The Clinical Course of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia After Previous Unilateral Recess-Resection Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. mmk@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2212623
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.9.1386
Abstract
- PURPOSE
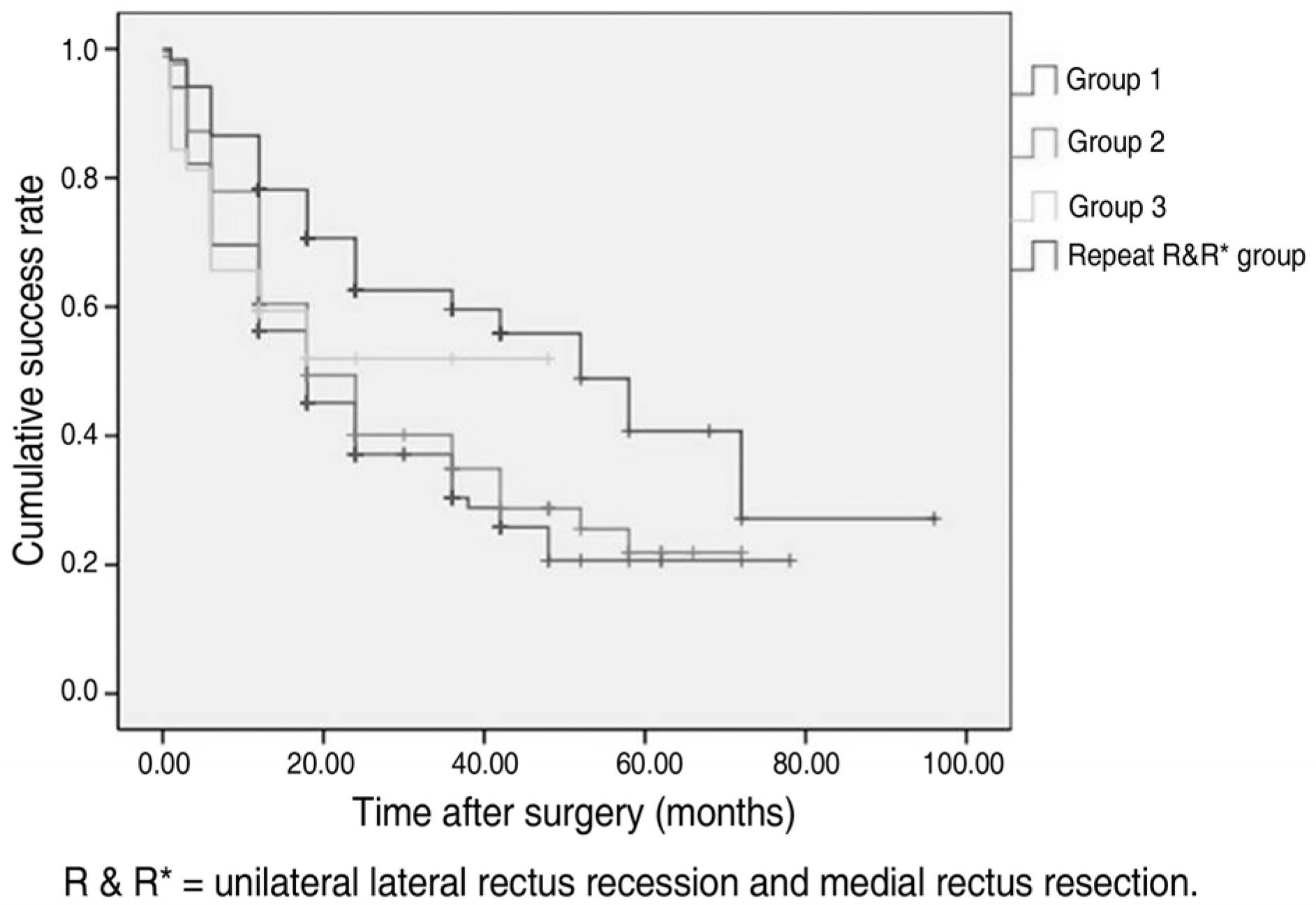
To investigate the clinical course of recess-resection (R & R) on the contralateral eye for recurrent intermittent exotropia after previous unilateral R & R surgery. METHODS: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients who had unilateral R & R surgery and patients who had a second R & R surgery on the contralateral eye for recurrent intermittent exotropia with at least 12 months of postoperative follow-up. RESULTS: Our study included 490 patients with unilateral R & R and 119 patients with contralateral R & R. Recurrence was defined as an ocular misalignment of greater than 11PD during follow-up. Cumulative probabilities of surgical success rates were 42.7% and 66.4%, respectively (p=0.000). CONCLUSIONS: Exotropia reappeared in recurrent intermittent exotropia after contralateral R & R. However, when considering a long-term prognosis, the cumulative probabilities of surgical success were significantly higher in the second surgery.
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Changes in Types of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia after Surgical Correction of Basic Type Intermittent Exotropia
Sung Ha Hwang, Hae Jung Paik
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(8):760-765. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.8.760.Long-Term Results of Intermittent Exotropia Surgery: Comparison between Motor and Functional Success
Ji Sun Baek, Myung Jin Cho, Ungsoo Samuel Kim, Yong Ran Kim, Sang Mook Kong, Seung Hee Baek
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(7):1064-1070. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.7.1064.Result Comparison after Reoperation in Recurrent Exotropia According to the Type of First Operation
Moses Kim, Mi Young Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(5):726-733. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.5.726.The Surgical Outcomes of Unilateral Lateral Rectus Recession in Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia after Unilateral Recession-Resection
A Young Choi, Young Chun Lee, Se Youp Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(11):1783-1788. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.11.1783.
Reference
-
References
1. Figueira EC, Hing S. Intermittent exotropia: comparison of treatments. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2006; 34:245–51.
Article2. Chia A, Seenyen L, Long QB. Surgical experiences with two- muscle surgery for the treatment of intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 2006; 10:206–11.3. Jeoung JW, Lee MJ, Hwang JM. Bilateral lateral rectus recession versus unilateral recess-resect procedure for exotropia with a dominant eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:683–8.
Article4. Fiorelli VM, Goldchmit M, Uesugui CF, Souza-Dias C. Intermittent exotropia: comparative surgical results of lateral recti- recession and monocular recess-resect. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2007; 70:429–32.5. Maruo T, Kubota N, Sakaue T, Usui C. Intermittent exotropia surgery in children: long term outcome regarding changes in binocular alignment. A Study of 666 Cases. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 2001; 16:265–70.6. Oh JY, Hwang JM. Survival analysis of 365 patients with exotropia after surgery. Eye. 2006; 20:1268–72.
Article7. Kim MM, Cho ST. Long-term surgical results of intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1994; 35:1321–6.8. Chang BL. Operative results in exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1983; 24:729–34.9. Park JL, Son MH, Yun IH, Won IG. The clinical analysis of surgical methods in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:526–32.10. Hahm IR, Yoon SW, Baek SH, Kong SM. The clinical course of recurrent exotropia after reoperation for exodeviation. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:140–4.
Article11. Kim SJ, Choi DG. The Clinical analysis after reoperation for recurrent intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:321–7.12. Kim SJ. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992; 33:95–100.13. Mun HJ, Kim MM. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in 25PD intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:2202–7.14. Im SK, Park SW, Park YG. Effects of bilateral lateral rectus recession and unilateral recession-resection in large angle exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:990–4.15. Lee SY, Sim JH, Lee YC. Comparison of surgical results according to surgical methods in simulated divergence excess exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:614–9.16. Jeong TS, You IC, Park SW, Park YG. Factor of surgical success with unilateral recessionand resection in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1987–92.17. Lew HL, Lee JB, Kim TK. Comparison of surgical results between bilateral rectus muscle recessions and lateral rectus muscle recession and muscle rectus resection in exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995; 36:115–9.18. Yang SW, Chang BL. Pathologic finding after recession and resection of extraocular muscles in rabbits. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1989; 3:75–9.19. Koo NK, Lee YC, Lee SY. Clinical study for the undercorrection factor in intermittent exotropia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2006; 20:182–7.
Article20. Roh JH, Paik HJ. Clinical study on factors associated with recurrence and reoperation in intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1114–9.
Article21. Lee SY, Lee YC. Comparison of surgical results by initial postoperative alignment following bilateral lateral rectus recession and unilateral lateral rectus recession-medial rectus resection in inter-mittent exotropes. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1999; 40:2604–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Course of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia After Previous Unilateral Recess-Resection Surgery
- Unilateral Recession-Resection Versus Re-resection of Medial Rectus in Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
- The Clinical Analysis after Reoperation for Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia
- The Effect of Unilateral Medial Rectus Muscle Resection in Patients with Recurrent Exotropia
- Clinical Features of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia after Reoperation for Intermittent Exotropia