018.33.1.29.Trends in Bloodstream Infections and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities at a University Hospital in Korea Between 2007 and 2016
Sangeun Lim, Joon-Sup Yeom, Eun-Jeong Joo, Hae Suk Cheong, Kyunghoon Lee, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Lab Med Online. 2019;9(2):63-72. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.63.Comprehensive Analysis of Blood Culture Performed at Nine University Hospitals in Korea
Jeong Hwan Shin, Sae Am Song, Mi-Na Kim, Nam Yong Lee, Eui-Chong Kim, Sunjoo Kim, Sun-Hoi Koo, Nam Hee Ryoo, Jae-Seok Kim, Ji-Hyun Cho
Korean J Lab Med. 2011;31(2):101-106. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.2.101.
Reference
-
References
1. Bryan CS. Clinical implications of positive blood cultures. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989; 2:329–53.
Article2. Hong MA, Oh KC, Ahn SI, Kim BR, Kim YH, Kim SS, et al. Trend of antimicrobial susceptibility test for bacterias isolsted from blood, urine, stool, and cerebrospinal fluid(1997–2001). Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2003; 10:167–77.3. Kwon HJ, Kim SY, Cho CY, Choi YY, Shin JH, Suh SP. Nosocomial infection in neonatal intensive care unit. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2002; 45:719–26.4. Lee YJ, Lee JG, Hwang BY, Jeong HW, Jung SJ, Kee SY, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of death among patients with vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) during 8 years (1994–2001) in a university hospital. Infect Chemother. 2003; 35:249–55.5. Kang CI, Kim DM, Yi JY, Park WB, Lee KD, Kim HB, et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae blood isolates over 5 years: Influence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing organisms. Infect Chemother. 2003; 35:365–69.6. Kim HO, Kang CG, Chong YS, Lee SY. Organisms isolated from blood at the Yonsei medical center, 1974–1983. Infect Chemother. 1985; 17:15–32.7. Kim HK, Lee KW, Chong YS, Kwon OH, Kim JM, Kim DS. Blood culture results at the Severance Hospital during 1984–1993. Infect Chemother. 1996; 28:151–66.8. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. National Nosocomoal Infections Surveillance (NNIS) System Report, data summary from January 1992 through June 2004, issued October 2004. Am J Infect Control. 2004; 32:470–85.9. Goldstein EJ. Anaerobic bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 23:97–101.
Article10. Diekema DJ, Messer SA, Brueggemann AB, Coffman SL, Doern GV, Herwaldt LA, et al. Epidemiology of candidemia: 3-year results from the emerging infections and the epidemiology of lowa organisms study. J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 40:1298–302.11. Hajjeh RA, Sofair AN, Harrison LH, Lyon GM, Arthington-Skaggs BA, Mirza SA, et al. Incidence of bloodstream infections due to Candida species and in vitro susceptibilities of isolates collected from 1998 to 2000 in a population-based active surveillance program. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:1519–27.12. Murray PR, Baron EJ, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 8th ed.Washington, D.C.: ASM press;2003. p. 188–9.13. Ahn YM, Lee SY. Studies on identification of glucose nonfer-menting gram-negative bacilli. Yonsei Med J. 1983; 16:126–47.14. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Twelfth informational supplement, M100-S12. Wayne, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;1998.15. Hall KK, Lyman JA. Updated review of blood culture contamination. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. 788–802.
Article16. Mylotte JM, Tayara A. Blood cultures: clinical aspects and controversies. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000; 19:157–63.
Article17. Seo SY, Lee MA. The serogroup and antivicrobial resistance of salmonella spp. Isolated from the clinical specments during 6 years in a tertiary university hospital. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 7:72–6.18. Vidal F, Mensa J, Almela M, Olona M, Martinez JA, Marco F, et al. Bacteraemia in adults due to glucose non-fermentative Gram-negative bacilli other than P. aeruginosa. QJM. 2003; 96:227–34.19. Kim EC, Hur MN, Han KS, Park MH. Antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from blood of Seoul national university hospital patients. J Korean Soc Chemother. 1999; 17:53–9.20. Blairon L, De Gheldre Y, Delaere B, Sonet A, Bosly A, Glupczynski Y. A 62-month retrospective epidemiological survey of anaerobic bacteraemia in a university hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006; 12:527–32.
Article21. Zahar JR, Farhat H, Chachaty E, Meshaka P, Antoun S, Nitenberg G. Incidence and clinical significance of anaerobic bacteraemia in cancer patients: a 6-year retrospective study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005; 11:724–9.
Article22. Singhal R, Chaudhry R, Dhawan B. Anaerobic bacteraemia in a tertiary care hospital of North India. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2006; 24:235–6.
Article23. Edmond MB, Wallace SE, McClish DK, Pfaller MA, Jones RN, Wenzel RP. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in United States hospitals: a three-year analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:239–44.
Article24. Krcmery V, Barnes AJ. Non-albicans Candida spp. causing fungaemia: pathogenicity and antifungal resistance. J Hosp Infect. 2002; 50:243–60.
Article25. Gomella TL, Cunningham MD, editors. Neonatology: management, procedures, on-call problems, diseases and drugs. 5th ed.New York: McGrow-Hill;2004. p. 434–5.26. Kim KA, Shin SM, Moon HG, Park YH. Causative organisms of neonatal sepsis. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 1999; 16:60–8.
Article27. Orrett FA, Changoor E. Bacteremia in children at a regional hospital in Trinidad. Int J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:145–51.
Article28. Berkley JA, Ross A, Mwangi I, Osier FH, Mohammed M, Shebbe M, et al. Prognostic indicators of early and late death in children admitted to district hospital in Kenya: cohort study. BMJ. 2003; 326:361.
Article29. Uh Y, Lee HH, Lee KW, Chong YS. The species and antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures of patients. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1991; 26:417–30.30. Lee K, Lim CH, Cho JH, Lee WG, Uh Y, Kim HJ, et al. High prevalence of ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and increase of imipenem-resistant Psedomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter spp. in Korea: a KONSAR program in 2004. Yonsei Med J. 2006; 47:634–45.31. Leclercq R, Derlot E, Duval J, Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:157–61.32. Hong SG, Kim SJ, Jeong SH, Chang CH, Cho SR, Ahn JY, et al. Prevalence and diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Korea. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 6:149–55.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trends in Five-year Blood Cultures of Patients at a University Hospital (2003~2007)
- Characteristics of Microorganisms Isolated from Blood Cultures at a University Hospital Located in an Island Region During 2003~2007
- Trends of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test for Bacterias Isolated from Blood, Urine, Stool, and Cerebrospinal Fluid(1997~2001)
- The species and antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures of patients
- A Study on Microorganisms Isolated from Clinical Specimens and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility